Android Tab大总结 Fragment+TabPageIndicator+ViewPager
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/24740977
Android现在实现Tab类型的界面方式越来越多,今天就把常见的实现方式给大家来个总结。目前写了:
1、传统的ViewPager实现
2、FragmentManager+Fragment实现
3、ViewPager+FragmentPagerAdapter实现
4、TabPageIndicator+ViewPager+FragmentPagerAdapter
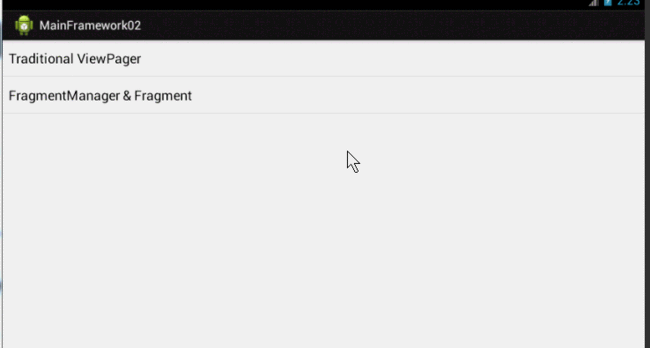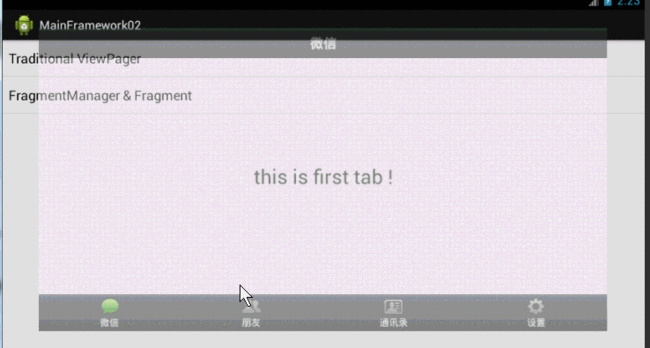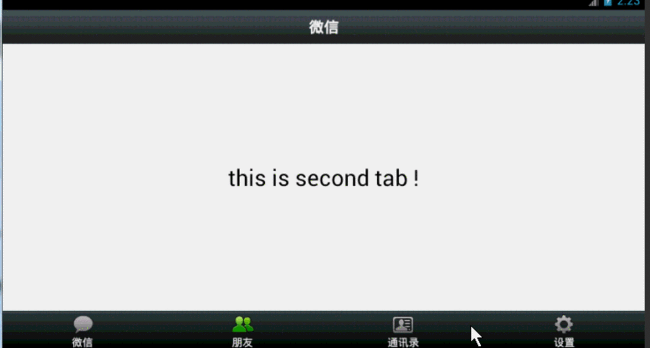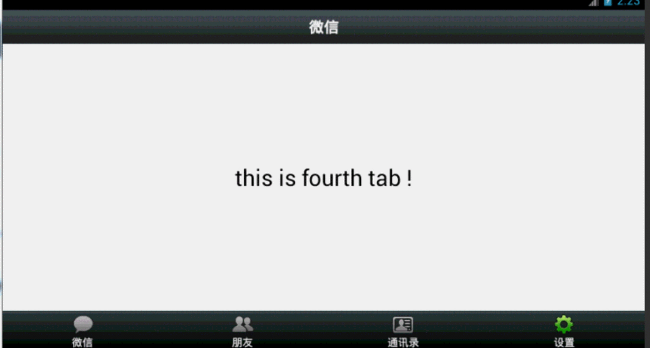
1、传统的ViewPager实现
主要就是ViewPager+ViewAdapter这个还是比较常见的,就不多说了
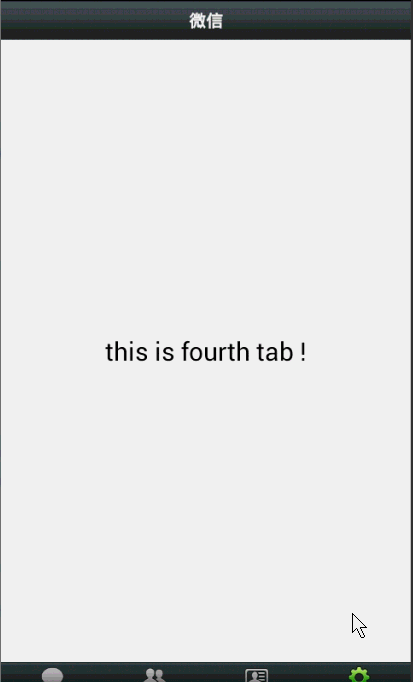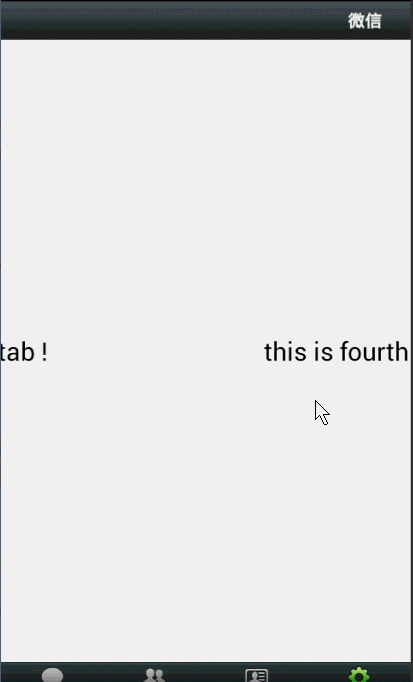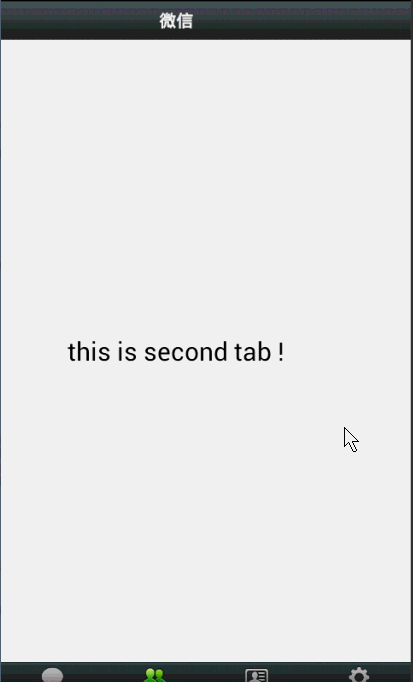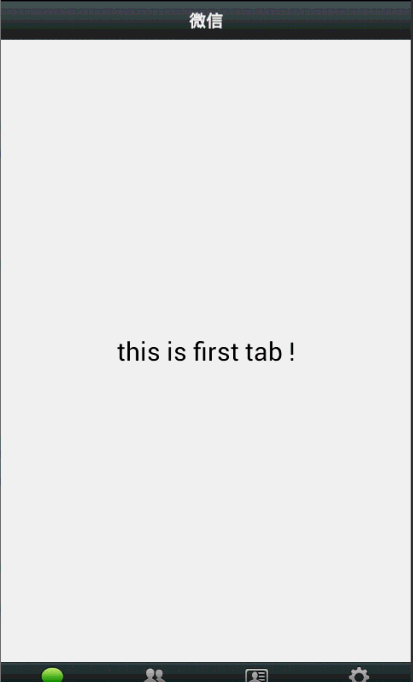
效果图:
代码:
package com.example.mainframework02;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.view.PagerAdapter;
import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager;
import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager.OnPageChangeListener;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.ImageButton;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
public class TraditionalViewPagerAcvitity extends Activity
{
/**
* ViewPager
*/
private ViewPager mViewPager;
/**
* ViewPager的适配器
*/
private PagerAdapter mAdapter;
private List<View> mViews;
private LayoutInflater mInflater;
private int currentIndex;
/**
* 底部四个按钮
*/
private LinearLayout mTabBtnWeixin;
private LinearLayout mTabBtnFrd;
private LinearLayout mTabBtnAddress;
private LinearLayout mTabBtnSettings;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
mViewPager = (ViewPager) findViewById(R.id.id_viewpager);
/**
* 初始化View
*/
initView();
mViewPager.setAdapter(mAdapter);
mViewPager.setOnPageChangeListener(new OnPageChangeListener()
{
@Override
public void onPageSelected(int position)
{
resetTabBtn();
switch (position)
{
case 0:
((ImageButton) mTabBtnWeixin.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_weixin))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_weixin_pressed);
break;
case 1:
((ImageButton) mTabBtnFrd.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_friend))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_find_frd_pressed);
break;
case 2:
((ImageButton) mTabBtnAddress.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_contact))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_address_pressed);
break;
case 3:
((ImageButton) mTabBtnSettings.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_setting))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_settings_pressed);
break;
}
currentIndex = position;
}
@Override
public void onPageScrolled(int arg0, float arg1, int arg2)
{
}
@Override
public void onPageScrollStateChanged(int arg0)
{
}
});
}
protected void resetTabBtn()
{
((ImageButton) mTabBtnWeixin.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_weixin))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_weixin_normal);
((ImageButton) mTabBtnFrd.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_friend))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_find_frd_normal);
((ImageButton) mTabBtnAddress.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_contact))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_address_normal);
((ImageButton) mTabBtnSettings.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_setting))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_settings_normal);
}
private void initView()
{
mTabBtnWeixin = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_weixin);
mTabBtnFrd = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_friend);
mTabBtnAddress = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_contact);
mTabBtnSettings = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_setting);
mViews = new ArrayList<View>();
View first = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.main_tab_01, null);
View second = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.main_tab_02, null);
View third = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.main_tab_03, null);
View fourth = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.main_tab_04, null);
mViews.add(first);
mViews.add(second);
mViews.add(third);
mViews.add(fourth);
mAdapter = new PagerAdapter()
{
@Override
public void destroyItem(ViewGroup container, int position, Object object)
{
container.removeView(mViews.get(position));
}
@Override
public Object instantiateItem(ViewGroup container, int position)
{
View view = mViews.get(position);
container.addView(view);
return view;
}
@Override
public boolean isViewFromObject(View arg0, Object arg1)
{
return arg0 == arg1;
}
@Override
public int getCount()
{
return mViews.size();
}
};
}
}
评价:所有的代码都集中在一个Activity中,显得代码比较乱。
2、FragmentManager+Fragment实现
主要利用了Fragment在主内容界面对Fragment的add,hide等事务操作。
效果图:
代码:
主Activity
package com.example.mainframework02.fragment;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.ImageButton;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import com.example.mainframework02.R;
public class FragmentMainActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener
{
private MainTab02 mTab02;
private MainTab01 mTab01;
private MainTab03 mTab03;
private MainTab04 mTab04;
/**
* 底部四个按钮
*/
private LinearLayout mTabBtnWeixin;
private LinearLayout mTabBtnFrd;
private LinearLayout mTabBtnAddress;
private LinearLayout mTabBtnSettings;
/**
* 用于对Fragment进行管理
*/
private FragmentManager fragmentManager;
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.fragment_main);
initViews();
fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
setTabSelection(0);
}
private void initViews()
{
mTabBtnWeixin = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_weixin);
mTabBtnFrd = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_friend);
mTabBtnAddress = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_contact);
mTabBtnSettings = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_setting);
mTabBtnWeixin.setOnClickListener(this);
mTabBtnFrd.setOnClickListener(this);
mTabBtnAddress.setOnClickListener(this);
mTabBtnSettings.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
switch (v.getId())
{
case R.id.id_tab_bottom_weixin:
setTabSelection(0);
break;
case R.id.id_tab_bottom_friend:
setTabSelection(1);
break;
case R.id.id_tab_bottom_contact:
setTabSelection(2);
break;
case R.id.id_tab_bottom_setting:
setTabSelection(3);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
/**
* 根据传入的index参数来设置选中的tab页。
*
*/
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
private void setTabSelection(int index)
{
// 重置按钮
resetBtn();
// 开启一个Fragment事务
FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
// 先隐藏掉所有的Fragment,以防止有多个Fragment显示在界面上的情况
hideFragments(transaction);
switch (index)
{
case 0:
// 当点击了消息tab时,改变控件的图片和文字颜色
((ImageButton) mTabBtnWeixin.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_weixin))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_weixin_pressed);
if (mTab01 == null)
{
// 如果MessageFragment为空,则创建一个并添加到界面上
mTab01 = new MainTab01();
transaction.add(R.id.id_content, mTab01);
} else
{
// 如果MessageFragment不为空,则直接将它显示出来
transaction.show(mTab01);
}
break;
case 1:
// 当点击了消息tab时,改变控件的图片和文字颜色
((ImageButton) mTabBtnFrd.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_friend))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_find_frd_pressed);
if (mTab02 == null)
{
// 如果MessageFragment为空,则创建一个并添加到界面上
mTab02 = new MainTab02();
transaction.add(R.id.id_content, mTab02);
} else
{
// 如果MessageFragment不为空,则直接将它显示出来
transaction.show(mTab02);
}
break;
case 2:
// 当点击了动态tab时,改变控件的图片和文字颜色
((ImageButton) mTabBtnAddress.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_contact))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_address_pressed);
if (mTab03 == null)
{
// 如果NewsFragment为空,则创建一个并添加到界面上
mTab03 = new MainTab03();
transaction.add(R.id.id_content, mTab03);
} else
{
// 如果NewsFragment不为空,则直接将它显示出来
transaction.show(mTab03);
}
break;
case 3:
// 当点击了设置tab时,改变控件的图片和文字颜色
((ImageButton) mTabBtnSettings.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_setting))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_settings_pressed);
if (mTab04 == null)
{
// 如果SettingFragment为空,则创建一个并添加到界面上
mTab04 = new MainTab04();
transaction.add(R.id.id_content, mTab04);
} else
{
// 如果SettingFragment不为空,则直接将它显示出来
transaction.show(mTab04);
}
break;
}
transaction.commit();
}
/**
* 清除掉所有的选中状态。
*/
private void resetBtn()
{
((ImageButton) mTabBtnWeixin.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_weixin))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_weixin_normal);
((ImageButton) mTabBtnFrd.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_friend))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_find_frd_normal);
((ImageButton) mTabBtnAddress.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_contact))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_address_normal);
((ImageButton) mTabBtnSettings.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_setting))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_settings_normal);
}
/**
* 将所有的Fragment都置为隐藏状态。
*
* @param transaction
* 用于对Fragment执行操作的事务
*/
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
private void hideFragments(FragmentTransaction transaction)
{
if (mTab01 != null)
{
transaction.hide(mTab01);
}
if (mTab02 != null)
{
transaction.hide(mTab02);
}
if (mTab03 != null)
{
transaction.hide(mTab03);
}
if (mTab04 != null)
{
transaction.hide(mTab04);
}
}
}
各个TabFragment,一共四个TabFragment,下面贴出两个,基本都一样。
package com.example.mainframework02.fragment;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
public class MainTab01 extends Fragment
{
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
return inflater.inflate(com.example.mainframework02.R.layout.main_tab_01, container, false);
}
}
package com.example.mainframework02.fragment;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import com.example.mainframework02.R;
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
public class MainTab02 extends Fragment
{
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.main_tab_02, container, false);
}
}
评价:每个Fragment中的控件的处理,都是独立到各自的类中,相对来说主Activity简化了不少,可惜没有左右滑动的效果了。
3、ViewPager+Fragment实现
主要通过ViewPager和FragmentPagerAdapter一起来实现。
效果图:
代码:
主Activity
package com.example.mainframework03;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentActivity;
import android.support.v4.app.FragmentPagerAdapter;
import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager;
import android.support.v4.view.ViewPager.OnPageChangeListener;
import android.widget.ImageButton;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity
{
private ViewPager mViewPager;
private FragmentPagerAdapter mAdapter;
private List<Fragment> mFragments = new ArrayList<Fragment>();
/**
* 底部四个按钮
*/
private LinearLayout mTabBtnWeixin;
private LinearLayout mTabBtnFrd;
private LinearLayout mTabBtnAddress;
private LinearLayout mTabBtnSettings;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mViewPager = (ViewPager) findViewById(R.id.id_viewpager);
initView();
mAdapter = new FragmentPagerAdapter(getSupportFragmentManager())
{
@Override
public int getCount()
{
return mFragments.size();
}
@Override
public Fragment getItem(int arg0)
{
return mFragments.get(arg0);
}
};
mViewPager.setAdapter(mAdapter);
mViewPager.setOnPageChangeListener(new OnPageChangeListener()
{
private int currentIndex;
@Override
public void onPageSelected(int position)
{
resetTabBtn();
switch (position)
{
case 0:
((ImageButton) mTabBtnWeixin.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_weixin))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_weixin_pressed);
break;
case 1:
((ImageButton) mTabBtnFrd.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_friend))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_find_frd_pressed);
break;
case 2:
((ImageButton) mTabBtnAddress.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_contact))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_address_pressed);
break;
case 3:
((ImageButton) mTabBtnSettings.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_setting))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_settings_pressed);
break;
}
currentIndex = position;
}
@Override
public void onPageScrolled(int arg0, float arg1, int arg2)
{
}
@Override
public void onPageScrollStateChanged(int arg0)
{
}
});
}
protected void resetTabBtn()
{
((ImageButton) mTabBtnWeixin.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_weixin))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_weixin_normal);
((ImageButton) mTabBtnFrd.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_friend))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_find_frd_normal);
((ImageButton) mTabBtnAddress.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_contact))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_address_normal);
((ImageButton) mTabBtnSettings.findViewById(R.id.btn_tab_bottom_setting))
.setImageResource(R.drawable.tab_settings_normal);
}
private void initView()
{
mTabBtnWeixin = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_weixin);
mTabBtnFrd = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_friend);
mTabBtnAddress = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_contact);
mTabBtnSettings = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_tab_bottom_setting);
MainTab01 tab01 = new MainTab01();
MainTab02 tab02 = new MainTab02();
MainTab03 tab03 = new MainTab03();
MainTab04 tab04 = new MainTab04();
mFragments.add(tab01);
mFragments.add(tab02);
mFragments.add(tab03);
mFragments.add(tab04);
}
}
还有4个TabFragment,下面贴一个,四个基本一样
package com.example.mainframework03;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v4.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
public class MainTab01 extends Fragment
{
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.main_tab_01, container, false);
}
}
评价:实现效果和第一种效果一模一样,每个Fragment独自处理自己内部的逻辑,代码整洁很多,并且支持左右滑动。感觉是第一种和第二种的结合版本。
4、TabPageIndicator+ViewPager+FragmentPagerAdapter
实现方式和3是一致的,但是使用了TabPageIndicator作为tab的指示器,效果还是不错的,这个之前写过,就不再贴代码了。
效果图:
参考:Android 使用Fragment,ViewPagerIndicator 制作csdn app主要框架
好了,就总结了这么多,肯定还有很多别的实现方式,大家可以留言,有时间会继续完善这篇总结的。