- 《昼颜》里的日本女人:相遇要万种风情,分手要残忍绝情
迷影咖啡
作者:迷之菌子神奇菇迷影咖啡:一本正经做烘焙,胡说八道聊电影漫天萤火虫消散之时良宵就将过去,人们也说含苞待放的花蕾总会开了又谢,因紧紧相拥而面红耳赤的躯体,便是我们经历过这热爱的证明。夫妻关系介绍《昼颜》是2014年电视剧《昼颜:工作日下午三点的恋人们》的续集,故事发在电视剧情节结束的三年后,讲述了已经恢复独身的纱和偶然与曾经的出轨对象北野重逢后再次陷入感情漩涡的故事。《昼颜》制作灵感源自利佳子在
- 教育微创新的意蕴
知北老师
我是1992年参加工作的,一毕业就被分配到一所全县最偏僻落后的农村学校——付窝中学,12年后被调往一所已经连续十年全县倒数第一,也是很偏僻落后的农村学校——北宋镇第三中学。三年后到了北宋镇第一中学工作,这所学校教学质量也是连续几年落后了。2014年我到了北京市育英学校,这所学校是京城名校。2016年7月,我被育英学校派往原密云区第七中学工作,这是一所城乡接合部薄弱学校。学校现名为北京市育英学校密云
- word字号和mathtype磅值关系及批量修改
小铁匠-Ma
office小技巧经验分享
word字号和mathtype磅值关系及批量修改1.字号与磅值关系字号「八号」对应磅值5字号「七号」对应磅值5.5字号「小六」对应磅值6.5字号「六号」对应磅值7.5字号「小五」对应磅值9字号「五号」对应磅值10.5字号「小四」对应磅值12字号「四号」对应磅值14字号「小三」对应磅值15字号「三号」对应磅值16字号「小二」对应磅值18字号「二号」对应磅值22字号「小一」对应磅值24字号「一号」对应
- 社交电商是什么意思通俗的说
氧惠好项目
社交电商是目前电商发展的一个非常热门的领域,它将传统的电商和社交媒体相结合,让用户可以在社交平台上完成购物、支付等操作。社交电商不同于传统电商,它更加注重用户的社交性和互动性,通过社交媒体的传播,吸引用户关注,让产品能够更加快速地传播。京东密令红包:最爱领红包828红包多多148今天给大家分享我长期在做的副业,也在这里赚到人生第3桶金!氧惠APP佣金高,资质靠谱,各大应用市场均可搜索使用。【氧惠】
- c++中如何判断变量的数据类型,并输出
xnrbjy
c++开发语言
C++中如果想要判断变量的数据类型,可以使用typeid运算符。该运算符返回一个std::type_info类型的对象,可以使用name()方法获取其名称从而确定变量的类型,例如:#include#includeusingnamespacestd;intmain(){inta=123;floatb=3.14;boolc=true;chard='A';stringe="HelloWorld";cou
- 入伏(五)
喜马ma
图片发自App入伏13今天我看见很多蜻蜓在飞飞得很低想起小学时学的那点知识在这闷热的午后真能来一场暴雨太过瘾了入伏14有点像瓢虫的昆虫喜欢吃葡萄叶喜欢交配在炎热的夏天如果你在葡萄园看见两只昆虫它们不是在吃葡萄叶就是在交配请记住它们的名字叫葡萄十星红甲
- v-for 实例
琪33
v-for实例v-for实例{{item}}{{index+1}}:{{student.name}}-{{student.age}}varapp=newVue({el:'#app',data:{items:[53,23,76,14,54,36,28],students:[{name:'jspang',age:32},{name:'Panda',age:30},{name:'PanPaN',age:
- ChatGPT一路狂飙?
何鲸洛
2月2日。根据投行瑞银集团在周三发布的一份研究报告。爆红聊天机器人ChatGPT的月活跃用户在今年1月份预计达到了1亿,这距离它推出只有2个月时间,成为史上增长最快的消费者应用。①ChatGPT一路火花带闪电?▽2014年。OpenAI创始人SamAltman早年曾执掌著名的硅谷孵化器YCombinator。2015年。Altman联合马斯克、彼得·泰尔、AWS、印度Infosys和YC等作为出资
- 谷歌浏览器驱动Chromedriver(114-120版本)文件以及驱动下载教程
pigerr杨
Pythonpythonchromedrivers
ChromeDriver官方网站GitHub||GoogleChromeLabs/chrome-for-testingChromeDriver113-125_JSONChromeforTestingavailability123-125zip白月黑羽Python基础|进阶|Qt图形界面|Django|自动化测试|性能测试|JS语言|JS前端|原理与安装
- docker怎么端口映射
Lance_mu
docker容器运维
1、默认固定的端口#Web服务器:WebApache或Nginx通常使用80端口HTTP:80HTTPS:443#数据库服务器MySQL:3306PostgreSQL:5432MongoDB:27017Redis:6379#邮件服务器SMTP:25POP3:110IMAP:143#其他服务SSH:22FTP:21DNS(域名解析):53代理服务器Squid:3128版本控制系统Git:9418(S
- 2018-12-02
子分小
姓名:张颖公司:菲尔德国际英语【反省总结第146天,始于20180709今天是20181202】【知~学习】六项精进大纲背诵3遍每天十个单词坚持第181天每天学习一篇英文文章第94天英语流利说课程第71天学习30分钟【行~实践】一、修身:(对自己个人)步行5000步二、齐家:(对家庭和家人)无三、建功:(对工作)完成与Arti活动课和两节Demo准备开班事宜{积善}:发愿从2018年7月9日起1年
- linux安装docker及docker-compose 部署spring boot项目
时而有事儿
dockerlinuxdockerlinuxspringboot
linux系统环境:centos5.14本篇描述的是在centos系统版本下安装docker,如果是ubuntu版本,请看这篇文章:linuxubuntu20安装docker和docker-compose-CSDN博客正文:安装docker和docker-compose安装docker---------运行命名等待安装完成遇到选择直接输入yyuminstall-yyum-utilsdevice-m
- Python dict字符串转json对象,小数精度丢失问题
朝如青丝 暮成雪
jsonpython
一前言JSON(JavaScriptObjectNotation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,dict是Python的一种数据格式。本篇介绍一个float数据转换时精度丢失的案例。二问题描述importjsontest_str1='{"π":3.1415926535897932384626433832795028841971}'test_str2='{"value":10.00000}'print
- 计算机网络知识点汇总
蓝小俊
第1章概述P36习题3、7、14、15、17、22、24、262.“协议”与“服务”的异同点?答:(1)协议是控制两个对等实体进行通信的规则的集合。在协议的控制下,两个对等实体间的通信使得本层能够向上一层提供服务,而要实现本层协议,还需要使用下面一层提供服务。(2)协议和服务的概念的区分:1、协议的实现保证了能够向上一层提供服务。本层的服务用户只能看见服务而无法看见下面的协议。下面的协议对上面的服
- C语言演示多线程编程条件下自旋锁和屏障的使用
嫦娥妹妹等等我
开发语言c语言开源
主线故事:有4个人玩游戏输了,惩罚:1分别使用4台不同的ATM机给我存钱2必须一块一块的存3存完还得在ATM上看一下我的余额设计模式:1每个人使用一条单独的线程,再准备一个计时线程用来输出时间2存钱涉及到对共享资源的读写,是原子操作需要用锁保护这里使用自旋锁3都存完钱后需要等待在各自的ATM上回显余额这里使用屏障技术4如果在主线程中回显对应他们给我打电话告诉我存完了我自己看一下则不需要使用屏障因为
- 小红书打广告引流 小红书引流招式大全
九千营销
随着社交媒体的不断发展,越来越多的品牌开始在小红书上进行推广和引流。小红书是一个以用户分享购物心得和生活方式为主要内容的社交平台,拥有超过1亿的用户,尤其是女性用户占比极高。那么如何在小红书上打广告引流呢?以下提供一些实用的方法:防失联【xhs1.net】业务全能,有需求请联系微:jiu991144,jiu994455Q:74146394928110454【tg:jiuke1】1.与网红合作小红书
- 日更写作和跑步100天倒计时62
凯文日知录
#成功日记#打卡第3天@2018-11-4(星期天):一,100天写作倒计时62天;二,每天运动,14公里跑步,100个深蹲,2分钟平板支撑;三,看了一部电影《特工》韩国片;四,网易云课堂英语打卡第9天;五,看《谁说你不能坚持》;六,#成功日记#打卡第3天。今日有感:1、看电影的感觉是,人要有超越政治和商业的眼光,去真正的为人民做点事情,历史会给你最好的回复。2、重庆万州大巴事件,让我们看到了,人
- 罗永浩将首度直播卖“云”;武汉大学回应开设雷军班;.NET 7自5月14日起将不被支持 | 极客头条
极客日报
.net
「极客头条」——技术人员的新闻圈!CSDN的读者朋友们好,「极客头条」来啦,快来看今天都有哪些值得我们技术人关注的重要新闻吧。整理|苏宓出品|CSDN(ID:CSDNnews)一分钟速览新闻点!90后华为「天才少年」稚晖君又获新融资百度智能云推出大模型应用全家桶,7款产品全新升级武汉大学回应开设雷军班:招15人,本博贯通知情人士辟谣腾讯大规模裁员罗永浩将首度直播卖“云”联发科携手阿里云,天玑930
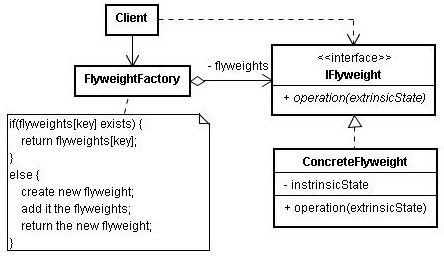
- 【二】【设计模式】建造者模式
妖精七七_
设计模式设计模式建造者模式
建造者模式的引入//C10_1.cpp#include#include"SystemConfig.h"intmain(){SystemConfigconfig("mysql://127.0.0.1/","xiaomu","xiaomumemeda","redis://127.0.0.1/","xiaomuredis","xiaomuredispw","kafka://127.0.0.1","xia
- 大话设计模式之工厂模式
码农客栈
设计模式开发语言
工厂模式(FactoryPattern)是一种创建型设计模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式,而无需指定将要创建的对象的确切类。通过使用工厂模式,我们可以将对象的创建和使用分离,从而使代码更具灵活性和可维护性。在工厂模式中,通常会有三种角色:工厂接口(FactoryInterface):声明了一个用于创建对象的接口,这样所有具体工厂类都必须实现该接口。具体工厂(ConcreteFactory):实
- 《外观模式(极简c++)》
Bovinitwo
设计模式(极简c++版)c++开发语言
本文章属于专栏-概述-《设计模式(极简c++版)》-CSDN博客模式说明方案:外观模式提供了一个统一的接口,简化了一组复杂子系统的访问方式。优点:将客户端与子系统解耦,降低了复杂性。提高了代码的灵活性和可维护性。缺点:可能导致外观类过于庞大,承担了过多的责任。增加了系统的抽象层,有时会影响性能。本质思想:外观模式的本质思想是为一组复杂的子系统提供一个简单的接口,隐藏其复杂性,使得客户端可以更轻松地
- 《技术资讯》:X0179AZ @福克斯波罗FOXBORO阀门定位器
baisheng321
阀门定位器中间件
《技术资讯》:X0179AZ@福克斯波罗FOXBORO阀门定位器《技术资讯》:X0179AZ@福克斯波罗FOXBORO阀门定位器《技术资讯》:X0179AZ@福克斯波罗FOXBORO阀门定位器一、FOXBORO福克斯波罗公司简介,FOXBORO福克斯波是哪国品牌Foxboro品牌于2014年1月被施耐德电气(SchneiderElectric)收购。他们一直于为您提供产品和服务以及的仪表和屡获殊荣
- 大话设计模式之代理模式
码农客栈
设计模式代理模式
代理模式(ProxyPattern)是一种结构型设计模式,它允许通过代理对象控制对另一个对象的访问。代理对象充当客户端和实际对象之间的中介,客户端通过代理对象间接访问实际对象,从而可以在访问控制、缓存、延迟加载等方面提供额外的功能。在代理模式中,通常会有三种角色:Subject(抽象主题):声明了真实对象和代理对象的共同接口,这样在任何使用真实对象的地方都可以使用代理对象。RealSubject(
- C#学习笔记
2301_79022588
学习笔记
一、事件派发器在C#中,事件派发器通常是指事件委托和事件处理程序的组合,用于实现一种观察者设计模式。它允许对象在状态发生变化时通知其他对象,从而实现对象之间的解耦。事件派发器的基本组成部分:事件委托(EventDelegate):事件委托是一种特殊的委托,用于封装可以被调用的方法。它定义了事件的签名,即指定了事件处理程序方法的参数和返回类型。通常,事件委托声明在事件派发器类的外部,并且使用dele
- ZCMU 1214: 斐波那契数列
H2BB
c语言
#includeintmain(){inta,b,d,c,i;while(scanf("%d",&a)!=EOF){b=1;c=1;if(a==0){printf("1\n");}else{for(i=1;i<=a;i++){d=b+c;c=b;b=d;}printf("%d\n",c);}}return0;}
- 2024.3.25力扣(1200-1400)刷题记录
Circusxxx
2024年3月力扣刷题记录leetcode算法python
一、1784.检查二进制字符串字段1.使用0分割。分割出来的结果是含有“1”的串和空串。classSolution:defcheckOnesSegment(self,s:str)->bool:#使用0分割returnsum(len(c)!=0forcins.split("0"))bool:#除了前面可以出现0,后面不能出现#1最后出现的位置必须在0第一次出现位置的前面idx_one=0idx_ze
- javascript的数据类型及转换
田小田txt
一、JavaScript数据类型:共有string,number,boolean,object,function五种数据类型;其中Object,Date,Array为对象型;2个不包含任何值的数据类型:null,undefined。二、Typeof查看数据类型:typeof"John"//返回stringtypeof3.14//返回numbertypeofNaN//返回numbertypeoffa
- 【设计模式】Java 设计模式之桥接模式(Bridge)
新手村长
Java设计模式设计模式java桥接模式
桥接模式(BridgePattern)是结构型设计模式的一种,它主要解决的是抽象部分与实现部分的解耦问题,使得两者可以独立变化。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,因为该模式涉及如何组合接口和它们的实现。将抽象部分与实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立地变化。一、桥接模式概述桥接模式的主要思想是将抽象与实现进行解耦,使得二者可以独立进行变化。在桥接模式中,抽象部分和实现部分被分离出来,抽象部分定义了一个抽
- C++面试题
虾仁A
面试c++
目录一、堆和栈的区别二、C++中new、delte和malloc的区别三、什么是源对象四、C++有哪些设计模式五,你使用过C++哪些类型的指针一、堆和栈的区别特性堆栈申请方式由程序员显式申请和释放由系统自动分配和释放分配方式动态分配自动分配分配效率相对较慢,需要遍历内存链表寻找合适空间相对较快,系统直接分配内存地址不连续的内存区域连续的内存区域大小限制大小灵活,上限取决于虚拟内存大小固定,通常较小
- Windows如何安装poppler库,python的PDF转PPTX项目
跨不过
pdf
资源库在这里下载https://github.com/oschwartz10612/poppler-windows/releases/tag/v21.03.0其他的参考这篇博客,里面提到的资源链接失效了https://blog.csdn.net/wy01415/article/details/110257130
- LeetCode[位运算] - #137 Single Number II
Cwind
javaAlgorithmLeetCode题解位运算
原题链接:#137 Single Number II
要求:
给定一个整型数组,其中除了一个元素之外,每个元素都出现三次。找出这个元素
注意:算法的时间复杂度应为O(n),最好不使用额外的内存空间
难度:中等
分析:
与#136类似,都是考察位运算。不过出现两次的可以使用异或运算的特性 n XOR n = 0, n XOR 0 = n,即某一
- 《JavaScript语言精粹》笔记
aijuans
JavaScript
0、JavaScript的简单数据类型包括数字、字符创、布尔值(true/false)、null和undefined值,其它值都是对象。
1、JavaScript只有一个数字类型,它在内部被表示为64位的浮点数。没有分离出整数,所以1和1.0的值相同。
2、NaN是一个数值,表示一个不能产生正常结果的运算结果。NaN不等于任何值,包括它本身。可以用函数isNaN(number)检测NaN,但是
- 你应该更新的Java知识之常用程序库
Kai_Ge
java
在很多人眼中,Java 已经是一门垂垂老矣的语言,但并不妨碍 Java 世界依然在前进。如果你曾离开 Java,云游于其它世界,或是每日只在遗留代码中挣扎,或许是时候抬起头,看看老 Java 中的新东西。
Guava
Guava[gwɑ:və],一句话,只要你做Java项目,就应该用Guava(Github)。
guava 是 Google 出品的一套 Java 核心库,在我看来,它甚至应该
- HttpClient
120153216
httpclient
/**
* 可以传对象的请求转发,对象已流形式放入HTTP中
*/
public static Object doPost(Map<String,Object> parmMap,String url)
{
Object object = null;
HttpClient hc = new HttpClient();
String fullURL
- Django model字段类型清单
2002wmj
django
Django 通过 models 实现数据库的创建、修改、删除等操作,本文为模型中一般常用的类型的清单,便于查询和使用: AutoField:一个自动递增的整型字段,添加记录时它会自动增长。你通常不需要直接使用这个字段;如果你不指定主键的话,系统会自动添加一个主键字段到你的model。(参阅自动主键字段) BooleanField:布尔字段,管理工具里会自动将其描述为checkbox。 Cha
- 在SQLSERVER中查找消耗CPU最多的SQL
357029540
SQL Server
返回消耗CPU数目最多的10条语句
SELECT TOP 10
total_worker_time/execution_count AS avg_cpu_cost, plan_handle,
execution_count,
(SELECT SUBSTRING(text, statement_start_of
- Myeclipse项目无法部署,Undefined exploded archive location
7454103
eclipseMyEclipse
做个备忘!
错误信息为:
Undefined exploded archive location
原因:
在工程转移过程中,导致工程的配置文件出错;
解决方法:
- GMT时间格式转换
adminjun
GMT时间转换
普通的时间转换问题我这里就不再罗嗦了,我想大家应该都会那种低级的转换问题吧,现在我向大家总结一下如何转换GMT时间格式,这种格式的转换方法网上还不是很多,所以有必要总结一下,也算给有需要的朋友一个小小的帮助啦。
1、可以使用
SimpleDateFormat SimpleDateFormat
EEE-三位星期
d-天
MMM-月
yyyy-四位年
- Oracle数据库新装连接串问题
aijuans
oracle数据库
割接新装了数据库,客户端登陆无问题,apache/cgi-bin程序有问题,sqlnet.log日志如下:
Fatal NI connect error 12170.
VERSION INFORMATION: TNS for Linux: Version 10.2.0.4.0 - Product
- 回顾java数组复制
ayaoxinchao
java数组
在写这篇文章之前,也看了一些别人写的,基本上都是大同小异。文章是对java数组复制基础知识的回顾,算是作为学习笔记,供以后自己翻阅。首先,简单想一下这个问题:为什么要复制数组?我的个人理解:在我们在利用一个数组时,在每一次使用,我们都希望它的值是初始值。这时我们就要对数组进行复制,以达到原始数组值的安全性。java数组复制大致分为3种方式:①for循环方式 ②clone方式 ③arrayCopy方
- java web会话监听并使用spring注入
bewithme
Java Web
在java web应用中,当你想在建立会话或移除会话时,让系统做某些事情,比如说,统计在线用户,每当有用户登录时,或退出时,那么可以用下面这个监听器来监听。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.ut
- NoSQL数据库之Redis数据库管理(Redis的常用命令及高级应用)
bijian1013
redis数据库NoSQL
一 .Redis常用命令
Redis提供了丰富的命令对数据库和各种数据库类型进行操作,这些命令可以在Linux终端使用。
a.键值相关命令
b.服务器相关命令
1.键值相关命令
&
- java枚举序列化问题
bingyingao
java枚举序列化
对象在网络中传输离不开序列化和反序列化。而如果序列化的对象中有枚举值就要特别注意一些发布兼容问题:
1.加一个枚举值
新机器代码读分布式缓存中老对象,没有问题,不会抛异常。
老机器代码读分布式缓存中新对像,反序列化会中断,所以在所有机器发布完成之前要避免出现新对象,或者提前让老机器拥有新增枚举的jar。
2.删一个枚举值
新机器代码读分布式缓存中老对象,反序列
- 【Spark七十八】Spark Kyro序列化
bit1129
spark
当使用SparkContext的saveAsObjectFile方法将对象序列化到文件,以及通过objectFile方法将对象从文件反序列出来的时候,Spark默认使用Java的序列化以及反序列化机制,通常情况下,这种序列化机制是很低效的,Spark支持使用Kyro作为对象的序列化和反序列化机制,序列化的速度比java更快,但是使用Kyro时要注意,Kyro目前还是有些bug。
Spark
- Hybridizing OO and Functional Design
bookjovi
erlanghaskell
推荐博文:
Tell Above, and Ask Below - Hybridizing OO and Functional Design
文章中把OO和FP讲的深入透彻,里面把smalltalk和haskell作为典型的两种编程范式代表语言,此点本人极为同意,smalltalk可以说是最能体现OO设计的面向对象语言,smalltalk的作者Alan kay也是OO的最早先驱,
- Java-Collections Framework学习与总结-HashMap
BrokenDreams
Collections
开发中常常会用到这样一种数据结构,根据一个关键字,找到所需的信息。这个过程有点像查字典,拿到一个key,去字典表中查找对应的value。Java1.0版本提供了这样的类java.util.Dictionary(抽象类),基本上支持字典表的操作。后来引入了Map接口,更好的描述的这种数据结构。
&nb
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-职责链模式-Chain Of Responsibility
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
/**
* 业务逻辑:项目经理只能处理500以下的费用申请,部门经理是1000,总经理不设限。简单起见,只同意“Tom”的申请
* bylijinnan
*/
abstract class Handler {
/*
- Android中启动外部程序
cherishLC
android
1、启动外部程序
引用自:
http://blog.csdn.net/linxcool/article/details/7692374
//方法一
Intent intent=new Intent();
//包名 包名+类名(全路径)
intent.setClassName("com.linxcool", "com.linxcool.PlaneActi
- summary_keep_rate
coollyj
SUM
BEGIN
/*DECLARE minDate varchar(20) ;
DECLARE maxDate varchar(20) ;*/
DECLARE stkDate varchar(20) ;
DECLARE done int default -1;
/* 游标中 注册服务器地址 */
DE
- hadoop hdfs 添加数据目录出错
daizj
hadoophdfs扩容
由于原来配置的hadoop data目录快要用满了,故准备修改配置文件增加数据目录,以便扩容,但由于疏忽,把core-site.xml, hdfs-site.xml配置文件dfs.datanode.data.dir 配置项增加了配置目录,但未创建实际目录,重启datanode服务时,报如下错误:
2014-11-18 08:51:39,128 WARN org.apache.hadoop.h
- grep 目录级联查找
dongwei_6688
grep
在Mac或者Linux下使用grep进行文件内容查找时,如果给定的目标搜索路径是当前目录,那么它默认只搜索当前目录下的文件,而不会搜索其下面子目录中的文件内容,如果想级联搜索下级目录,需要使用一个“-r”参数:
grep -n -r "GET" .
上面的命令将会找出当前目录“.”及当前目录中所有下级目录
- yii 修改模块使用的布局文件
dcj3sjt126com
yiilayouts
方法一:yii模块默认使用系统当前的主题布局文件,如果在主配置文件中配置了主题比如: 'theme'=>'mythm', 那么yii的模块就使用 protected/themes/mythm/views/layouts 下的布局文件; 如果未配置主题,那么 yii的模块就使用 protected/views/layouts 下的布局文件, 总之默认不是使用自身目录 pr
- 设计模式之单例模式
come_for_dream
设计模式单例模式懒汉式饿汉式双重检验锁失败无序写入
今天该来的面试还没来,这个店估计不会来电话了,安静下来写写博客也不错,没事翻了翻小易哥的博客甚至与大牛们之间的差距,基础知识不扎实建起来的楼再高也只能是危楼罢了,陈下心回归基础把以前学过的东西总结一下。
*********************************
- 8、数组
豆豆咖啡
二维数组数组一维数组
一、概念
数组是同一种类型数据的集合。其实数组就是一个容器。
二、好处
可以自动给数组中的元素从0开始编号,方便操作这些元素
三、格式
//一维数组
1,元素类型[] 变量名 = new 元素类型[元素的个数]
int[] arr =
- Decode Ways
hcx2013
decode
A message containing letters from A-Z is being encoded to numbers using the following mapping:
'A' -> 1
'B' -> 2
...
'Z' -> 26
Given an encoded message containing digits, det
- Spring4.1新特性——异步调度和事件机制的异常处理
jinnianshilongnian
spring 4.1
目录
Spring4.1新特性——综述
Spring4.1新特性——Spring核心部分及其他
Spring4.1新特性——Spring缓存框架增强
Spring4.1新特性——异步调用和事件机制的异常处理
Spring4.1新特性——数据库集成测试脚本初始化
Spring4.1新特性——Spring MVC增强
Spring4.1新特性——页面自动化测试框架Spring MVC T
- squid3(高命中率)缓存服务器配置
liyonghui160com
系统:centos 5.x
需要的软件:squid-3.0.STABLE25.tar.gz
1.下载squid
wget http://www.squid-cache.org/Versions/v3/3.0/squid-3.0.STABLE25.tar.gz
tar zxf squid-3.0.STABLE25.tar.gz &&
- 避免Java应用中NullPointerException的技巧和最佳实践
pda158
java
1) 从已知的String对象中调用equals()和equalsIgnoreCase()方法,而非未知对象。 总是从已知的非空String对象中调用equals()方法。因为equals()方法是对称的,调用a.equals(b)和调用b.equals(a)是完全相同的,这也是为什么程序员对于对象a和b这么不上心。如果调用者是空指针,这种调用可能导致一个空指针异常
Object unk
- 如何在Swift语言中创建http请求
shoothao
httpswift
概述:本文通过实例从同步和异步两种方式上回答了”如何在Swift语言中创建http请求“的问题。
如果你对Objective-C比较了解的话,对于如何创建http请求你一定驾轻就熟了,而新语言Swift与其相比只有语法上的区别。但是,对才接触到这个崭新平台的初学者来说,他们仍然想知道“如何在Swift语言中创建http请求?”。
在这里,我将作出一些建议来回答上述问题。常见的
- Spring事务的传播方式
uule
spring事务
传播方式:
新建事务
required
required_new - 挂起当前
非事务方式运行
supports
&nbs