Android开源中国客户端学习 异常处理模块 <12>
不得不说Osc的客户端的一些模块和商业系统很接近,这也是值得我们学习的地方。
osc的异常处理模块就是这样的一个模块,虽然个人认为功能有些耦合,但是不得不说还是很有参考价值的。
OSC的异常处理模块分为两大功能:
1.程序崩溃处理
由于种种原因,我们并不能保证我们的应用可以在所有手机上正常运行,开发过程中开发中印象最深的一个dialog也应该是”XXX已经停止运行“吧?虽然在ICS以后android的崩溃提示已经比较人性化,我们不能从中知晓是哪里出错。所以崩溃日志对于我们开发者就显得非常重要。
OSC在应用崩溃后会生成崩溃日志并提示用户把日志以email发送。虽然email发送这步可能没多少人做,但是我们既然拿到了日志,也就可以自行在自己的应用中将其发送到后台了,现在市场很多app都有崩溃日志上传这个功能。
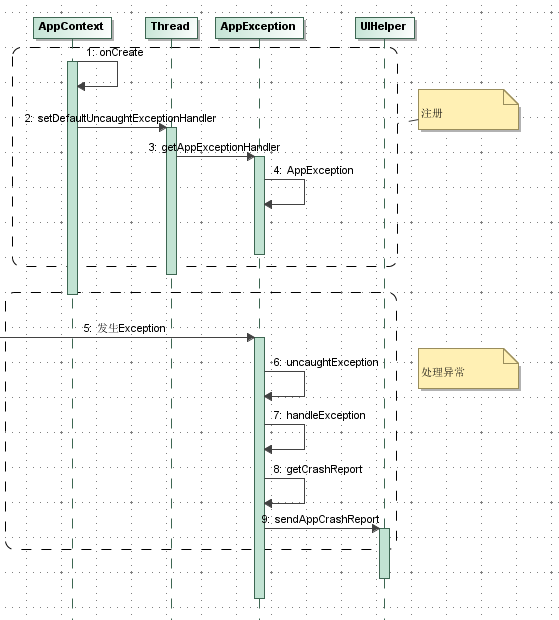
osc崩溃处理的时序图如下 注意不要忘了在androidmanifest中注册AppContext
分为两步:
a.注册崩溃处理,不让系统自己处理崩溃而让我们的app来处理
其实很简单在AppContext的onCreate中:
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
//注册App异常崩溃处理器
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(AppException.getAppExceptionHandler());
init();
}
setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler函数的作用:
Sets the default uncaught exception handler. This handler is invoked in case any Thread dies due to an unhandled exception.
其实就是如果这线程崩溃了就会调用这个handler的uncaughtException函数
b 自己处理崩溃
如果应用一旦崩溃就会执行:
2.这个函数中会获取崩溃日志并显示dialog提示用户上传
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread thread, Throwable ex) {
if(!handleException(ex) && mDefaultHandler != null) {
mDefaultHandler.uncaughtException(thread, ex);
}
} 然后就会生成崩溃日志并显示dialog 提示用户通过email把崩溃日志发送
/**
* 自定义异常处理:收集错误信息&发送错误报告
* @param ex
* @return true:处理了该异常信息;否则返回false
*/
private boolean handleException(Throwable ex) {
if(ex == null) {
return false;
}
final Context context = AppManager.getAppManager().currentActivity();//为了获取 应用的版本
if(context == null) {
return false;
}
final String crashReport = getCrashReport(context, ex);
//显示异常信息&发送报告
new Thread() {
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
UIHelper.sendAppCrashReport(context, crashReport);
Looper.loop();
}
}.start();
return true;
} 生成崩溃日志代码
获取日志代码
/**
* 获取APP崩溃异常报告
* @param ex
* @return
*/
private String getCrashReport(Context context, Throwable ex) {
PackageInfo pinfo = ((AppContext)context.getApplicationContext()).getPackageInfo();
StringBuffer exceptionStr = new StringBuffer();
exceptionStr.append("Version: "+pinfo.versionName+"("+pinfo.versionCode+")\n");
exceptionStr.append("Android: "+android.os.Build.VERSION.RELEASE+"("+android.os.Build.MODEL+")\n");
exceptionStr.append("Exception: "+ex.getMessage()+"\n");
StackTraceElement[] elements = ex.getStackTrace();
for (int i = 0; i < elements.length; i++) {
exceptionStr.append(elements[i].toString()+"\n");
}
return exceptionStr.toString();
}
2.应用运行中的非崩溃异常处理(比如网络异常的捕获)
个人感觉这个功能不应该在AppException中处理,但是确实这些错误应该在一个类(可以称为非崩溃异常中心)中处理。
以获取图片的异常为例:
函数中有
if (statusCode != HttpStatus.SC_OK) {
throw AppException.http(statusCode);
} 一句,如果返回code不是200就抛出一个异常:注意虽然还是在AppException中进行处理的但是确实和上面的崩溃没多少关系
public static AppException http(int code) {
return new AppException(TYPE_HTTP_CODE, code, null);
} 看看这个构造函数
private AppException(byte type, int code, Exception excp) {
super(excp);
this.type = type;
this.code = code;
if(Debug){
this.saveErrorLog(excp);
}
} 这里就把log保存到本地了 适时上传到服务器就可以分析这些异常了
/**
* 保存异常日志
* @param excp
*/
public void saveErrorLog(Exception excp) {
String errorlog = "errorlog.txt";
String savePath = "";
String logFilePath = "";
FileWriter fw = null;
PrintWriter pw = null;
try {
//判断是否挂载了SD卡
String storageState = Environment.getExternalStorageState();
if(storageState.equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)){
savePath = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getAbsolutePath() + "/OSChina/Log/";
File file = new File(savePath);
if(!file.exists()){
file.mkdirs();
}
logFilePath = savePath + errorlog;
}
//没有挂载SD卡,无法写文件
if(logFilePath == ""){
return;
}
File logFile = new File(logFilePath);
if (!logFile.exists()) {
logFile.createNewFile();
}
fw = new FileWriter(logFile,true);
pw = new PrintWriter(fw);
pw.println("--------------------"+(new Date().toLocaleString())+"---------------------");
excp.printStackTrace(pw);
pw.close();
fw.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(pw != null){ pw.close(); }
if(fw != null){ try { fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { }}
}
}