win32下的双缓冲绘图技术
一:双缓冲原理
为了解决窗口刷新频率过快所带来的闪烁问题,利用双缓冲技术进行绘图。所谓双缓冲技术,就是将资源加载到内存,然后复制内存数据到设备DC(这个比较快),避免了直接在设备DC上绘图(这个比较慢)。打个简单的比方:有个画家在街边办了一个即时画展,在同一块画布上根据观众的要求画不同的图像,每当有一位观众制定要看什么画时,画家先把之前画布上的东西全部擦干净,再重新绘画。显然有一些经典的画像是大家都想看的,按照以前的老办法,画家每次都要重新画这幅图像,但这种擦了画,画了擦的方式很费时。所以画家想了一个办法,把这些经典画像预先用一块或几块画布画下来,等有人需要看时,把这些预备好的画布贴在现有画布的前面,这样就能满足观众的实时性要求。那么这些事先预备好的画布就相当于内存DC,把资源放在内存DC里,等到要刷新显示时,将内存DC上的东西“贴”到当前窗口DC上,就可以减少延时带来的闪烁问题,这就是双缓冲的原理。
详细介绍见后面的几片博文。下面举两个例子:
二: 例子
例子一:加载位图
代码:
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
int wmId, wmEvent;
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hdc;
switch (message)
{
case WM_COMMAND:
wmId = LOWORD(wParam);
wmEvent = HIWORD(wParam);
// Parse the menu selections:
switch (wmId)
{
case IDM_ABOUT:
DialogBox(hInst, MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_ABOUTBOX), hWnd, About);
break;
case IDM_EXIT:
DestroyWindow(hWnd);
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
break;
case WM_PAINT:
hdc = BeginPaint(hWnd, &ps);
// TODO: Add any drawing code here...
myDraw(hdc);
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);
break;
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
myDraw函数的实现:
const int g_picHeight = 1024;
const int g_picWidth = 675;
void myDraw(HDC &dc)
{
RECT rect;
HBITMAP hOrgBitmap;
HBITMAP hOldBitmap;
int disHeight, disWidth;
GetClientRect(g_hWnd, &rect);//获取客户区大小
disHeight = rect.bottom-rect.top;
disWidth = rect.right-rect.left;
//加载图片
hOrgBitmap = (HBITMAP)::LoadImage(hInst, _T("test2.bmp"), IMAGE_BITMAP, g_picWidth, g_picHeight, LR_LOADFROMFILE);
HDC mDc = ::CreateCompatibleDC(dc);//创建当前上下文的兼容dc(内存DC)
hOldBitmap = (HBITMAP)::SelectObject(mDc, hOrgBitmap);//将位图加载到内存DC
//拷贝内存DC数据块到当前DC,自动拉伸
::StretchBlt(dc, 0, 0, disWidth, disHeight, mDc, 0, 0, g_picWidth, g_picHeight, SRCCOPY);
//恢复内存原始数据
::SelectObject(mDc, hOldBitmap);
//删除资源,防止泄漏
::DeleteObject(hOrgBitmap);
::DeleteDC(mDc);
}
结果:
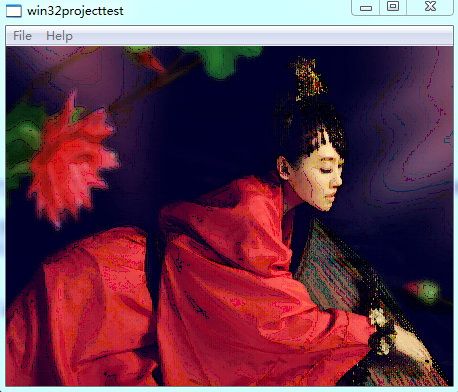
调整窗口大小,发现无闪烁现象。
例子二:画各种直线和曲线。这是一个稍微复杂点的例子,是我平时做的一个demo。可以顺便熟悉一下Windows绘图的一些操作。
代码:
void CRTVIEW_win32DlgDlg::OnPaint()
{
if (IsIconic())
{
/********此段代码忽略*********/
}
else
{
CDialog::OnPaint(); //调用基类的默认控件绘制
CRect ctrlRect;
CStatic *pDegreePicCtrl = (CStatic *)GetDlgItem(IDC_STC_DEGREEPIC);
pDegreePicCtrl->GetClientRect(&ctrlRect);//获取静态控件尺寸
CDC *pdc = pDegreePicCtrl->GetWindowDC();//获取控件DC
CDC dcMemory;
dcMemory.CreateCompatibleDC(pdc);//创建内存DC
CBitmap *pOldMapMemory;
CBitmap mapMemory;
mapMemory.CreateCompatibleBitmap(pdc, ctrlRect.Width(), ctrlRect.Height());//创建控件DC的兼容位图。其实就是与控件DC大小相同的一块区域
pOldMapMemory = dcMemory.SelectObject(&mapMemory);//加载兼容位图,只有制定了“桌布”尺寸之后,你才能在内存DC上面绘图
DrawDegreePicBkGrd(&dcMemory);//在内存DC上绘图
pdc->BitBlt(0, 0, ctrlRect.Width(), ctrlRect.Height(), &dcMemory, 0, 0, SRCCOPY);//将内存DC上的内容复制到控件DC上
dcMemory.SelectObject(pOldMapMemory);//还原原来的内存DC
::DeleteObject(mapMemory);//删除兼容位图资源
::DeleteDC(dcMemory);//删除内存DC
ReleaseDC(pdc);//释放控件DC
}
}
void CRTVIEW_win32DlgDlg::DrawDegreePicBkGrd(CDC *pdc)
{
CRect stcRect, picRect;
CStatic *pDegreePicCtrl = (CStatic *)GetDlgItem(IDC_STC_DEGREEPIC);
pDegreePicCtrl->GetClientRect(&stcRect);
if(stcRect.Width() > stcRect.Height()) {
int diff = (stcRect.Width() - stcRect.Height()) / 2;
picRect.left = stcRect.left + diff;
picRect.right = stcRect.right - diff;
picRect.top = stcRect.top;
picRect.bottom = stcRect.bottom;
} else {
int diff = (stcRect.Height() - stcRect.Width()) / 2;
picRect.left = stcRect.left;
picRect.right = stcRect.right;
picRect.top = stcRect.top + diff;
picRect.bottom = stcRect.bottom - diff;
}
CBrush *pOldBrush;
/**************画圆形***************/
CBrush newBrush1;
newBrush1.CreateSolidBrush(RGB(0, 255, 0));
pOldBrush = pdc->SelectObject(&newBrush1);
pdc->Ellipse(&picRect);
/**************画原点***************/
CRect orgRect(stcRect.Width()/2-2, stcRect.Height()/2-2, stcRect.Width()/2+2, stcRect.Height()/2+2);
CBrush newBrush2;
newBrush2.CreateSolidBrush(RGB(255,0,0));
pOldBrush = pdc->SelectObject(&newBrush2);
pdc->Ellipse(&orgRect);
pdc->SelectObject(pOldBrush);
/*************画刻度***************/
CPoint center(stcRect.Width()/2, stcRect.Height()/2);
double radias = (double)picRect.Width()/2;
CPen newPen(PS_SOLID, 1, RGB(255,0,0));
CPen *poldPen = pdc->SelectObject(&newPen);
CPoint startPoint, endPoint;
for(int i=0; i<360; i=i+5) {
double cosval = cos(DEGREETORADIAN(i));
double sinval = sin(DEGREETORADIAN(i));
startPoint.x = center.x + int(radias * cosval); //当前角度对应的圆上的点的x坐标
startPoint.y = center.y - int(radias * sinval); //当前角度对应的圆上的点的y坐标
if(i%10 == 0) {
endPoint.x = startPoint.x - int(10 * cosval);
endPoint.y = startPoint.y + int(10 * sinval);
} else {
endPoint.x = startPoint.x - int(5 * cosval);
endPoint.y = startPoint.y + int(5 * sinval);
}
pdc->MoveTo(startPoint);
pdc->LineTo(endPoint);
}
pdc->SelectObject(poldPen);
}
效果:
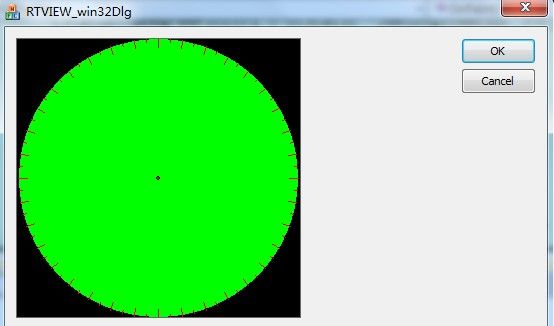
三:小结
这两个例子里面,其实每次重绘都是重新申请内存DC,然后复制到窗口DC。虽然这样子比较繁琐,但是也不影响效果,如果在响应onpaint消息时,不擦除背景(如调用Invalidate(FALSE)),也不会产生闪烁。不过最好的办法,就是文章开头说的,只画一次,把那个内存DC的句柄保存下来,每次在onpaint里面重绘时,直接调用BitBlt复制即可。不过要注意这些句柄对象的销毁,以免内存泄漏。
下面这些文章也可以看看:
1 http://baike.baidu.com/view/1149326.htm
2 http://blog.csdn.net/xsc2001/article/details/5378601
3 http://www.cppblog.com/wrhwww/archive/2011/03/01/140913.html
4 http://www.cnblogs.com/afarmer/archive/2012/03/31/2427315.html
5 http://www.programlife.net/mfc-draw-pictures-with-memory-dc-buffer.html
6 http://blog.csdn.net/zxzerster/article/details/5659775