HelloWord例子:客户端向请求SOAP消息中注入报头块(使用配置方式)
服务端:
HelloWord.java:
package ch03.ts;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.xml.ws.Holder;
@WebService
public interface HelloWord {
@WebMethod
void sayHello(@WebParam(name="name") String name,
@WebParam(name="wh",mode=WebParam.Mode.INOUT) Holder<String> wh,
@WebParam(name="hf",mode=WebParam.Mode.OUT) Holder<String> hf);
}
HelloWordImpl.java:
package ch03.ts;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.xml.ws.Holder;
@WebService(endpointInterface = "ch03.ts.HelloWord")
public class HelloWordImpl implements HelloWord {
@Override
public void sayHello(String name, Holder<String> wh, Holder<String> hf) {
System.out.println(name + "!" + wh.value);
wh.value = "你们好";
hf.value = "同学们";
}
}
HelloWordPublisher.java:
package ch03.ts;
import javax.xml.ws.Endpoint;
public class HelloWordPublisher {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Endpoint.publish("http://localhost:7654/ts", new HelloWordImpl());
}
}
根据服务端产生的WSDL文档生成客户端的代码:
HelloWord.java:
package hw1;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebParam;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlSeeAlso;
import javax.xml.ws.Action;
import javax.xml.ws.Holder;
import javax.xml.ws.RequestWrapper;
import javax.xml.ws.ResponseWrapper;
/**
* This class was generated by the JAX-WS RI.
* JAX-WS RI 2.2.4-b01
* Generated source version: 2.2
*/
@WebService(name = "HelloWord", targetNamespace = "http://ts.ch03/")
@XmlSeeAlso({
ObjectFactory.class
})
public interface HelloWord {
/**
* @param wh
* @param name
* @param hf
*/
@WebMethod
@RequestWrapper(localName = "sayHello", targetNamespace = "http://ts.ch03/",
className = "hw1.SayHello")
@ResponseWrapper(localName = "sayHelloResponse", targetNamespace = "http://ts.ch03/",
className = "hw1.SayHelloResponse")
@Action(input = "http://ts.ch03/HelloWord/sayHelloRequest",
output = "http://ts.ch03/HelloWord/sayHelloResponse")
public void sayHello(
@WebParam(name = "name", targetNamespace = "")
String name,
@WebParam(name = "wh", targetNamespace = "", mode = WebParam.Mode.INOUT)
Holder<String> wh,
@WebParam(name = "hf", targetNamespace = "", mode = WebParam.Mode.OUT)
Holder<String> hf);
}
HelloWordImplService.java,这个文件中请注意@HandlerChain(file="handler-chain.xml")这句代码,我们后面讲解:
package hw1;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.jws.HandlerChain;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import javax.xml.ws.Service;
import javax.xml.ws.WebEndpoint;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceClient;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceException;
import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceFeature;
/**
* This class was generated by the JAX-WS RI.
* JAX-WS RI 2.2.4-b01
* Generated source version: 2.2
*/
@WebServiceClient(name = "HelloWordImplService", targetNamespace = "http://ts.ch03/",
wsdlLocation = "http://localhost:7654/ts?wsdl")
@HandlerChain(file = "handler-chain.xml")
public class HelloWordImplService extends Service{
private final static URL HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION;
private final static WebServiceException HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_EXCEPTION;
private final static QName HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_QNAME =
new QName("http://ts.ch03/", "HelloWordImplService");
static {
URL url = null;
WebServiceException e = null;
try {
url = new URL("http://localhost:7654/ts?wsdl");
} catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
e = new WebServiceException(ex);
}
HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION = url;
HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_EXCEPTION = e;
}
public HelloWordImplService() {
super(__getWsdlLocation(), HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_QNAME);
}
public HelloWordImplService(WebServiceFeature... features) {
super(__getWsdlLocation(), HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_QNAME, features);
}
public HelloWordImplService(URL wsdlLocation) {
super(wsdlLocation, HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_QNAME);
}
public HelloWordImplService(URL wsdlLocation, WebServiceFeature... features) {
super(wsdlLocation, HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_QNAME, features);
}
public HelloWordImplService(URL wsdlLocation, QName serviceName) {
super(wsdlLocation, serviceName);
}
public HelloWordImplService(URL wsdlLocation, QName serviceName,
WebServiceFeature... features) {
super(wsdlLocation, serviceName, features);
}
/**
* @return
* returns HelloWord
*/
@WebEndpoint(name = "HelloWordImplPort")
public HelloWord getHelloWordImplPort() {
return super.getPort(new QName("http://ts.ch03/", "HelloWordImplPort"),
HelloWord.class);
}
/**
*
* @param features
* A list of {@link javax.xml.ws.WebServiceFeature} to configure
* on the proxy. Supported features not in the <code>features</code>
* parameter will have their default values.
* @return
* returns HelloWord
*/
@WebEndpoint(name = "HelloWordImplPort")
public HelloWord getHelloWordImplPort(WebServiceFeature... features) {
return super.getPort(new QName("http://ts.ch03/", "HelloWordImplPort"),
HelloWord.class, features);
}
private static URL __getWsdlLocation() {
if (HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_EXCEPTION!= null) {
throw HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_EXCEPTION;
}
return HELLOWORDIMPLSERVICE_WSDL_LOCATION;
}
}
handle-chain.xml文件,作用后面再解释:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes" ?> <javaee:handler-chains xmlns:javaee="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"> <javaee:handler-chain> <javaee:handler> <javaee:handler-class>fibC.UUIDHandler</javaee:handler-class> </javaee:handler> </javaee:handler-chain> </javaee:handler-chains>
SayHello.java:
package hw1;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
/**
* <p>Java class for sayHello complex type.
* <p>The following schema fragment specifies the expected
* content contained within this class.
* <pre>
* <complexType name="sayHello">
* <complexContent>
* <restriction base="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}anyType">
* <sequence>
* <element name="name" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string"
* minOccurs="0"/>
* <element name="wh" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string"
* minOccurs="0"/>
* </sequence>
* </restriction>
* </complexContent>
* </complexType>
* </pre>
*/
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "sayHello", propOrder = {
"name",
"wh"
})
public class SayHello {
protected String name;
protected String wh;
/**
* Gets the value of the name property.
* @return
* possible object is
* {@link String }
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
* Sets the value of the name property.
* @param value
* allowed object is
* {@link String }
*/
public void setName(String value) {
this.name = value;
}
/**
* Gets the value of the wh property.
* @return
* possible object is
* {@link String }
*/
public String getWh() {
return wh;
}
/**
* Sets the value of the wh property.
* @param value
* allowed object is
* {@link String }
*/
public void setWh(String value) {
this.wh = value;
}
}
SayHelloResponse.java:
package hw1;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlAccessorType;
import javax.xml.bind.annotation.XmlType;
/**
* <p>Java class for sayHelloResponse complex type.
* <p>The following schema fragment specifies the expected
* content contained within this class.
* <pre>
* <complexType name="sayHelloResponse">
* <complexContent>
* <restriction base="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}anyType">
* <sequence>
* <element name="wh" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string"
* minOccurs="0"/>
* <element name="hf" type="{http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema}string"
* minOccurs="0"/>
* </sequence>
* </restriction>
* </complexContent>
* </complexType>
* </pre>
*/
@XmlAccessorType(XmlAccessType.FIELD)
@XmlType(name = "sayHelloResponse", propOrder = {
"wh",
"hf"
})
public class SayHelloResponse {
protected String wh;
protected String hf;
/**
* Gets the value of the wh property.
* @return
* possible object is
* {@link String }
*/
public String getWh() {
return wh;
}
/**
* Sets the value of the wh property.
* @param value
* allowed object is
* {@link String }
*/
public void setWh(String value) {
this.wh = value;
}
/**
* Gets the value of the hf property.
* @return
* possible object is
* {@link String }
*/
public String getHf() {
return hf;
}
/**
* Sets the value of the hf property.
* @param value
* allowed object is
* {@link String }
*/
public void setHf(String value) {
this.hf = value;
}
}
HelloWordClient1.java:
package hw1;
import javax.xml.ws.Holder;
public class HelloWordClient1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "老师";
Holder<String> wh = new Holder<String>();
wh.value = "你好";
Holder<String> hf = new Holder<String>();
HelloWordImplService service = new HelloWordImplService();
HelloWord port = service.getPort(HelloWord.class);
port.sayHello(name, wh, hf);
System.out.println(hf.value + "," + wh.value);
}
}
ObjectFactory.java,package-info.java省略。
为客户端编写的请求SOAP消息处理程序:
UUIDHandler.java,只是在SOAP消息的Head部分增加一个UUID的唯一标识:
package fibC;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.UUID;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import javax.xml.soap.SOAPConstants;
import javax.xml.soap.SOAPEnvelope;
import javax.xml.soap.SOAPException;
import javax.xml.soap.SOAPHeader;
import javax.xml.soap.SOAPHeaderElement;
import javax.xml.soap.SOAPMessage;
import javax.xml.ws.handler.MessageContext;
import javax.xml.ws.handler.soap.SOAPHandler;
import javax.xml.ws.handler.soap.SOAPMessageContext;
/**
* SOAP处理程序(Handler)
* @author FUHD
*/
public class UUIDHandler implements SOAPHandler<SOAPMessageContext> {
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(SOAPMessageContext context) {
Boolean request = (Boolean)context.get(MessageContext.MESSAGE_OUTBOUND_PROPERTY);
if(request){
UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
try {
SOAPMessage msg = context.getMessage();
SOAPEnvelope env = msg.getSOAPPart().getEnvelope();
SOAPHeader hdr = env.getHeader();
if(hdr == null) hdr = env.addHeader();
QName qname = new QName("http://ts.ch03/","uuid");
SOAPHeaderElement helem = hdr.addHeaderElement(qname);
helem.setActor(SOAPConstants.URI_SOAP_ACTOR_NEXT);
helem.addTextNode(uuid.toString());
msg.saveChanges();
msg.writeTo(System.out);
} catch (SOAPException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean handleFault(SOAPMessageContext context) {
try {
context.getMessage().writeTo(System.out);
} catch (SOAPException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
@Override
public void close(MessageContext context) {
}
@Override
public Set<QName> getHeaders() {
return null;
}
}
UUIDHandler是一个客户端SOAP消息处理程序,当底层SOAP请求消息构建完毕并发送到服务端之前,底层处理框架便调用handleMessage方法。具体处理过程如下:
客户端无论何时向服务端发送一个请求,客户端层的JWS库都将会为这个请求创建一个SOAP消息。
一旦消息被创建,在真正发送之前,JWS Handle框架调用UUIDHandler回调方法。由于封装类UUIDHandler实现了SOAPHandler接口,因此回调方法 handleMessage可以访问整个SOAP消息,同时handleMessage回调方法向SOAP消息的报头中注入一个UUID值。
一旦UUIDHandler完成了它的处理工作,被注入报头块的SOAP消息将以它所预定的路线到达最终接收者。
handleMessage方法有一个类型为SOAPMessageContext的参数,通过这参数可以访问底层的SOAP消息。我们回到方法handleMessage上来,首先在此方法中检查SOAP消息是不是一个待发送消息。针对待发送消息,处理程序产生一个UUID值并放在SOAP消息的报头块中。无论在SOAP1.1还是SOAP1.2中,SOAP报头并不是必需的。因此处理程序首先检查已经创建的SOAP消息是否拥有一个报头,如果没有的话,向SOAP信封增加一个。接下来,将一个报头的java实现类SOAPHeaderElement对象实例加入SOAP报头中,同时通过set方法设置其“actor”字段属性。下面是这部分代码:
SOAPHeaderElement helem = hdr.addHeaderElement(qname); helem.setActor(SOAPConstants.URI_SOAP_ACTOR_NEXT); //默认值
UUID作为一个XML文本节点加入报头中,然后保存SOAP消息的所有更改。发出的SOAP消息反映了这个更改,更改后的SOAP消息报头部分如下:
<S:Envelope xmlns:S="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"> <S:Header> <uuid xmlns="http://ts.ch03/" xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" SOAP-ENV:actor="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/actor/next"> 8f8971d6-bc28-4de3-82de-eb04f99114e3 </uuid> </S:Header> <S:Body> <ns2:sayHello xmlns:ns2="http://ts.ch03/"> <name>老师</name> <wh>你好</wh> </ns2:sayHello> </S:Body> </S:Envelope>
目前,UUIDHandler是客户端的SOAP处理程序责任链中的唯一处理程序。当然也可以添加其他SOAP处理程序,每一个SOAP处理程序在这个责任链中都有一个位置。SOAP处理程序链可以通过代码创建,但是通过一个可部署的文件来描述这个链则显得更为清晰。我们再来看看HelloWordImplService.java中的@HandlerChain(file="handler-chain.xml")注解与handler-chain.xml部署文件就能够理解它们的作用了。注解@HandlerChain中file属性的值为部署文件的路径,这里是类路径,另外还要注意这个注解是使用在哪个类上的!!!还要注意一点就是部署文件名称是任意的。
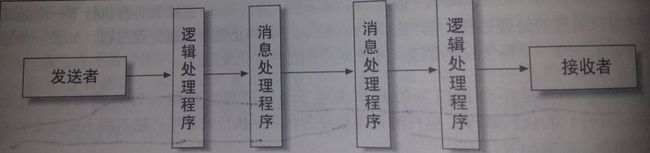
如果还有其他的处理程序,任意LogicalHandler和SOAPHandler的复合实现,均可以在fibC.UUIDHandler之前或之后列出。每种类型的Handler方法按照部署文件描述的自顶向下顺序执行,除非其中一个正在执行的Handler方法终止了后续所有的处理。方法handleMessage和handleFault返回boolean值。返回true意味着将会执行下一个处理程序并继续消息的处理过程。而当返回false时,将停止整个消息处理过程。如果一个处理程序停止处理一个待发送的消息,那么这个消息将终止发送。
部署文件中处理程序自顶向下的顺序决定了该处理程序中每一种处理方法(比如SOAPHandler)的执行顺序。运行时处理程序方法实际执行的顺序可能不同于配置文件中定义的顺序,原因如下:
针对一个出站消息,实现了LogicalHandler接口的handleMessage方法或handleFault方法先于同一位置下实现了SOAPHandler接口的方法执行。
针对一个入站消息,实现了SOAPHandler接口的handlerMessage或handleFault方法将先于同一位置下实现了LogicalHandler接口的方法执行。
比如,假设一个处理程序部署文件按照如下顺序自顶向下地列出了SOAP处理程序(SH)和逻辑处理程序(LH): SH1,LH1,SH2,SH3,LH2。针对一个待发送消息,这些处理程序按照如下列出的自顶向下的顺序执行:LH1,LH2,SH1,SH2,SH3。针对入站消息,处理程序自顶向下的执行顺序为:SH1,SH2,SH3,LH1,LH2。
下图描绘了逻辑处理程序和SOAP处理程序运行时的实际顺序,如图: