Pattern-No.05 设计模式之装饰者模式
1、装饰者模式定义:动态的将责任附加到对象上。若要扩展功能,装饰者提供了比继承更有弹性的替代方案。装饰者与被装饰者拥有共同的超类,继承的目的是继承类型,而不是行为。
2、要点
具体被装饰者和抽象装饰类都继承于抽象被装饰者类,继承的是类型,而不是行为
行为来自装饰者和基础组件,或与其他装饰者之间的组合关系。装饰者通常是用其他类似于工厂或生成器这样的模式创建的
可以用一个或多个装饰者包装一个对象
装饰者可以在所委托被装饰者的行为之前或之后,加上自己的行为,以达到特定的目的
对象可以在任何时候被装饰,所以可以在运行时动态的,不限量的用你喜欢的装饰者来装饰对象
装饰模式中使用继承的关键是想达到装饰者和被装饰对象的类型匹配,而不是获得其行为
装饰者一般对组件的客户是透明的,除非客户程序依赖于组件的具体类型。在实际项目中可以根据需要为装饰者添加新的行为,做到“半透明”装饰者
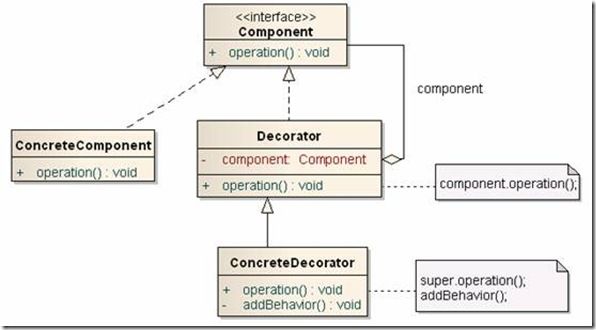
3、设计图
4、案例实现
1)不同的饮料添加不同类型的佐料
package com.shma.decorate;
/**
* 被装饰者和装饰者公共的抽象类,被装饰者和装饰者都继承这个抽象类
* @author admin
*
*/
public abstract class Beverage {
//饮料描述
protected String description = "Unknown Beverage";
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
/**
* 计算饮料价格
* @return
*/
public abstract double cost();
}
package com.shma.decorate;
/**
* 佐料装饰者抽象类
* 所有的具体佐料对象集成这个抽象类
* 这个抽象类又集成自Beverage抽象类
* @author admin
*
*/
public abstract class CondimentDecorator extends Beverage {
protected Beverage beverage;
/**
* 佐料具体实现类需要重写描述这个方法
*/
public abstract String getDescription();
}
package com.shma.decorate.beverage;
import com.shma.decorate.Beverage;
/**
* 具体饮料类
* @author admin
*
*/
public class DarkRoast extends Beverage {
public DarkRoast() {
description = "Dark Roast Coffee";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0.99;
}
}
package com.shma.decorate.beverage;
import com.shma.decorate.Beverage;
/**
* 具体饮料类
* @author admin
*
*/
public class Decaf extends Beverage {
public Decaf() {
description = "Decaf Coffee";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 1.05;
}
}
package com.shma.decorate.beverage;
import com.shma.decorate.Beverage;
public class Espresso extends Beverage {
public Espresso() {
description = "Espresso";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 1.99;
}
}
package com.shma.decorate.beverage;
import com.shma.decorate.Beverage;
public class HouseBlend extends Beverage {
public HouseBlend() {
description = "House Blend Coffee";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return .89;
}
}
package com.shma.decorate.condiment;
import com.shma.decorate.Beverage;
import com.shma.decorate.CondimentDecorator;
/**
* 佐料具体实现类
* @author admin
*
*/
public class Milk extends CondimentDecorator {
public Milk(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", Milk";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return .10 + beverage.cost() ;
}
}
package com.shma.decorate.condiment;
import com.shma.decorate.Beverage;
import com.shma.decorate.CondimentDecorator;
public class Mocha extends CondimentDecorator {
public Mocha(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", Mocha";
}
public double cost() {
return .20 + beverage.cost();
}
}
package com.shma.decorate.condiment;
import com.shma.decorate.Beverage;
import com.shma.decorate.CondimentDecorator;
public class Soy extends CondimentDecorator {
public Soy(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", Soy";
}
public double cost() {
return .15 + beverage.cost();
}
}
package com.shma.decorate.condiment;
import com.shma.decorate.Beverage;
import com.shma.decorate.CondimentDecorator;
public class Whip extends CondimentDecorator {
public Whip(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", Whip";
}
public double cost() {
return .10 + beverage.cost();
}
}
package com.shma.decorate;
import com.shma.decorate.beverage.DarkRoast;
import com.shma.decorate.beverage.Espresso;
import com.shma.decorate.beverage.HouseBlend;
import com.shma.decorate.condiment.Mocha;
import com.shma.decorate.condiment.Soy;
import com.shma.decorate.condiment.Whip;
public class TestAppMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Beverage beverage = new Espresso();
System.out.println(beverage.getDescription()
+ " $" + beverage.cost());
Beverage beverage2 = new DarkRoast();
beverage2 = new Mocha(beverage2);
beverage2 = new Mocha(beverage2);
beverage2 = new Whip(beverage2);
System.out.println(beverage2.getDescription()
+ " $" + beverage2.cost());
Beverage beverage3 = new HouseBlend();
beverage3 = new Soy(beverage3);
beverage3 = new Mocha(beverage3);
beverage3 = new Whip(beverage3);
System.out.println(beverage3.getDescription()
+ " $" + beverage3.cost());
}
}
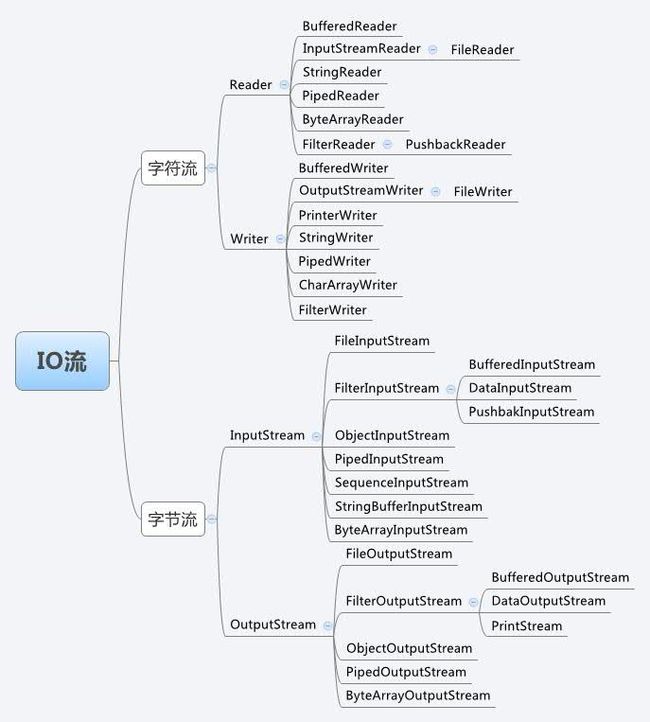
2)java.io中使用装饰者模式解析
一个类的功能扩展可以有两种方式 :
(1) 类的继承 ( 高耦合,会产生更多的子类,从而引起类的爆炸 )
(2) 对象组合即装饰模式 ( 降耦,不会创造更多的子类 ) 动态的为对象添加功能) 所以类应该对扩展开放,对修改关闭 。
装饰者模式中的四个概念对应io中的类
(1) 抽象的构件角色( Component):它是一个接口,定义了要实现的方法和功能,在io中,InputStream、OutputStream、Writer、Reader接口类实现了抽象构建角色
(2) 具体的构件角色(ConcreteComponent):它实现了Component接口,是其具体的功能实现。在io中BufferedReader、BufferedWriter、FileInputStream、FileOutputStream等类实现了具体的构件角色
(3) 装饰角色(Decorator):它是一个类,该类也实现了 Component 接口,同时也必须持有接口 Component 的对象的引用,该类也实现了 Component 接口中的方法。
i:该类的构造方法需要传递过来一个 Component 对象的引用
ii:重写的方法(即是添加的功能)需要调用 Component 对象的该方法
在io中,FilterInputStream、FilterReader、FilterOutputStream、FilterWriter等接口类定义了该功能
(4) 具体的装饰角色( Decorator 类的子类,可以有一个,也可以有多个):这些类继承了类 Decorator, 要重写父类的方法(要添加的功能),和自身的构造方法
i:构造方法要用到 super
ii:第一步: super 父类的该方法;第二步:添加自己的功能(一些方法、属性)
以InputStream为例:
(1) InputStream为抽象类
public abstract class InputStream implements Closeable {
public abstract int read() throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return read(b, 0, b.length);
}
public int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
int c = read();
if (c == -1) {
return -1;
}
b[off] = (byte)c;
int i = 1;
try {
for (; i < len ; i++) {
c = read();
if (c == -1) {
break;
}
b[off + i] = (byte)c;
}
} catch (IOException ee) {
}
return i;
}
public long skip(long n) throws IOException {
long remaining = n;
int nr;
if (skipBuffer == null)
skipBuffer = new byte[SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE];
byte[] localSkipBuffer = skipBuffer;
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
}
while (remaining > 0) {
nr = read(localSkipBuffer, 0,
(int) Math.min(SKIP_BUFFER_SIZE, remaining));
if (nr < 0) {
break;
}
remaining -= nr;
}
return n - remaining;
}
public void close() throws IOException {}
...
}
(2) FileInputStream实现了InputStream的接口
public class FileInputStream extends InputStream {
/* File Descriptor - handle to the open file */
private FileDescriptor fd;
private FileChannel channel = null;
public FileInputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException {
this(name != null ? new File(name) : null);
}
public native int read() throws IOException; //通过调用c读取文件数据
private native int readBytes(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException;
public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException {
return readBytes(b, 0, b.length);
}
......
}
(3) FilterInputStream是装饰者抽象类,它继承InputStream,同时拥有InputStream引用对象,过滤流类,起装饰器作用,用于对输入装配各种功能
public class FilterInputStream extends InputStream {
/**
* The input stream to be filtered.
*/
protected volatile InputStream in;
protected FilterInputStream(InputStream in) {
this.in = in;
}
public int read() throws IOException {
return in.read();
}
.......
}
(4) BufferedInputStream:使输入流具有缓冲功能,是一种可以装配缓冲功能的装饰器
public class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
private static int defaultBufferSize = 8192;
protected volatile byte buf[];
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) {
this(in, defaultBufferSize);
}
public BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) {
super(in);
if (size <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Buffer size <= 0");
}
buf = new byte[size];
}
private void fill() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = getBufIfOpen();
if (markpos < 0)
pos = 0; /* no mark: throw away the buffer */
else if (pos >= buffer.length) /* no room left in buffer */
if (markpos > 0) { /* can throw away early part of the buffer */
int sz = pos - markpos;
System.arraycopy(buffer, markpos, buffer, 0, sz);
pos = sz;
markpos = 0;
} else if (buffer.length >= marklimit) {
markpos = -1; /* buffer got too big, invalidate mark */
pos = 0; /* drop buffer contents */
} else { /* grow buffer */
int nsz = pos * 2;
if (nsz > marklimit)
nsz = marklimit;
byte nbuf[] = new byte[nsz];
System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, nbuf, 0, pos);
if (!bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, nbuf)) {
// Can't replace buf if there was an async close.
// Note: This would need to be changed if fill()
// is ever made accessible to multiple threads.
// But for now, the only way CAS can fail is via close.
// assert buf == null;
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
buffer = nbuf;
}
count = pos;
int n = getInIfOpen().read(buffer, pos, buffer.length - pos);
if (n > 0)
count = n + pos;
}
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
if (pos >= count) {
fill();
if (pos >= count)
return -1;
}
return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff;
}
......
}