使用EntityFramework6.1的DbCommandInterceptor拦截生成的SQL语句
开始
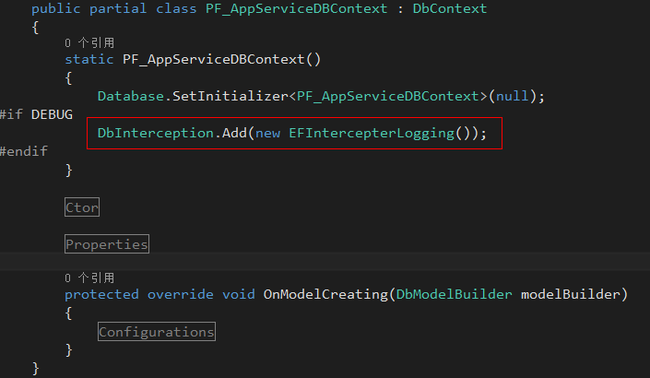
EF6.1也出来不少日子了,6.1相比6.0有个很大的特点就是新增了System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.Interception 命名空间,此命名空间下的对象可以允许我们更加方便的了解到EF运行时的一些信息,当然我们最想看的还是EF生成的Sql语句,话不多讲,开始干吧;
class EFIntercepterLogging : DbCommandInterceptor { private readonly Stopwatch _stopwatch = new Stopwatch(); public override void ScalarExecuting(System.Data.Common.DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<object> interceptionContext) { base.ScalarExecuting(command, interceptionContext); _stopwatch.Restart(); } public override void ScalarExecuted(System.Data.Common.DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<object> interceptionContext) { _stopwatch.Stop(); if (interceptionContext.Exception != null) { Trace.TraceError("Exception:{1} \r\n --> Error executing command: {0}", command.CommandText, interceptionContext.Exception.ToString()); } else { Trace.TraceInformation("\r\n执行时间:{0} 毫秒\r\n-->ScalarExecuted.Command:{1}\r\n", _stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds, command.CommandText); } base.ScalarExecuted(command, interceptionContext); } public override void NonQueryExecuting(System.Data.Common.DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<int> interceptionContext) { base.NonQueryExecuting(command, interceptionContext); _stopwatch.Restart(); } public override void NonQueryExecuted(System.Data.Common.DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<int> interceptionContext) { _stopwatch.Stop(); if (interceptionContext.Exception != null) { Trace.TraceError("Exception:{1} \r\n --> Error executing command:\r\n {0}", command.CommandText, interceptionContext.Exception.ToString()); } else { Trace.TraceInformation("\r\n执行时间:{0} 毫秒\r\n-->NonQueryExecuted.Command:\r\n{1}", _stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds, command.CommandText); } base.NonQueryExecuted(command, interceptionContext); } public override void ReaderExecuting(System.Data.Common.DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<System.Data.Common.DbDataReader> interceptionContext) { base.ReaderExecuting(command, interceptionContext); _stopwatch.Restart(); } public override void ReaderExecuted(System.Data.Common.DbCommand command, DbCommandInterceptionContext<System.Data.Common.DbDataReader> interceptionContext) { _stopwatch.Stop(); if (interceptionContext.Exception != null) { Trace.TraceError("Exception:{1} \r\n --> Error executing command:\r\n {0}", command.CommandText, interceptionContext.Exception.ToString()); } else { Trace.TraceInformation("\r\n执行时间:{0} 毫秒 \r\n -->ReaderExecuted.Command:\r\n{1}", _stopwatch.ElapsedMilliseconds, command.CommandText); } base.ReaderExecuted(command, interceptionContext); } }
上面这段代码需要命名空间:
using System.Data.Entity.Infrastructure.Interception;
using System.Diagnostics;
从方法名我们可以看出大致就三类:读取类的sql,[Reader],非读取类的sql,[NonQuery],还有[Scalar],这类用的比较少,跟原始的ADO.NET命令类型基本一样,不多讲.每个sql语句类型的方法都有执行前Executing,执行后Executed,从命名上我们就可以看出AOP的身影哈,接下来看如何使用它...
嗯,对没错,就是这么简单,当然你还可以把红线里那句代码放在Global文件里.
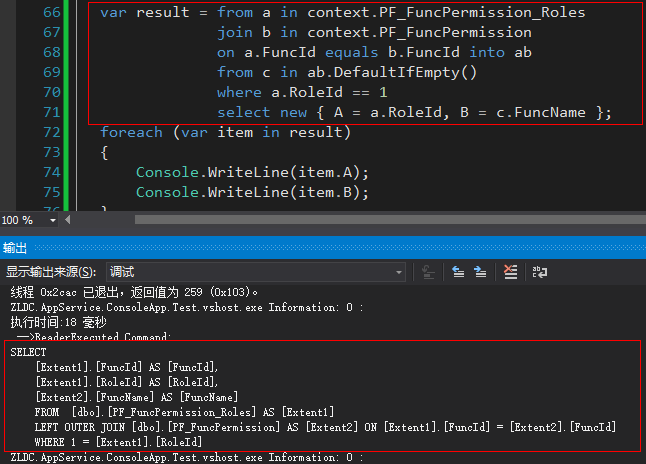
我们看看运行效果
个人感觉是比用什么插件,第三方类库,SqlProfile什么的方便点点,用博客园的Google搜索了一下,貌似没发现其他园友写这个方法,可能是太简单了,都不愿意写,还是麻烦推荐一下让更多的园友看到!