车牌识别--模板库C语言数组的制作
在车牌识别中,字符模板匹配的模板库是很大的。
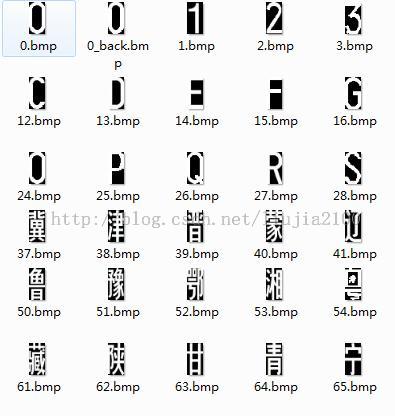
包括 10个阿拉伯数字以及26个英文字母还有几十个汉字,每个库都是一张小图片,加载起来也比较繁琐。
后面还有可能为提高识别增加额外的模板库。
之前的处理中,是把这些库的图片文件放到一个文件夹中,程序启动后,再一个一个读取,这样文件的数量就比较多。
原图片模板如下:
程序稳定后,我们就不要这些字符模板库了,可以用数组的形式代替,就是把这些文件数据保存一个c语言数组里面,直接编译到程序中,运行程序的时候直接使用,不用一个一个加载,再去匹配。
目前使用的moan库图片是20x40的8bit灰度BMP格式文件,其信息头长度54+256x4=1078,直接略过信息头和调色板获取图片数据信息
模板制作的c代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define CHAR_NUM 66
#define CHAR_WIDHT 20
#define CHAR_HEIGHT 40
char template[CHAR_NUM][CHAR_WIDHT * CHAR_HEIGHT];
int readstr(FILE *inFIL, unsigned char *srcBmp)
{
int width,height, headlength;
int i,j,line8;
unsigned char *temp;
unsigned char temp1;
width = CHAR_WIDHT;
height = CHAR_HEIGHT;
headlength = 1078;//54 + 256 * 4;
line8=(width*8+31)/32*4;
temp=(char *)malloc(height * line8 * sizeof(char));
fseek(inFIL, headlength, SEEK_SET);
fread(temp, line8 * height,1, inFIL);
if(temp==NULL)
{
printf("\n读取失败\n");
return -1;
}
for(i=0;i<height;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<width;j++)
{
temp1 = temp[i*line8+j];
if(temp1 > 150)
temp1 = 255;
else
temp1 = 0;
srcBmp[(height-i-1)*width+j]= temp1;// (temp1 > 150 ? 255:0);//(byte)(0.299*bitmap[temp[i*line8+j]].bitb+0.578*bitmap[temp[i*line8+j]].bitg+0.114*bitmap[temp[i*line8+j]].bitr);
}
}
free(temp);
temp=NULL;
return 0;
}
int readtemplate(char *path, char src[CHAR_NUM][CHAR_WIDHT * CHAR_HEIGHT])
{
FILE *f[72];
int i;
char str[100];
for(i = 0; i <= CHAR_NUM; i++)
{
sprintf(str, "%s%d.bmp", path, i);
f[i]=fopen(str,"rb");
if(f[i]==NULL)
{
printf("can't open patch:%s\n", str);
return -1;
}
readstr(f[i], src[i]);
fclose(f[i]);
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int i, j;
FILE *f;
unsigned char p;
char buf[5];
f = fopen("Template.h", "wb");
if(f == NULL)
{
printf("Can't open the file\n");
return -1;
}
if(readtemplate(".\\test\\moban\\", template) != 0)
{
printf("readtemplate error\n");
return -1;
}
for(i = 0; i < CHAR_NUM; i++)
for(j = 0; j < CHAR_WIDHT * CHAR_HEIGHT; j ++)
{
if((j%800 == 0))
fwrite("\n",strlen("\n"),1,f);
p = template[i][j];
sprintf(buf,"%4d,", p);
fwrite(buf,strlen(buf),1,f);
}
fclose(f);
return 0;
}
制作后的数组如下(变量名自行添加)
之前算法是一个一个读取,然后重新复制一遍
void readmoban(char *path,struct BMP_Plate *img2)
{
FILE *f[72];
int i;
char str[80];
for(i=0;i<=66;i++)
{
sprintf(str,"%s%d.bmp", path, i);
f[i]=fopen(str,"rb");
if(f[i]==NULL)
{
printf("can't open moban:%d,%s\n", i, str);
exit(-1);
}
readstr(f[i],img2->strc[i]);
displayGray(img2->strc[i],20,40,0,0);
fclose(f[i]);
}
}
现在,只需要,指定数组指针,不用加载图片,也不用复制
int readtemplate(char *moban,struct BMP_Plate *img2)
{
int i;
#if 0
for(i = 0; i <= CHAR_NUM; i++)
{
memcpy(img2->strc[i],&moban[i * TEMPPLATE_SIZE], TEMPPLATE_SIZE);
}
#else
for(i = 0; i <= CHAR_NUM; i++)
{
img2->strc[i] = &moban[i * TEMPPLATE_SIZE];
}
#endif
return 0;
}不用再重新复制数据了,优化了代码,节省了时间(其实节省的也不是很多^^ )。
作者:liujia2100 发表于2014-6-1 23:10:17 原文链接
阅读:91 评论:0 查看评论