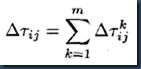蚁群算法java实现以及TSP问题蚁群算法求解
1. 蚁群算法简介
蚁群算法(Ant Clony Optimization, ACO)是一种群智能算法,它是由一群无智能或有轻微智能的个体(Agent)通过相互协作而表现出智能行为,从而为求解复杂问题提供了一个新的可能性。蚁群算法最早是由意大利学者Colorni A., Dorigo M. 等于1991年提出。经过20多年的发展,蚁群算法在理论以及应用研究上已经得到巨大的进步。
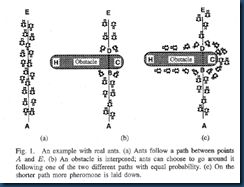
蚁群算法是一种仿生学算法,是由自然界中蚂蚁觅食的行为而启发的。在自然界中,蚂蚁觅食过程中,蚁群总能够按照寻找到一条从蚁巢和食物源的最优路径。图(1)显示了这样一个觅食的过程。
图(1)蚂蚁觅食
在图1(a)中,有一群蚂蚁,假如A是蚁巢,E是食物源(反之亦然)。这群蚂蚁将沿着蚁巢和食物源之间的直线路径行驶。假如在A和E之间突然出现了一个障碍物(图1(b)),那么,在B点(或D点)的蚂蚁将要做出决策,到底是向左行驶还是向右行驶?由于一开始路上没有前面蚂蚁留下的信息素(pheromone),蚂蚁朝着两个方向行进的概率是相等的。但是当有蚂蚁走过时,它将会在它行进的路上释放出信息素,并且这种信息素会议一定的速率散发掉。信息素是蚂蚁之间交流的工具之一。它后面的蚂蚁通过路上信息素的浓度,做出决策,往左还是往右。很明显,沿着短边的的路径上信息素将会越来越浓(图1(c)),从而吸引了越来越多的蚂蚁沿着这条路径行驶。
2. TSP问题描述
蚁群算法最早用来求解TSP问题,并且表现出了很大的优越性,因为它分布式特性,鲁棒性强并且容易与其它算法结合,但是同时也存在这收敛速度慢,容易陷入局部最优(local optimal)等缺点。
TSP问题(Travel Salesperson Problem,即旅行商问题或者称为中国邮递员问题),是一种,是一种NP-hard问题,此类问题用一般的算法是很大得到最优解的,所以一般需要借助一些启发式算法求解,例如遗传算法(GA),蚁群算法(ACO),微粒群算法(PSO)等等。
TSP问题可以分为两类,一类是对称TSP问题(Symmetric TSP),另一类是非对称问题(Asymmetric TSP)。所有的TSP问题都可以用一个图(Graph)来描述:
令
V={c1, c2, …, ci, …, cn},i = 1,2, …, n,是所有城市的集合. ci表示第i个城市, n为城市的数目;
E={(r, s): r,s∈ V}是所有城市之间连接的集合;
C = {crs: r,s∈ V}是所有城市之间连接的成本度量(一般为城市之间的距离);
如果crs = csr, 那么该TSP问题为对称的,否则为非对称的。
一个TSP问题可以表达为:
求解遍历图G = (V, E, C),所有的节点一次并且回到起始节点,使得连接这些节点的路径成本最低。
3. 蚁群算法原理
假如蚁群中所有蚂蚁的数量为m,所有城市之间的信息素用矩阵pheromone表示,最短路径为bestLength,最佳路径为bestTour。每只蚂蚁都有自己的内存,内存中用一个禁忌表(Tabu)来存储该蚂蚁已经访问过的城市,表示其在以后的搜索中将不能访问这些城市;还有用另外一个允许访问的城市表(Allowed)来存储它还可以访问的城市;另外还用一个矩阵(Delta)来存储它在一个循环(或者迭代)中给所经过的路径释放的信息素;还有另外一些数据,例如一些控制参数(![]() ,
,![]() ,
,![]() ,Q),该蚂蚁行走玩全程的总成本或距离(tourLength),等等。假定算法总共运行MAX_GEN次,运行时间为t。
,Q),该蚂蚁行走玩全程的总成本或距离(tourLength),等等。假定算法总共运行MAX_GEN次,运行时间为t。
蚁群算法计算过程如下:
(1)初始化
设t=0,初始化bestLength为一个非常大的数(正无穷),bestTour为空。初始化所有的蚂蚁的Delt矩阵所有元素初始化为0,Tabu表清空,Allowed表中加入所有的城市节点。随机选择它们的起始位置(也可以人工指定)。在Tabu中加入起始节点,Allowed中去掉该起始节点。
(2)为每只蚂蚁选择下一个节点。
为每只蚂蚁选择下一个节点,该节点只能从Allowed中以某种概率(公式1)搜索到,每搜到一个,就将该节点加入到Tabu中,并且从Allowed中删除该节点。该过程重复n-1次,直到所有的城市都遍历过一次。遍历完所有节点后,将起始节点加入到Tabu中。此时Tabu表元素数量为n+1(n为城市数量),Allowed元素数量为0。接下来按照(公式2)计算每个蚂蚁的Delta矩阵值。最后计算最佳路径,比较每个蚂蚁的路径成本,然后和bestLength比较,若它的路径成本比bestLength小,则将该值赋予bestLength,并且将其Tabu赋予BestTour。
其中
表示选择城市j的概率,k表示第k个蚂蚁,
表示城市i,j在第t时刻的信息素浓度,
表示从城市i到城市j的可见度,
,
表示城市i,j之间的成本(或距离)。由此可见
越小,
越大,也就是从城市i到j的可见性就越大。
表示蚂蚁k在城市i与j之间留下的信息素。
表示蚂蚁k经过一个循环(或迭代)锁经过路径的总成本(或距离),即tourLength.
,
,Q均为控制参数。
(3)更新信息素矩阵
令t = t + n,按照(公式3)更新信息素矩阵phermone。
为t+n时刻城市i与j之间的信息素浓度。
为控制参数,
为城市i与j之间信息素经过一个迭代后的增量。并且有
其中
由公式计算得到。
(4)检查终止条件
如果达到最大代数MAX_GEN,算法终止,转到第(5)步;否则,重新初始化所有的蚂蚁的Delt矩阵所有元素初始化为0,Tabu表清空,Allowed表中加入所有的城市节点。随机选择它们的起始位置(也可以人工指定)。在Tabu中加入起始节点,Allowed中去掉该起始节点,重复执行(2),(3),(4)步。
(5)输出最优值
4. Java实现
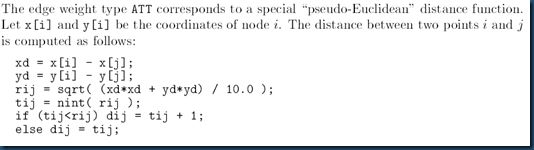
在该java实现中我们选择使用tsplib上的数据att48,这是一个对称tsp问题,城市规模为48,其最优值为10628.其距离计算方法如图(2)所示:
图(2)att48距离计算方法
实现中,使用了两个java类,一个Ant类,一个ACO类。
具体实现代码如下(此代码借鉴了蚁群优化算法的JAVA实现):
Ant类:
package ch01;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Vector;
public class Ant implements Cloneable {
private Vector<Integer> tabu; //禁忌表
private Vector<Integer> allowedCities; //允许搜索的城市
private float[][] delta; //信息数变化矩阵
private int[][] distance; //距离矩阵
private float alpha;
private float beta;
private int tourLength; //路径长度
private int cityNum; //城市数量
private int firstCity; //起始城市
private int currentCity; //当前城市
public Ant(){
cityNum = 30;
tourLength = 0;
}
/**
* Constructor of Ant
* @param num 蚂蚁数量
*/
public Ant(int num){
cityNum = num;
tourLength = 0;
}
/**
* 初始化蚂蚁,随机选择起始位置
* @param distance 距离矩阵
* @param a alpha
* @param b beta
*/
public void init(int[][] distance, float a, float b){
alpha = a;
beta = b;
allowedCities = new Vector<Integer>();
tabu = new Vector<Integer>();
this.distance = distance;
delta = new float[cityNum][cityNum];
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
Integer integer = new Integer(i);
allowedCities.add(integer);
for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
delta[i][j] = 0.f;
}
}
Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
firstCity = random.nextInt(cityNum);
for (Integer i:allowedCities) {
if (i.intValue() == firstCity) {
allowedCities.remove(i);
break;
}
}
tabu.add(Integer.valueOf(firstCity));
currentCity = firstCity;
}
/**
* 选择下一个城市
* @param pheromone 信息素矩阵
*/
public void selectNextCity(float[][] pheromone){
float[] p = new float[cityNum];
float sum = 0.0f;
//计算分母部分
for (Integer i:allowedCities) {
sum += Math.pow(pheromone[currentCity][i.intValue()], alpha)*Math.pow(1.0/distance[currentCity][i.intValue()], beta);
}
//计算概率矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
boolean flag = false;
for (Integer j:allowedCities) {
if (i == j.intValue()) {
p[i] = (float) (Math.pow(pheromone[currentCity][i], alpha)*Math.pow(1.0/distance[currentCity][i], beta))/sum;
flag = true;
break;
}
}
if (flag == false) {
p[i] = 0.f;
}
}
//轮盘赌选择下一个城市
Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis());
float sleectP = random.nextFloat();
int selectCity = 0;
float sum1 = 0.f;
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
sum1 += p[i];
if (sum1 >= sleectP) {
selectCity = i;
break;
}
}
//从允许选择的城市中去除select city
for (Integer i:allowedCities) {
if (i.intValue() == selectCity) {
allowedCities.remove(i);
break;
}
}
//在禁忌表中添加select city
tabu.add(Integer.valueOf(selectCity));
//将当前城市改为选择的城市
currentCity = selectCity;
}
/**
* 计算路径长度
* @return 路径长度
*/
private int calculateTourLength(){
int len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
len += distance[this.tabu.get(i).intValue()][this.tabu.get(i+1).intValue()];
}
return len;
}
public Vector<Integer> getAllowedCities() {
return allowedCities;
}
public void setAllowedCities(Vector<Integer> allowedCities) {
this.allowedCities = allowedCities;
}
public int getTourLength() {
tourLength = calculateTourLength();
return tourLength;
}
public void setTourLength(int tourLength) {
this.tourLength = tourLength;
}
public int getCityNum() {
return cityNum;
}
public void setCityNum(int cityNum) {
this.cityNum = cityNum;
}
public Vector<Integer> getTabu() {
return tabu;
}
public void setTabu(Vector<Integer> tabu) {
this.tabu = tabu;
}
public float[][] getDelta() {
return delta;
}
public void setDelta(float[][] delta) {
this.delta = delta;
}
public int getFirstCity() {
return firstCity;
}
public void setFirstCity(int firstCity) {
this.firstCity = firstCity;
}
}
ACO类:
package ch01;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
*
* @author BIAO YU
*
*
*/
public class ACO {
private Ant[] ants; //蚂蚁
private int antNum; //蚂蚁数量
private int cityNum; //城市数量
private int MAX_GEN; //运行代数
private float[][] pheromone; //信息素矩阵
private int[][] distance; //距离矩阵
private int bestLength; //最佳长度
private int[] bestTour; //最佳路径
//三个参数
private float alpha;
private float beta;
private float rho;
public ACO(){
}
/** constructor of ACO
* @param n 城市数量
* @param m 蚂蚁数量
* @param g 运行代数
* @param a alpha
* @param b beta
* @param r rho
*
**/
public ACO(int n, int m, int g, float a, float b, float r) {
cityNum = n;
antNum = m;
ants = new Ant[antNum];
MAX_GEN = g;
alpha = a;
beta = b;
rho = r;
}
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
/**
* 初始化ACO算法类
* @param filename 数据文件名,该文件存储所有城市节点坐标数据
* @throws IOException
*/
private void init(String filename) throws IOException{
//读取数据
int[] x;
int[] y;
String strbuff;
BufferedReader data = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filename)));
distance = new int[cityNum][cityNum];
x = new int[cityNum];
y = new int[cityNum];
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum; i++) {
strbuff = data.readLine();
String[] strcol = strbuff.split(" ");
x[i] = Integer.valueOf(strcol[1]);
y[i] = Integer.valueOf(strcol[2]);
}
//计算距离矩阵 ,针对具体问题,距离计算方法也不一样,此处用的是att48作为案例,它有48个城市,距离计算方法为伪欧氏距离,最优值为10628
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum - 1; i++) {
distance[i][i] = 0; //对角线为0
for (int j = i + 1; j < cityNum; j++) {
double rij = Math.sqrt(((x[i] - x[j]) * (x[i] - x[j])+ (y[i] - y[j]) * (y[i] - y[j]))/10.0);
int tij = (int) Math.round(rij);
if (tij < rij) {
distance[i][j] = tij + 1;
distance[j][i] = distance[i][j];
}else {
distance[i][j] = tij;
distance[j][i] = distance[i][j];
}
}
}
distance[cityNum - 1][cityNum - 1] = 0;
//初始化信息素矩阵
pheromone=new float[cityNum][cityNum];
for(int i=0;i<cityNum;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<cityNum;j++){
pheromone[i][j]=0.1f; //初始化为0.1
}
}
bestLength=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
bestTour=new int[cityNum+1];
//随机放置蚂蚁
for(int i=0;i<antNum;i++){
ants[i]=new Ant(cityNum);
ants[i].init(distance, alpha, beta);
}
}
public void solve(){
for (int g = 0; g < MAX_GEN; g++) {
for (int i = 0; i < antNum; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < cityNum; j++) {
ants[i].selectNextCity(pheromone);
}
ants[i].getTabu().add(ants[i].getFirstCity());
if (ants[i].getTourLength() < bestLength) {
bestLength = ants[i].getTourLength();
for (int k = 0; k < cityNum + 1; k++) {
bestTour[k] = ants[i].getTabu().get(k).intValue();
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < cityNum; j++) {
ants[i].getDelta()[ants[i].getTabu().get(j).intValue()][ants[i].getTabu().get(j+1).intValue()] = (float) (1./ants[i].getTourLength());
ants[i].getDelta()[ants[i].getTabu().get(j+1).intValue()][ants[i].getTabu().get(j).intValue()] = (float) (1./ants[i].getTourLength());
}
}
//更新信息素
updatePheromone();
//重新初始化蚂蚁
for(int i=0;i<antNum;i++){
ants[i].init(distance, alpha, beta);
}
}
//打印最佳结果
printOptimal();
}
//更新信息素
private void updatePheromone(){
//信息素挥发
for(int i=0;i<cityNum;i++)
for(int j=0;j<cityNum;j++)
pheromone[i][j]=pheromone[i][j]*(1-rho);
//信息素更新
for(int i=0;i<cityNum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<cityNum;j++){
for (int k = 0; k < antNum; k++) {
pheromone[i][j] += ants[k].getDelta()[i][j];
}
}
}
}
private void printOptimal(){
System.out.println("The optimal length is: " + bestLength);
System.out.println("The optimal tour is: ");
for (int i = 0; i < cityNum + 1; i++) {
System.out.println(bestTour[i]);
}
}
public Ant[] getAnts() {
return ants;
}
public void setAnts(Ant[] ants) {
this.ants = ants;
}
public int getAntNum() {
return antNum;
}
public void setAntNum(int m) {
this.antNum = m;
}
public int getCityNum() {
return cityNum;
}
public void setCityNum(int cityNum) {
this.cityNum = cityNum;
}
public int getMAX_GEN() {
return MAX_GEN;
}
public void setMAX_GEN(int mAX_GEN) {
MAX_GEN = mAX_GEN;
}
public float[][] getPheromone() {
return pheromone;
}
public void setPheromone(float[][] pheromone) {
this.pheromone = pheromone;
}
public int[][] getDistance() {
return distance;
}
public void setDistance(int[][] distance) {
this.distance = distance;
}
public int getBestLength() {
return bestLength;
}
public void setBestLength(int bestLength) {
this.bestLength = bestLength;
}
public int[] getBestTour() {
return bestTour;
}
public void setBestTour(int[] bestTour) {
this.bestTour = bestTour;
}
public float getAlpha() {
return alpha;
}
public void setAlpha(float alpha) {
this.alpha = alpha;
}
public float getBeta() {
return beta;
}
public void setBeta(float beta) {
this.beta = beta;
}
public float getRho() {
return rho;
}
public void setRho(float rho) {
this.rho = rho;
}
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ACO aco = new ACO(48, 100, 1000, 1.f, 5.f, 0.5f);
aco.init("D:\\workspace\\myeclipse\\Algo\\ch01\\data.txt");
aco.solve();
}
}
5. 总结
蚁群算法和其它的启发式算法一样,在很多场合都得到了应用,并且取得了很好的结果。但是同样存在着很多的缺点,例如收敛速度慢,容易陷入局部最优,等等。对于这些问题,还需要进一步的研究和探索,另外蚁群算法的数学机理至今还没有得到科学的解释,这也是当前研究的热点和急需解决的问题之一。注:TSP数据文件以及两篇早期的关于蚁群算法的文章包含在附件中,请点击此处下载附件。