异步编程
异步编程
前言
本文通过对线程的追踪来认识和理解异步编程,如有错误之处,还请各位多多批评指正。
追踪委托线程和UI线程
如果有对委托不甚了解的同学,可以查看 通过IL来认识和使用委托。我们以控制台程序为例来介绍利用委托实现异步编程,我们暂定控制台程序的线程为UI线程,通过委托进行的异步调用为委托线程。正如我们所知道的,所有的前台线程,即便在main函数执行结束之后仍然能够继续运行,但是通过委托线程在main函数执行结束之后也将结束运行,其特性更接近于后台线程,本文不将如何利用委托实现异步调用作为重点,而是通过对线程的追踪来认识和理解委托的异步调用。以下代码通过对委托方法,回调方法,main函数的线程ID进行追踪来探究异步调用每一步的执行线程。
namespace DelegateAsyncInvoke { public delegate string GetAString(string a); class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("ThreadID:{0} This is Main Method start", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); InvokeClass invokeClass = new InvokeClass(); GetAString firstMethod = invokeClass.GetString; CallBackClass callBackClass = new CallBackClass(); IAsyncResult ar = firstMethod.BeginInvoke("This is a async Invoke", callBackClass.CallBackMethod, callBackClass); //EndInvoke will not execute till BeginInvoke above execution finishing string result = firstMethod.EndInvoke(ar); Console.WriteLine("ThreadID:{0} This is Main Method end", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); Console.ReadKey(); } } /// <summary> /// this class is used to be invoked through delegate /// </summary> public sealed class InvokeClass { public string GetString(string a) {
Thread.Sleep(3000); Console.WriteLine("ThreadID:{0} This is delegate async invoke Method", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); return a; } } /// <summary> /// this class is used to call back through asynchronized invoke of delegate /// </summary> public sealed class CallBackClass { public void CallBackMethod(IAsyncResult ar) { if (ar.AsyncState != null) { CallBackClass callBackClass = ar.AsyncState as CallBackClass; Console.WriteLine("ThreadID:{0} This is Call Back Method",Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } } } }
运行结果
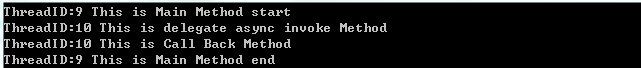
从运行结果可以看出委托方法和回调方法将在同一个线程上执行,UI线程将在委托实例调用EndInvoke方法之后结束执行。让我们用如下代码来代替EndInvoke方法,来进一步探究一下EndInvoke方法的工作原理。
while (true) { if (ar.AsyncWaitHandle.WaitOne(50, false)) { break; } }
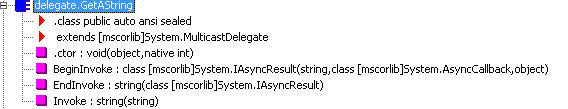
以上代码的意义是通过BeginInvoke的返回值IAsyncResult实现UI线程和委托线程的通信,UI线程一直等待委托线程执行完毕之后才向下执行。EndInvoke的参数为IAsyncResult,由此我们可以推测EndInvoke必须要实现UI线程和委托线程的通信,才能实现EndInvoke的功能。有同学为了获取异步调用的返回值,在回调方法上调用EndInvoke方法,结果发现Main函数结束执行之后,委托线程也随之结束了,可能正是这个原因所致。以下是对委托声明进行反编译获取的IL的代码,可惜的是无法看到每一个方法的内部代码,如果哪位大神有办法看到方法的内部代码,还请告知,先在此谢过了。
追踪异步线程和UI线程 - 对BackGroundWorker进行追踪
对于BackGroundWorker我们使用WinForm的程序进行追踪,本文不将如何使用BackGroundWorker作为重点,还请不了解BackGroundWorker的同学自行查资料。
我们从WinForm的入口程序看到WinForm程序只支持STAThread(单线程操作模式)。
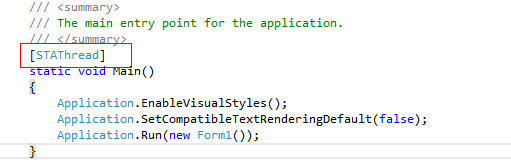
我们可以在方法上加上属性STAThread或MTAThread来决定方法是支持单线程模式还是多线程模式。所谓WinForm的单线程操作模式,也就是WinForm的UI线程只支持单线程操作。让我们用以下的代码对BackGroundWorker的异步线程进行追踪,同时对单线程操作模式进行探究。绿色背景代码为线程的追踪代码。
/// <summary> /// save all threads information /// </summary> private string ThreadInformation; public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } private void btnCalculate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { btnCalculate.Enabled = false; textBoxResult.Text = string.Empty; btnCancel.Enabled = true; progressBar1.Value = 0; ThreadInformation = "Thread Information"; ThreadInformation += string.Format("\nThreadID:{0} This is Main Method start", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); backgroundworker.RunWorkerAsync(new CalcInput(int.Parse(textBoxX.Text), int.Parse(textBoxY.Text))); ThreadInformation += string.Format("\nThreadID:{0} This is Main Method end", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); } /// <summary> /// BackGroundWorker work method /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> private void backgroundworker_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e) { ThreadInformation += string.Format("\nThreadID:{0} This is BackGroundWorker DoWork Method", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); CalcInput input = (CalcInput)e.Argument; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Thread.Sleep(500); backgroundworker.ReportProgress(i * 10); if (backgroundworker.CancellationPending) { e.Cancel = true; return; } } e.Result = input.x + input.y; } /// <summary> /// BackGroundWorker completion event /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> private void backgroundworker_RunWorkerCompleted(object sender, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs e) { ThreadInformation += string.Format("\nThreadID:{0} This is BackGroundWorker Completion Event Method", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); lblThreadInformation.Text = ThreadInformation; if (e.Cancelled) { textBoxResult.Text = "Cancelled"; } else { textBoxResult.Text = e.Result.ToString(); } btnCalculate.Enabled = true; btnCancel.Enabled = false; progressBar1.Value = 100; } private void btnCancel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { backgroundworker.CancelAsync(); } /// <summary> /// BackGroundWorker Progress changed event /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> private void backgroundworker_ProgressChanged(object sender, ProgressChangedEventArgs e) { ThreadInformation += string.Format("\nThreadID:{0} This is BackGroundWorker progress changed event", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); this.progressBar1.Value = e.ProgressPercentage; } } public struct CalcInput { public CalcInput(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public int x; public int y; }
线程的追踪信息。
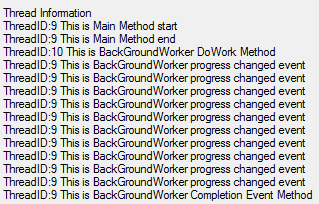
从线程的追踪信息来看,只有BackGroundWorker的DoWork方法运行在异步线程上,BackGroundWorker的Completion event方法和progress changed event 方法都运行在UI线程上,这两个方法负责输出最终的运行结果和修改进度条的值,我们把代码修改一下,把输出线程追踪信息的处理,即为控件赋值的操作移入DoWork方法尾部,来查看一下运行结果。(这步操作不要点击取消按钮)
DoWork的方法修改如下,绿色背景代码为对控件的赋值。
/// <summary> /// BackGroundWorker work method /// </summary> /// <param name="sender"></param> /// <param name="e"></param> private void backgroundworker_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e) { ThreadInformation += string.Format("\nThreadID:{0} This is BackGroundWorker DoWork Method", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId); CalcInput input = (CalcInput)e.Argument; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { Thread.Sleep(500); backgroundworker.ReportProgress(i * 10); if (backgroundworker.CancellationPending) { e.Cancel = true; return; } } e.Result = input.x + input.y; lblThreadInformation.Text = ThreadInformation; textBoxResult.Text = e.Result.ToString(); }
运行结果,看以看到界面上无法输出线程信息和计算结果,我们提到过WinForm程序的UI线程只支持单线程操作模式,只有UI线程能对控件进行操作,其他线程无法访问。
小结
本文只是通过对常见的应用进行一些探究,希望能从一个更简单的角度来理解多线程编程。还请各位能多多发表意见和看法,再次感谢大家了!!
附上源代码,sln文件请自己添加。
源码下载
