java中的RandomAccessFile的用法
Java的RandomAccessFile提供对文件的读写功能,与普通的输入输出流不一样的是RamdomAccessFile可以任意的访问文件的任何地方。这就是“Random”的意义所在。
RandomAccessFile的对象包含一个记录指针,用于标识当前流的读写位置,这个位置可以向前移动,也可以向后移动。RandomAccessFile包含两个方法来操作文件记录指针。
long getFilePoint():记录文件指针的当前位置。
void seek(long pos):将文件记录指针定位到pos位置。
RandomAccessFile包含InputStream的三个read方法,也包含OutputStream的三个write方法。同时RandomAccessFile还包含一系列的readXxx和writeXxx方法完成输入输出。
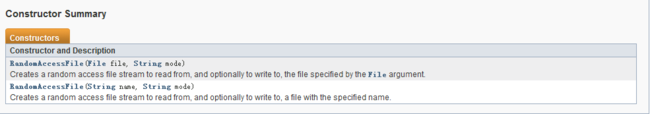
RandomAccessFile的构造方法如下
mode的值有四个
"r":以只读文方式打开指定文件。如果你写的话会有IOException。
"rw":以读写方式打开指定文件,不存在就创建新文件。
"rws":不介绍了。
"rwd":也不介绍。
下面是从中间开始读取文件:
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class work {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("work","r");
raf.seek(4);
byte []buffer=new byte[100];
int len=0;
while((len=raf.read(buffer, 0, 100))!=-1)
{
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
}
}
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class work {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("work","r");
raf.seek(4);
byte []buffer=new byte[100];
int len=0;
while((len=raf.read(buffer, 0, 100))!=-1)
{
System.out.println(new String(buffer,0,len));
}
}
}
下面是在文件最后加入内容:
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class work {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("work","rw");
raf.seek(raf.length());
raf.write("hello world!".getBytes());
raf.close();
}
}
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
public class work {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile("work","rw");
raf.seek(raf.length());
raf.write("hello world!".getBytes());
raf.close();
}
}