4. New Data Model
动机
数据模型是一个扩展并定义的基础应用程序的“problem domain”或者应用程序的结构。业务逻辑总是位于顶部的数据模型。这个步骤显示了如何根据另一个扩展是一个数据模型的定义。
我们的任务
1.后台 hybris 数据模型;2.CuppyTrail 和 Cuppy 之间添加一个依赖关系;3.在 cuppytrail-items.xml 添加 Stadium; 4.关系; 5.枚举类型;6.默认值;7.检查这个模型;8.更新 hybris 系统;9.类型系统本地化;10.学习 cuppytrail-items.xml
1.后台 hybris 数据模型
每个 extension 的数据模型文件名的定义<extensionName>-items.xml . 基本数据实体( 在 hybris 被称为 "items")定义itemtype元素,来定义项目之间的关系。例如,打开 Cuppy/resources/cuppy-items.xml 仔细查看了许多关系和itemtype定义Cuppy的数据模型。
hybris 的构建系统提取位于\ *-.xml 的文件 扩展并生成每itemtype的Java源文件来支持访问这些实体 hybris 的框架体系.
这里要记住的要点是,许多类生成itemtype分为三类:
1.用于创建模型类ServiceLayer鼓励合作伙伴发展他们的业务逻辑。下面我们将指定一个新的Itemtype体育场 和 我们可以使用 hybris 生成多个文件包括StadiumModel Java类。
2.通过创建基于REST URI来支持CRUD逻辑Web服务相关的类。当可选的扩展platformwebservices包括在你的配置只生成这些类。我们将看到如何在Java类StadiumDTO(S)和StadiumResoure(S)的web服务步道步骤中使用。
3.低层次的Jalo类。我们不会针对这些类,不鼓励使用的。
我们谨代表一个新的实体 - 体育场 - 和它的比赛对应每个球场的列表。比赛将在Cuppy扩展定义。
因此,我们的主要任务是:
在cuppytrail-items.xml 添加一个新的 item 和 定义一个新的数据实体体育场
在cuppytrail-items.xml 添加一个关系创造体育场和比赛之间的1对多的关系
在cuppytrail-items.xml 添加一个枚举类型,创造一个体育场的类型和体育场访问; 我们是创造2个新enumtypes.
在cuppytrail-items.xml添加默认值
在每个创建的类型添加默认值
2.添加CuppyTrail和Cuppy之间的依赖关系
作为数据模型,将取决于cuppy的数据模型,设置extensioninfo.xml以及在Eclipse构建路径依赖:
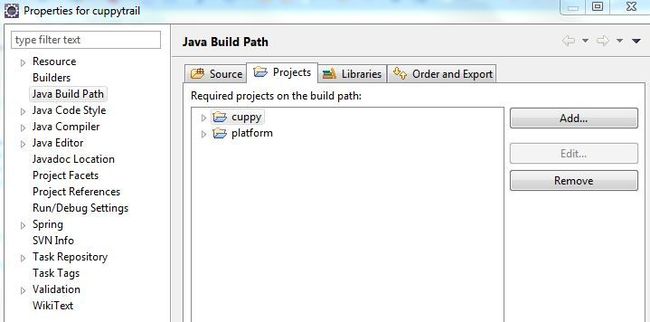
2.1 让Eclipse的Cuppytrail扩展名取决于Cuppy扩展:右击cuppytrail - build path - configure build path
2.2 告诉构建采用hybris框架的扩展Cuppytrail依赖于Cuppy扩展。打开cuppytrail/extensioninfo.xml 文件 添加下面代码 作为扩展元素中的第一个元素。
<requires-extension name="cuppy"/>
3.在 cuppytrail-items.xml 添加 Stadium
更换cuppytrail/resources/ cuppytrail-items.xml与下面的XML声明描述新体育场的ItemType及其属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<!--
[y] hybris Platform
Copyright (c) 2000-2013 hybris AG
All rights reserved.
This software is the confidential and proprietary information of hybris
("Confidential Information"). You shall not disclose such Confidential
Information and shall use it only in accordance with the terms of the
license agreement you entered into with hybris.
-->
<items xmlns:xsi="<a href="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" "="">http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="items.xsd">
<itemtypes>
<itemtype code="Stadium" generate="true" autocreate="true">
<deployment table="CuppyTrailStadium" typecode="10123" />
<attributes>
<attribute qualifier="code" type="java.lang.String" >
<persistence type="property"/>
<modifiers optional="false" unique="true"/>
</attribute>
<attribute qualifier="capacity" type="java.lang.Integer">
<descripion>Capacity</description>
<persistence type="property" />
</attribute>
</attributes>
</itemtype>
</itemtypes>
</items>
需要注意的是下面这些代码
itemtype code=Stadium generate=true autocreate=true
定义了一种新类型的 Stadium 隐式地从 GenericItem 延伸
autocreate=true 表示 Stadium 是一个新的类型
generate=true 创建所需的源代码(不是模型类)的类型
deployment table=CuppyTrailStadium typecode=10123
指定新类型是如何映射到数据库
table 定义了数据库表
typecode在内部使用例如创建项目PKS,TypeCodes介于0和10000通过hybris保留。不过也有一些例外。
您可以检查所使用的部署的TypeCodes在HAC: http://localhost:9001/maintain/deployments
attribute qualifier=code type=java.lang.String
创建一个新的属性 code 通过使用原子类型 java.lang.String
persistence type=property
persistence type=property
定义项目是如何存储的,property 反映了正常的持久化行为
modifiers ... /
高级的设置,如读写访问。
4.关系
使用标签的关系定义Stadium和Match之间的新关系StadiumMatchRelation
下面这段代码添加在cuppytrail/resources/cuppytrail-items.xml 的 itemtype标签里面
这个是one-to-many的关系,这意味着将通过一个额外的列映射在许多方面在表Match
<relations>//该标签与itemtypes标签同级 <relation code="StadiumMatchRelation" localized="false" generate="true" autocreate="true"> <sourceElement type="Stadium" qualifier="stadium" cardinality="one" /> <targetElement type="Match" qualifier="matches" cardinality="many"/> </relation> </relations>
5.枚举类型
添加以下的代码片段在:cuppytrail/resources/cuppytrail-items.xml
<enumtypes>//该标签与itemtypes标签同级 <enumtype code="StadiumType" autocreate="true" generate="true" dynamic="false"> <value code="openair"/> <value code="enclosed"/> </enumtype> <enumtype code="StadiumAccess" autocreate="true" generate="true" dynamic="true"> <value code="road"/> <value code="rail"/> <value code="plane"/> </enumtype> </enumtypes>
6.默认值
打开:cuppytrail/resources/cuppytrail-items.xml并且添加StadiumType到现有Stadium属性列表并定义默认值的OpenAir
<attribute type="StadiumType" qualifier="StadiumType">
<persistence type="property"/>
<defaultvalue>em().getEnumerationValue("StadiumType","openair")</defaultvalue>
</attribute>
保存并运行ant clean all (或者ant all),同时刷新eclipse里的所有的项目
完整的cuppytrail-items.xml文件应该是这样的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<!--
[y] hybris Platform
Copyright (c) 2000-2013 hybris AG
All rights reserved.
This software is the confidential and proprietary information of hybris
("Confidential Information"). You shall not disclose such Confidential
Information and shall use it only in accordance with the terms of the
license agreement you entered into with hybris.
-->
<!--
ATTENTION: This is just an example file. You have to edit it according to your needs.
-->
<items xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="items.xsd">
<enumtypes>
<enumtype code="StadiumType" autocreate="true" generate="true" dynamic="false">
<value code="openair"/>
<value code="enclosed"/>
</enumtype>
<enumtype code="StadiumAccess" autocreate="true" generate="true" dynamic="true">
<value code="road"/>
<value code="rail"/>
<value code="plane"/>
</enumtype>
</enumtypes>
<relations>
<relation code="StadiumMatchRelation"
localized="false" generate="true" autocreate="true">
<sourceElement type="Stadium" qualifier="stadium" cardinality="one"/>
<targetElement type="Match" qualifier="matches" cardinality="many"/>
</relation>
</relations>
<itemtypes>
<itemtype code="Stadium" generate="true" autocreate="true">
<deployment table="CuppyTrailStadium" typecode="10123" />
<attributes>
<attribute qualifier="code" type="java.lang.String" >
<persistence type="property"/>
<modifiers optional="false" unique="true"/>
</attribute>
<attribute qualifier="capacity" type="java.lang.Integer">
<description>Capacity</description>
<persistence type="property" />
</attribute>
<attribute type="StadiumType" qualifier="StadiumType">
<persistence type="property"/>
<defaultvalue>em().getEnumerationValue("StadiumType","openair")</defaultvalue>
</attribute>
</attributes>
</itemtype>
</itemtypes>
</items>
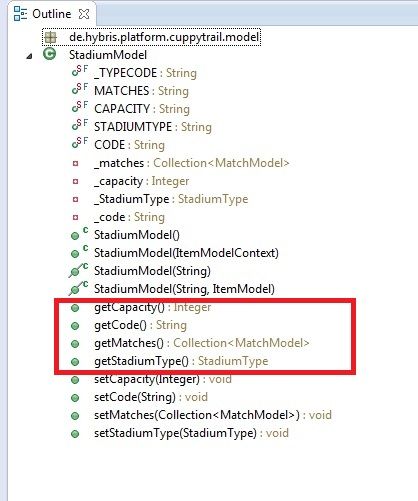
7.检查这个modal
在StadiumModel大纲视图显示,它提供了访问Code,Capacity 和 我们在cuppytrail-items.xml 的规定,同时也匹配的集合作为关系规定StadiumType特性。
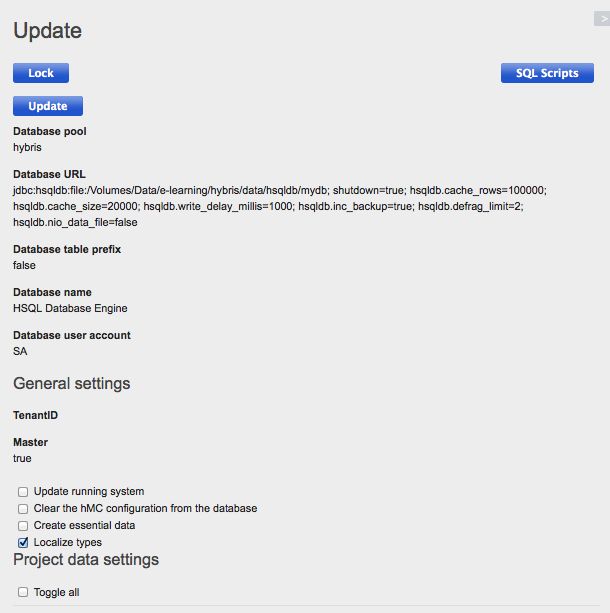
8.更新 hybris 系统
由于我们修改了的hybris数据模型(通过修改items.xml文件),我们必须通过更新系统对数据库发送更改。
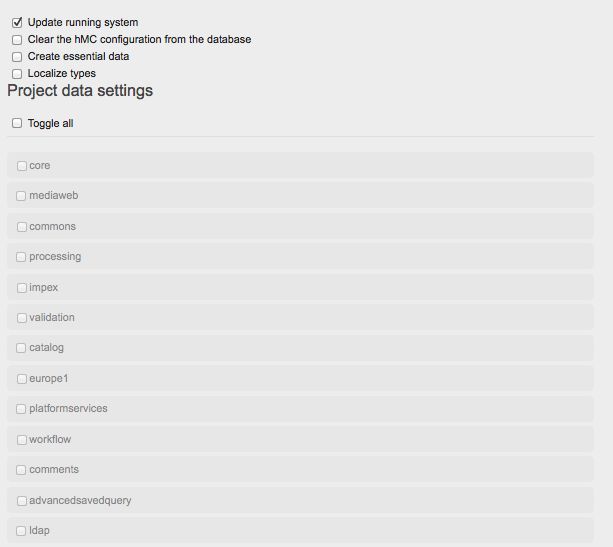
前往 Platform、Update采用 hybris Admin Console( hac:http://localhost:9001/platform/update )只选择第一个框更新运行的系统。
验证新的类型 Stadium体育场现在在hybris里是可见,要确认您的系统已经正确更新,我们应该检查的hybris“管理控制台(HMC)识别新型Stadium体育场:
打开 http://localhost:9001/hmc/hybris 并且登录 admin
打开 System/Types 查询 Stadium 。
9.类型系统本体化
通过定义新的类型,你也应该提供他们的本地化,例如:通过驾驶舱。
要做到这一点,我们需要添加 key = localization 字符串条目的类型系统本地化文件cuppytrail/resources/localization/cuppytrail-locales_en.properties
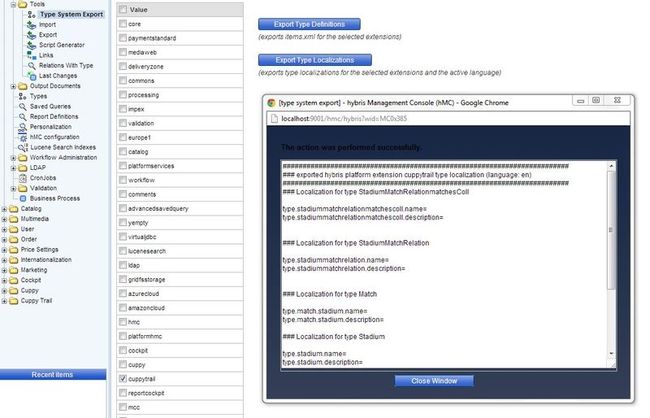
最简单的方法是从HMC做一个export(Export类型本地化)
复制这个输入框里的内容并粘贴到cuppytrail/resources/localization/cuppytrail-locales_en.propertiesandcuppytrail/resources/localization/cuppytrail-locales_en.properties
输入一些本地化的名称在这些键例如
type.stadiummatchrelationmatchescoll.name=StadiumMatchRelationMatchesColl type.stadiummatchrelationmatchescoll.description= ### Localization for type StadiumAccess type.stadiumaccess.name=StadiumAccess type.stadiumaccess.description= ### Localization for type StadiumType type.stadiumtype.name=StadiumType type.stadiumtype.description= ### Localization for type StadiumMatchRelation type.stadiummatchrelation.name=StadiumMatchRelation type.stadiummatchrelation.description= ### Localization for type Match type.match.stadium.name=Stadium type.match.stadium.description= ### Localization for type Stadium type.stadium.name=Stadium type.stadium.description= type.stadium.stadiumtype.name=Stadium type type.stadium.stadiumtype.description= type.stadium.capacity.name=Capacity type.stadium.capacity.description= type.stadium.code.name=Name type.stadium.code.description= type.stadium.matches.name=Matches type.stadium.matches.description= ### localization for enum values type.stadiumtype.openair.name=openair type.stadiumtype.enclosed.name=enclosed type.stadiumaccess.road.name=road type.stadiumaccess.rail.name=rail type.stadiumaccess.plane.name=plane
运行 ant all (或者 ant clean all)
更新系统只选择Localize types
10.研究这个文件cuppy-items.xml
在这一步中,我们已经创建了一个非常简单的items.xml文件,并讨论生成作为结果的文件。
Studycuppy/resources/cuppy-items.xml和低于它的UML表示要了解更复杂的数据模型与关系构建,属性,枚举。
该cuppy数据实体包括相关items:
用户users: Player(玩家), ProfilePicture(照片), PlayerPreferences, Country(国家)
足球队football teams: Country(国家), Team(队伍), News(新闻)
锦标赛tournaments: Competition(比赛), Match(比赛), Group(组)
下注bets: MatchBet(比赛赌注)
国家countries: Country(国家), Country Flag(国家国旗)
管理administration: TimePointStatistic(时间点的统计), OverallStatistic(总体统计), UpdateCompetitionCronJob(更新竞赛的cronjob)
浏览生成的Java文件,看看他们如何关联他们cuppy-items.xml定义,例如PlayerModel,TeamModel和CountryFlagModel。
总结
在这一步,你应该已经学会
如何将数据实体可以在扩展的items.xml文件中定义的元素的ItemType
如何关系可以在扩展的items.xml文件中定义的元素的关系
一下班,从这些新的实体,为什么自动生成
你有在items.xml文件中添加新的类型定义后,更新系统
类型定义应包括的类型系统的本地化