多线程处理大数组
今天领导给我们发了一篇文章文章,让我们学习一下。
文章链接:TAM - Threaded Array Manipulator
这是codeproject上的一篇文章,花了一番时间阅读了一下。文章主要是介绍当单线程处理大量数组遇到性能瓶颈时,使用多线程的方式进行处理,可以缩短数组的处理时间。
看了这篇文章后,感觉似曾相识,很多次,当我想要处理大数组时,我就会进行构思,然后想出的解决方案,与此文章中介绍的方案非常的相似。但是说来惭愧,此文章的作者有了构思后便动手写出了实现代码,然后还进行了性能测试,而我每次只是构思,觉得我能想出来就可以了,等到真正用的时候再把它写出来就行了。事实上,我大概已经构思过很多次了,但是还从来没有写过,直到看到这篇文章,我才下定决心,一定要将这个思路整理一遍。
当单线程处理大数组遇到性能瓶颈时应该怎样处理
虽然科技一直在进步,CPU的处理能力也一直在提高,但是当我们进入大数据时代后,CPU每秒钟都会面临着大量的数据需要处理,这个时候CPU的处理能力可能就会成为性能瓶颈。这是我们就要选择多核多CPU了,编程中也就是使用多线程进行处理。
首先看下单线程处理的例子
static void Main(string[] args) { int count = 100000000; double[] arrayForTest = new double[count]; Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < arrayForTest.Length; i++) { arrayForTest[i] = MathOperationFunc(arrayForTest[i]); } watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("经过 " + arrayForTest.Length + " 次循环共消耗时间 " + (watch.ElapsedMilliseconds / 1000.0) + " s"); } static double MathOperationFunc(double value) { return Math.Sin(Math.Sqrt(Math.Sqrt((double)value * Math.PI)) * 1.01); }
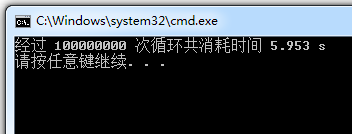
单线程处理的耗时
这个单线程的例子中对一个有10000000个元素的数组中的每个元素进行了数学计算,执行完毕共计耗时5.95秒。
然后看两个线程处理的例子
static void Main(string[] args) { //四线程测试 int threadCount = 2; Thread[] threads = new Thread[threadCount]; for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(ForTestInThread); threads[i].Name = threadCount + "线程测试" + (i + 1); threads[i].Start(); } } //工作线程 static void ForTestInThread() { int count = 50000000; double[] arrayForTest = new double[count]; Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < arrayForTest.Length; i++) { arrayForTest[i] = MathOperationFunc(arrayForTest[i]); } watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("线程:" + Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ",经过 " + arrayForTest.Length + " 次循环共消耗时间 " + (watch.ElapsedMilliseconds / 1000.0) + " s"); } //数据计算 static double MathOperationFunc(double value) { return Math.Sin(Math.Sqrt(Math.Sqrt((double)value * Math.PI)) * 1.01); }
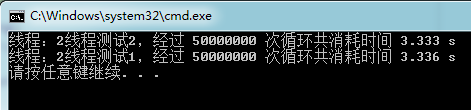
两个线程测试耗时
我们再来看一下四个线程的例子
static void Main(string[] args) { //四线程测试 int threadCount = 4; Thread[] threads = new Thread[threadCount]; for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) { threads[i] = new Thread(ForTestInThread); threads[i].Name = threadCount + "线程测试" + (i + 1); threads[i].Start(); } } //工作线程 static void ForTestInThread() { int count = 25000000; double[] arrayForTest = new double[count]; Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); for (int i = 0; i < arrayForTest.Length; i++) { arrayForTest[i] = MathOperationFunc(arrayForTest[i]); } watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("线程:" + Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ",经过 " + arrayForTest.Length + " 次循环共消耗时间 " + (watch.ElapsedMilliseconds / 1000.0) + " s"); } //数据计算 static double MathOperationFunc(double value) { return Math.Sin(Math.Sqrt(Math.Sqrt((double)value * Math.PI)) * 1.01); }
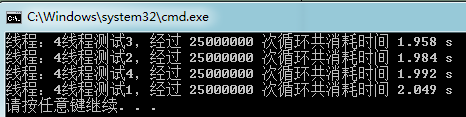
四个线程测试耗时
由上面的测试中可以看到,随着线程数的增多,任务被分解后每个线程执行的任务耗时由原来的 6秒 逐渐降到 2秒 左右,由此我们可以猜想当所有线程同时执行的时候,那么总任务的耗时就会下降,接下来让我们来进行更精确的测试。
Thread.Join方法简介
进行多线程测试时,经常会遇到这样的问题:主线程中如何等待所有线程执行结束后,再执行后续任务。
错误的做法
Thread[] threads = new Thread[threadCount]; for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) { int beginIndex = i*arrayForTest.Length/threadCount; int length = arrayForTest.Length/threadCount; threads[i] = new Thread(WorkerThread); var arg = new Tuple<double[], int, int>(arrayForTest, beginIndex, length); threads[i].Name = threadCount + "线程测试" + (i + 1).ToString(); threads[i].Start(arg); //等待所有线程结束
threads[i].Join();
}
这么做实际上所有的子线程均是串行执行的,并没有达到并行的效果。
正确的做法
Thread[] threads = new Thread[threadCount]; for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) { int beginIndex = i*arrayForTest.Length/threadCount; int length = arrayForTest.Length/threadCount; threads[i] = new Thread(WorkerThread); var arg = new Tuple<double[], int, int>(arrayForTest, beginIndex, length); threads[i].Name = threadCount + "线程测试" + (i + 1).ToString(); threads[i].Start(arg); } //等待所有线程结束 foreach (var thread in threads) { thread.Join(); }
多线程处理大数组的实现
了解了Thread.Join后,就可以进行多线程处理大数组的代码编写了:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int count = 100000000; double[] arrayForTest = new double[count]; Stopwatch totalWatch = new Stopwatch(); totalWatch.Start(); ThreadTest(arrayForTest, 2); totalWatch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("总任务,经过 " + arrayForTest.Length + " 次循环共消耗时间 " + (totalWatch.ElapsedMilliseconds / 1000.0) + " s"); } //大循环测试 static void ForTest(double[] arrayForTest, int beingIndex, int offset, Func<double, double> func) { for (int i = beingIndex; i < beingIndex + offset; i++) { arrayForTest[i] = func(arrayForTest[i]); } } //数学计算 static double MathOperationFunc(double value) { return Math.Sin(Math.Sqrt(Math.Sqrt((double)value * Math.PI)) * 1.01); } static void ThreadTest(double[] arrayForTest, int threadCount) { //启动线程 Thread[] threads = new Thread[threadCount]; for (int i = 0; i < threadCount; i++) { //为每个线程分配任务 int beginIndex = i*arrayForTest.Length/threadCount; int length = arrayForTest.Length/threadCount; threads[i] = new Thread(WorkerThread); var arg = new Tuple<double[], int, int>(arrayForTest, beginIndex, length); threads[i].Name = threadCount + "线程测试" + (i + 1).ToString(); threads[i].Start(arg); threads[i].Join(); } //等待所有线程结束 foreach (var thread in threads) { thread.Join(); } } //工作线程 static void WorkerThread(object arg) { Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); var argArray = arg as Tuple<double[], int, int>; if (argArray == null) return; ForTest(argArray.Item1, argArray.Item2, argArray.Item3, MathOperationFunc); watch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("线程:" + Thread.CurrentThread.Name + ",经过 " + argArray.Item3 + " 次循环共消耗时间 " + (watch.ElapsedMilliseconds/1000.0) + " s"); } }
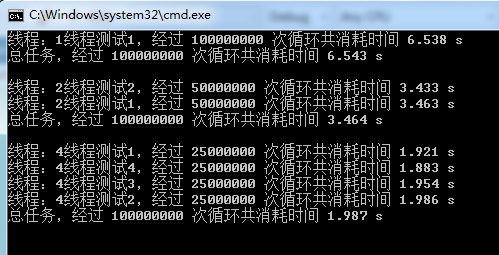
这样多线程处理大数组的功能代码就编写完成了,那么性能是如何呢,用事实说话,效果如下:
由图可以看出,将一个大任务分解到两个线程中去执行后,大任务总体的执行时间会缩短,但是与两个线程中耗时最长的线程的执行时间有关。
同时执行耗时由原来的6秒逐渐降到2秒左右。可见在多核的机器上,多线程是可以提高性能的。
所以当单线程处理大数组遇到性能瓶颈时可以考虑通过多线程来处理。
既然这个多线程处理大数组的功能效果非常好,那么何不把它封装为一个类,添加到自己的类库中,这样就可以随时使用了:
class BigArrayFor { /// <summary> /// 执行任务时,使用的线程数 /// </summary> public int ThreadCount { get; set; } /// <summary> /// 处理大数组中每个元素的方法 /// </summary> public Func<double, double> ForFunc { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// 需要处理的大数组 /// </summary> public double[] ArrayForTest { get; private set; } /// <summary> /// 实例化处理大数组的类 /// </summary> /// <param name="arrayForTest">需要处理的大数组</param> /// <param name="forFunc">处理大数组中每个元素的方法</param> public BigArrayFor(double[] arrayForTest, Func<double, double> forFunc) { if (arrayForTest == null || forFunc == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException(); } ThreadCount = 4; ForFunc = forFunc; ArrayForTest = arrayForTest; } /// <summary> /// 开始处理大数组 /// </summary> public void Run() { //启动线程 Thread[] threads = new Thread[ThreadCount]; for (int i = 0; i < ThreadCount; i++) { //为每个线程分配任务 int beginIndex = i * (ArrayForTest.Length / ThreadCount); int length = ArrayForTest.Length / ThreadCount; threads[i] = new Thread(WorkerThread); var arg = new Tuple<double[], int, int>(ArrayForTest, beginIndex, length); threads[i].Name = ThreadCount + "线程测试" + (i + 1); threads[i].Start(arg); } //等待所有线程结束 foreach (var thread in threads) { thread.Join(); } } private void WorkerThread(object arg) { var argArray = arg as Tuple<double[], int, int>; if (argArray == null) return; ForTest(argArray.Item1, argArray.Item2, argArray.Item3, ForFunc); } //大循环测试 private void ForTest(double[] arrayForTest, int beingIndex, int offset, Func<double, double> func) { for (int i = beingIndex; i < beingIndex + offset; i++) { arrayForTest[i] = func(arrayForTest[i]); } } }
好了,大数组循环类完成了,到目前为止,最多也只测试过4个线程同时处理大数组的效果,那么线程数继续增多,是不是执行时间会随之缩短呢,万事俱备,让我们开始更详细的测试吧
static void Main(string[] args) { //多线程操作大数组 int count = 100000000; double[] arrayForTest = new double[count]; //一个线程 ThreadTest(arrayForTest, 1); //两个线程 ThreadTest(arrayForTest, 2); //四个线程 ThreadTest(arrayForTest, 4); //八个线程 ThreadTest(arrayForTest, 8); //十六个线程 ThreadTest(arrayForTest, 16); //二十五个线程 ThreadTest(arrayForTest, 25); //三十二个线程 ThreadTest(arrayForTest, 32); } static void ThreadTest(double[] arrayForTest, int threadCount) { BigArrayFor bigArrayFor = new BigArrayFor(arrayForTest, MathOperationFunc); bigArrayFor.ThreadCount = threadCount; Stopwatch totalWatch = new Stopwatch(); totalWatch.Start(); bigArrayFor.Run(); totalWatch.Stop(); Console.WriteLine(bigArrayFor.ThreadCount + " 个线程,经过 " + arrayForTest.Length + " 次循环,共消耗时间 " + (totalWatch.ElapsedMilliseconds / 1000.0) + " s"); Console.WriteLine(); }
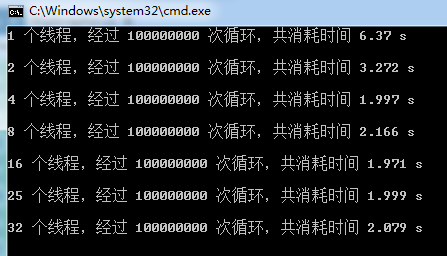
然后看测试效果
我们可以看到,随着线程数量的增多,处理数组所需的总体时间并不是随着线性的缩短,这是因为当线程数量超过CPU的核数后,会增加很多的线程调度的时间,当线程超过一定数量后,性能反而会下降。
总结
在多核机器上,当单线程处理大数组遇到性能瓶颈时,可以考虑使用多线程进行处理,但是线程数量要适量,否则会因为线程调度导致性能下降。