J2SE习题(2)
第四、五周练习题
1.a. Define a class called BlogEntry that could be used to store an entry for aWeblog. The class should have instance variables to store the poster’s
username, text of the entry, and the date of the entry using the Date class from
this chapter. Add a constructor that allows the user of the class to set all
instance variables. Also add a method, DisplayEntry , that outputs all of the
instance variables, and another method called getSummary that returns the
first 10 words from the text (or the entire text if it is less than 10 words). Test
your class from your main method.
源代码:
package cn.wenhao.www.exercise1;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*类的作用:Weblog实体类
*
*@author 一叶扁舟
*@version 1.0
*@创建时间: 2014年10月4日 下午8:21:07
*/
public class BlogEntry {
//用户的名字
private String userName;
//用户发表的日志的内容
private String text;
//用户发表日志的日期
private String date;
//无參数的构造函数
public BlogEntry(){}
/**
* @param userName username
* @param text 日志文本
* @param date 日志发表的日期
*/
public BlogEntry(String userName, String text, String date) {
super();
this.userName = userName;
this.text = text;
this.date = date;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getText() {
return text;
}
public void setText(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String string) {
this.date = string;
}
public String toString() {
System.out.println("作者:" + userName + "\n 日志内容:\n" + text + "\n日志发表时间:"
+ date);
return null;
}
//日志的概要
public String getSummary(){
String str = null;
if(text.length() <= 10){
str = text;
}else{//截取text字符串的前十个字符
str = text.substring(0, 10);
}
return str;
}
}
package cn.wenhao.www.exercise1;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
*类的作用:用来測试BlogEntry实体类
*
*
*@author 一叶扁舟
*@version 1.0
*@创建时间: 2014年10月4日 下午8:24:39
*/
public class TestBlogEntry {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlogEntry blog = new BlogEntry();
blog.setUserName("一叶扁舟");
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");//设置日期格式
blog.setDate(df.format(new Date()));
blog.setText("一叶扁舟,今天心情非常好,尽管有点累,可是过的非常充实……");
System.out.println("日志概要:"+blog.getSummary());
blog.toString();
}
}
測试效果图:
2.b. Define a class called Counter whose objects count things. An object of
this class records a count that is a nonnegative integer. Include methods to set
the counter to 0, to increase the count by 1, and to decrease the count by 1. Be
sure that no method allows the value of the counter to become negative.
Include an accessor method that returns the current count value and a method
that outputs the count to the screen. There should be no input method or other
mutator methods. The only method that can set the counter is the one that sets
it to 0. Also, include a toString method and an equals method. Write a program
(or programs) to test all the methods in your class definition.
源代码:
package cn.wenhao.www.exercise2;
/**
* 类的作用:用来统计数据的工具类
*
*
* @author 一叶扁舟
* @version 1.0
* @创建时间: 2014年10月4日 下午10:17:43
*/
public class Counter {
private int count = 0;
// 重置方法:数据清零
public void reSet() {
count = 0;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + count;
return result;
}
// 推断数据是否相等
public boolean equals(int obj) {
return this.count == obj;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "count=" + count;
}
// 计数器自己主动添加1
public void increase() {
count++;
}
// 计数器自己主动减1
public void decrease() {
count--;
// 保证数据不能为负数
if (count < 0)
count = 0;
}
// 获取当前值
public int currentValue() {
return count;
}
}
package cn.wenhao.www.exercise2;
/**
*类的作用:測试Counter这个类
*
*
*@author 一叶扁舟
*@version 1.0
*@创建时间: 2014年10月4日 下午10:48:08
*/
public class TestCount {
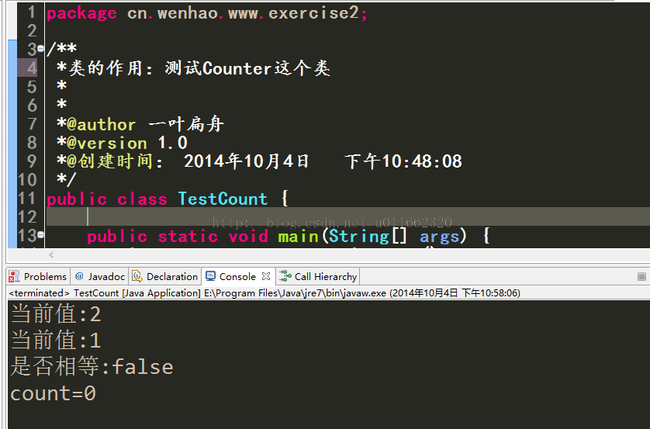
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter counter = new Counter();
//计数器添加1;
counter.increase();
counter.increase();
System.out.println("当前值:"+counter.currentValue());
counter.decrease();
System.out.println("当前值:"+counter.currentValue());
boolean flag = counter.equals(1);
System.out.println("是否相等:"+flag);
//数据清零
counter.reSet();
System.out.println(counter.toString());
}
}
代码測试效果图:
3.c. Write a Temperature class that has two instance variables: a temperature
value (a floating-point number) and a character for the scale, either C for
Celsius or F for Fahrenheit. The class should have four constructor methods:
one for each instance variable (assume zero degrees if no value is specified and
Celsius if no scale is specified), one with two parameters for the two instance
variables, and a no-argument constructor (set to zero degrees Celsius).
Include the following:
(1) two accessor methods to return the temperature—one to return the
degrees Celsius, the other to return the degrees Fahrenheit—use the following
formulas to write the two methods, and round to the nearest tenth of a degree:
DegreesC = 5*(degreesF - 32)/9
DegreesF = (9*degreesC)/5 + 32;
(2) three mutator methods: one to set the value, one to set the scale ( F or C ),
andone to set both;
(3) three comparison methods: an equals method to test whether
two temperatures are equal, one method to test whether one temperature is
greaterthan another, and one method to test whether one temperature is less
than another (note that a Celsius temperature can be equal to a Fahrenheit
temperature as indicated by the above formulas);
(4) a suitable toString method. Then write a driver program (or programs) that
tests all the methods. Be sure to use each of the constructors, to include at least
one true and one false case for each of the comparison methods, and to test at
least the following temperature equalities:
0.0 degrees C = 32.0 degrees F
–40.0 degrees C = –40.0 degrees F
100.0 degrees C = 212.0 degrees F.
源代码:
package cn.wenhao.www.exercise3;
/**
* 类的作用:摄氏度(C)、华氏摄氏度(F)的转换和比較
*
*
* @author 一叶扁舟
* @version 1.0
* @创建时间: 2014年10月8日 上午10:02:08
*/
public class Temperature {
// 温度的数值
private float value;
// 温度的单位(C/F)
private char unit;
// 无參数的构造函数,设置默认值
public Temperature() {
this.value = 0;
this.unit = 'C';
}
/**
* @param value
* 温度的数值
*/
public Temperature(float value) {
this.value = value;
}
/**
* @param unit
* 温度的单位
*/
public Temperature(char unit) {
this.unit = unit;
}
/**
* @param value
* 温度的数值
* @param unit
* 温度的单位
*/
public Temperature(float value, char unit) {
this.unit = unit;
this.value = value;
}
/**
* @return 摄氏度的数值
*/
public float getDegreesC() {
float temp;
// 说明单位是C,不用转换直接返回
if (this.unit == 'C') {
temp = this.value;
} else {
// 反之说明是华氏摄氏度,须要依据公式进行转换 DegreesC = 5*(degreesF - 32)/9
temp = 5 * (this.value - 32) / 9;
}
return temp;
}
/**
* @return 华氏摄氏度
*/
public float getDegreesF() {
float temp;
// 说明单位是F,不用转换直接返回
if (this.unit == 'F') {
temp = this.value;
} else {
// 反之说明是摄氏度,须要依据公式进行转换 DegreesF = (9*degreesC)/5 + 32;
temp = (this.value * 9) / 5 + 32;
}
return temp;
}
// 设置数据
public void setValue(float value) {
this.value = value;
}
public void setUnit(char unit) {
this.unit = unit;
}
public void setBoth(float value, char unit) {
this.value = value;
this.unit = unit;
}
// 三个比較的方法
public boolean equals(Temperature temperature) {
// 首先要推断是否单位一致,单位一直直接比較数值大小
if (this.unit == temperature.unit) {
if (this.value == temperature.value) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
} else {// 单位不一致,先将单位转换一致再进行比較
if (this.getDegreesC() == temperature.getDegreesC()) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
// 小于方法
public boolean lessThan(Temperature temperature) {
// 直接统一单位(摄氏度),然后直接进行比較
if (this.getDegreesC() < temperature.getDegreesC()) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
// 大于方法
public boolean moreThan(Temperature temperature) {
// 直接统一单位(摄氏度),然后直接进行比較
if (this.getDegreesC() > temperature.getDegreesC()) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// return "摄氏度为:" + this.getDegreesC() + "C\t"
// + "华氏摄氏度为:" + this.getDegreesF()
// + "F";
return "温度为:"+this.value+" degrees "+this.unit+" ";
}
}
package cn.wenhao.www.exercise3;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
*类的作用:測试Temperature这个类
*
*
*@author 一叶扁舟
*@version 1.0
*@创建时间: 2014年10月8日 上午10:52:22
*/
public class TestTemperature {
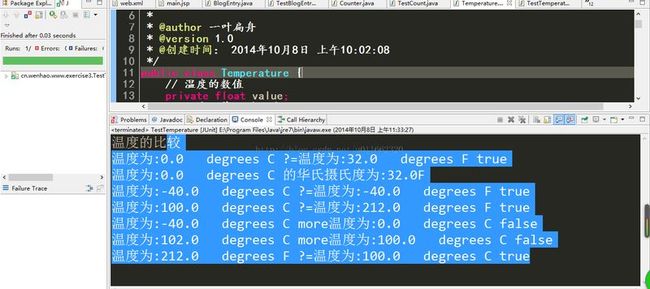
@Test
public void testTemperature() throws Exception {
//创建四个构造函数
/*
* 0.0 degrees C = 32.0 degrees F
–40.0 degrees C = –40.0 degrees F
100.0 degrees C = 212.0 degrees F.
*/
Temperature temperature1 = new Temperature();
Temperature temperature2 = new Temperature(32.0f,'F');
Temperature temperature3= new Temperature(-40.0f);
Temperature temperature4= new Temperature('F');
Temperature temperature5 = new Temperature(100.0f,'C');
Temperature temperature6 = new Temperature(212.0f,'F');
System.out.println("温度的比較");
System.out.println(temperature1.toString()+"?="+temperature2.toString()+
temperature2.equals(temperature1));
System.out.println(temperature1.toString()+"的华氏摄氏度为:"+temperature1.getDegreesF()+"F");
temperature3.setUnit('C');
System.err.println(temperature3.toString()+"more"+temperature1.toString()+temperature3.moreThan(temperature1));
temperature4.setValue(-40.0f);
System.out.println(temperature3.toString()+"?="+temperature4.toString()+
temperature2.equals(temperature1));
System.out.println(temperature5.toString()+"?="+temperature6.toString()+
temperature2.equals(temperature1));
//又一次设置temperature1
temperature1.setBoth(102, 'C');
System.err.println(temperature1.toString()+"more"+temperature5.toString()+temperature1.lessThan(temperature5));
System.err.println(temperature6.toString()+"?="+temperature5.toString()+temperature5.equals(temperature6));
}
}
代码效果图:
4.d. Create a class named Pizza that stores information about a single pizza. It
should contain the following:
Private instance variables to store the size of the pizza (either small,
medium,or large), the number of cheese toppings, the number of pepperoni
toppings, and the number of ham toppings.
Constructor(s) that set all of the instance variables.
Public methods to get and set the instance variables.
A public method named calcCost( ) that returns a double that is the cost
of the pizza.
Pizza cost is determined by:
Small: $10 + $2 per topping
Medium: $12 + $2 per topping
Large: $14 + $2 per topping
• A public method named getDescription( ) that returns a String containing
the pizza size, quantity of each topping, and the pizza cost as calculated
by calcCost( ) .
Write test code to create several pizzas and output their descriptions. For
example, a large pizza with one cheese, one pepperoni and two ham toppings
代码:
package cn.wenhao.www.exercise4;
import org.omg.CORBA.PUBLIC_MEMBER;
/**
*类的作用:比萨饼的计算
*
*
*@author 一叶扁舟
*@version 1.0
*@创建时间: 2014年10月8日 下午12:28:46
*/
public class Pizza {
//比萨饼的大小
private Size size;
//cheese的数量
private int numCheese;
//pepperoni的数量
private int numPepperoni;
//ham的数量
private int numHam;
public Pizza(){
this.size = Size.small;
}
/**
* @param size
* @param numCheese
* @param numPepperoni
* @param numHam
*/
public Pizza(Size size, int numCheese, int numPepperoni, int numHam) {
this.size = size;
this.numCheese = numCheese;
this.numPepperoni = numPepperoni;
this.numHam = numHam;
}
public Size getSize() {
return size;
}
public void setSize(Size size) {
this.size = size;
}
public int getNumCheese() {
return numCheese;
}
public void setNumCheese(int numCheese) {
this.numCheese = numCheese;
}
public int getNumPepperoni() {
return numPepperoni;
}
public void setNumPepperoni(int numPepperoni) {
this.numPepperoni = numPepperoni;
}
public int getNumHam() {
return numHam;
}
public void setNumHam(int numHam) {
this.numHam = numHam;
}
//计算买一个比萨饼的的价钱
public int calcCost(){
int sum =0;
int costSize = 0;
if(Size.small == size){
costSize = 10;
}else if (size == Size.meium) {
costSize = 12;
}else{
costSize = 14;
}
sum = costSize + (this.numCheese + this.numHam + this.numPepperoni )* 2;
return sum;
}
public String getDescription(){
return "size:"+ size + "\nnumCheese:" +this.numCheese+"\nnumHam:"+this.numHam+"\nnumPepperoni:"+this.numPepperoni+"\n总价:"+this.calcCost()+"$";
}
}
package cn.wenhao.www.exercise4;
/**
*类的作用:比萨饼的大小表示形式:小,中,大
*
*
*@author 一叶扁舟
*@version 1.0
*@创建时间: 2014年10月8日 下午12:40:34
*/
public enum Size {
small,meium,large
}
package cn.wenhao.www.exercise4;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
*类的作用:測试pizza类
*
*
*@author 一叶扁舟
*@version 1.0
*@创建时间: 2014年10月8日 下午1:11:02
*/
public class TestPizza {
@Test
public void testPizza() {
Pizza pizza1 = new Pizza(Size.small, 2, 4, 0);
System.out.println(pizza1.getDescription());
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
pizza1.setSize(Size.large);
pizza1.setNumPepperoni(1);
pizza1.setNumCheese(3);
pizza1.setNumHam(2);
System.out.println(pizza1.getDescription());
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
}
@Test
public void testPizza2() {
Pizza pizza = new Pizza();
System.out.println(pizza.getDescription());
}
}
代码測试效果图:

