跟JBPM学设计模式之组合模式
跟JBPM学设计模式之组合模式
模式简介
组合模式,将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分与整体”的层次结构。组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
合成模式属于对象的结构模式,合成模式将对象组织到树形的结构中,可以用来描述整体与部分的关系。合成模式可以是客户端将单纯元素和复合元素同等的看待。
树形结构在各种类型的语言中发挥了巨大的作用,一个基于集成类型的等级结构就是一个树结构;同样一个基于合成的对象的结构也是一个树结构。在编程中我们一般遇到的树结构都是连通的有方向的树形结构。
有向树结构可以分为三种,从上到下、从下到上、双向的。这三种图中,树的节点和他们之间的关系都是一样的,但是连接他们的关系的方向却是不一样的。
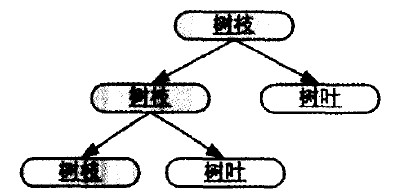
在由上到下的树图(如下图1-1)中,每一个树枝节点都有箭头指向它的所有子节点,从而客户可以要求每个树枝节点都给出自己所有的子节点,而一个节点却并不知道它的父节点。在这样的树结构中信息可以按照箭头自上向下传播。
图 1-1
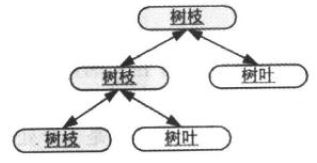
在一个由下向上的树图(如下图1-2)中,每个节点的箭头都指向它的父节点,但是一个父节点却不知道其子节点。信息可以按照箭头所指的方向自下向上传播。
图 1-2
在一个双向的树图(如下图1-3)中,每一个节点都同时知道它的父节点和子节点。信息可以按照箭头的方向向两个方向传播。
图 1-3
一个树结构是由两种节点组成的,树枝节点和树叶节点。前者可以包括子节点,后者不能有子节点。所以可以说树枝节点是承载树叶节点的容器。
组合模式的结构如下图1-4中所示,在图中我们可以看到其涉及到三个角色:
抽象构件角色(Compnent):这是一个抽象角色,它给参加组合的对象规定共有的接口和默认行为。
树叶构件角色(Leaf):代表参加组合的树叶对象,树叶对象没有子对象,规定了参加组合的原始对象的行为。
树枝构件角色(Composite):代表参加组合的有子对象的对象,给出了树枝构件对象的行为.
图 1-4
合成模式可以不提供父对象的管理方法,但是必须提供诸如添加、删除、获取子对象的的管理方法;所以根据所实现的接口的是否提供相应的管理方法分为两种形式,分别称为安全式和透明式。虽然这是模式的实现问题,但是却影响到模式结构的细节。
透明式组合模式(如下图1-5),在Component里声明所有用来管理子类对象的方法。这样所有的构件类都具有相同的接口。从接口层次看来,树枝对象和树叶对象是没有区别的,客户可以同等的对待所有的对象。但是其缺点就是不够安全,因为树叶节点是不可能有子对象的,因此其管理子对象的方法是没有意义的,但是编译时期不会出错,而只会在运行时期才会出错。
图 1-5
安全式组合模式(如下图1-6),在Composite里声明所有管理子类对象的方法。这样的做法是安全的做法,因为树叶节点本来根本就没有管理子类对象的方法,因此,如果对树叶对象使用这些方法,程序就会在编译器出错,而不是等到运行时才出错。
图 1-6
JBPM中的组合模式
JBPM中的活动节点模型具有透明组合模式的特征。我们知道JBPM中的节点有复合类型,也就是可以承载子节点;虽然从业务上来说,只有group类型的节点才能承载子节点,但是从JBPM的ActivityImpl的模型设计上来看,任何类型的节点都有ActivityImpl承载,自然任何类型的节点都可以承载子节点。具体的结构图如下1-7所示
图1-7
抽象构件角色:这里由Activity和CompositeElement共同完成抽象构件角色。前者向客户提供节点相关的业务功能接口,后者提供树叶构件需要具有的管理子类对象的方法接口。
/** the short display name given to this element. */
String getName();
/** the list of outgoing transitions.
* Caution: the actual member is returned. No copy is made. */
List<? extends Transition> getOutgoingTransitions();
/** the default outgoing transition. */
Transition getDefaultOutgoingTransition();
/** the first leaving transition with the given name or null of no
* such leaving transition exists. If the multiple transitions have
* the given transition name, the first (in order of { @link #getOutgoingTransitions()})
* will be returned.
*
* @param transitionName is the name of the transition to take. A null value will
* match the first unnamed transition. */
Transition getOutgoingTransition(String transitionName);
/** indicates if a leaving transition with the given transitionName exists.
* A null value matches an unnamed transition. */
boolean hasOutgoingTransition(String transitionName);
/** indicates if this activity has leaving transitions */
boolean hasOutgoingTransitions();
/** the leaving transitions, keyed by transition name. If a transition with
* the same name occurs mutltiple times, the first one is returned.
* Leaving transitions with a null value for their name are not included
* in the map.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made. In fact, the
* returned map is maintained as a cache. So updates to the map will
* influence subsequent retrievals of outgoing transitions by name. */
Map<String, ? extends Transition> getOutgoingTransitionsMap();
/** searches for the given transitionName in this activity and then up the
* parent chain. Returns null if no such transition is found. */
Transition findOutgoingTransition(String transitionName);
/** the list of arriving transitions.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made. */
List<? extends Transition> getIncomingTransitions();
/** indicates if this activity has arriving transitions */
boolean hasIncomingTransitions();
/** retrieve the parent activity in the composite activity structure. This is
* different from { @link ObservableElement#getParent()} in that it is restricted
* to the parent activities. It doesn't take into account the process definition. */
Activity getParentActivity();
/** indicates if this processDefinition has activities. */
boolean hasActivities();
/** the list of direct composite activities. Recursively contained
* activities are not included in the list.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made. */
List<? extends Activity> getActivities();
/** indicates if an activity with the given name exists directly in
* this element. Only the direct contained activities are
* searched. No recursive search is made. */
boolean hasActivity(String activityName);
/** the first composite activity with the given name or null of no
* such activity exists. Only the direct contained activities are
* searched. No recursive search is made. */
Activity getActivity(String activityName);
/** searches for the given activity in this element recursively,
* including this activity and all child activities. The search
* is done depth-first. A null value for activityName matches a activity
* without a name. */
Activity findActivity(String activityName);
/** the composite activities, keyed by activity name. If an activity
* with the same name occurs mutltiple times, the first in the list
* is included in the map. Activities with a null value for their name
* are not included in the map.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made. In fact, the
* returned map is maintained as a cache. So updates to the map will
* influence subsequent retrievals of activities by name. */
Map<String, ? extends Activity> getActivitiesMap();
/** the type of this activity which corresponds to the xml tag */
String getType();
}
/** indicates if this processDefinition has activities. */
boolean hasActivities();
/** the list of direct composite activities. Recursively contained
* activities are not included in the list.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made. */
List<? extends Activity> getActivities();
/** indicates if an activity with the given name exists directly in
* this element. Only the direct contained activities are
* searched. No recursive search is made. */
boolean hasActivity(String activityName);
/** the first composite activity with the given name or null of no
* such activity exists. Only the direct contained activities are
* searched. No recursive search is made. */
Activity getActivity(String activityName);
/** searches for the given activity in this element recursively,
* including this activity and all child activities. The search
* is done depth-first. A null value for activityName matches a activity
* without a name. */
Activity findActivity(String activityName);
/** the composite activities, keyed by activity name. If an activity
* with the same name occurs mutltiple times, the first in the list
* is included in the map. Activities with a null value for their name
* are not included in the map.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made. In fact, the
* returned map is maintained as a cache. So updates to the map will
* influence subsequent retrievals of activities by name. */
Map<String, ? extends Activity> getActivitiesMap();
}
树枝构件角色:树枝构件由CompositeElementImpl担当,其具体实现对节点的管理功能。同时ActivityImpl直接继承CompositeElementImpl,所以它也是树枝构件。
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected List<ActivityImpl> activities;
transient protected Map<String, ActivityImpl> activitiesMap;
// nested activities //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /
/**
* creates a nested activity. Also the nested activity's parent pointer will be set
* appropriatly.
*/
public ActivityImpl createActivity() {
return createActivity( null);
}
/**
* creates a nested activity with the given name. Also the nested activity's parent pointer will be set
* appropriatly.
* @param activityName may be null.
*/
public ActivityImpl createActivity(String activityName) {
ActivityImpl activity = new ActivityImpl();
activity.setName(activityName);
addActivity(activity);
return activity;
}
public Activity addActivity(ActivityImpl activity) {
activity.setProcessDefinition(processDefinition);
if (activities== null) {
activities = new ArrayList<ActivityImpl>();
}
if (! activities.contains(activity)) {
activities.add(activity);
}
activitiesMap = null;
return activity;
}
/** removes the given activity from the nested activities.
* Also the activity's parent will be nulled.
* This method will do nothing if the activity is null or if
* the activity is not in the list of nested activities.
* If the activity is actually removed from the list of
* activities, the activity's source will be nulled.
* In case this is the activity that was in the
* activitiesMap and another activity exists with the same
* name, that activity (the first) will be put in the
* activitiesMap as a replacement for the removed activity.
*/
public boolean removeActivity(ActivityImpl activity) {
if ( (activity!= null)
&& (activities!= null)
) {
boolean isRemoved = activities.remove(activity);
if (isRemoved) {
activity.setParentActivity( null);
if (activities.isEmpty()) {
activities = null;
}
activitiesMap = null;
}
return isRemoved;
}
return false;
}
/** the first nested activity with the given name or null of no
* such activity exists.
*/
public ActivityImpl getActivity(String activityName) {
return (getActivitiesMap()!= null ? activitiesMap.get(activityName) : null);
}
/** is this activity present ? */
public boolean hasActivity(String activityName) {
return ((getActivitiesMap()!= null) && (activitiesMap.containsKey(activityName)));
}
public ActivityImpl findActivity(String activityName) {
if (activities!= null) {
for(ActivityImpl n : activities) {
ActivityImpl activity = n.findActivity(activityName);
if (activity!= null) {
return activity;
}
}
}
return null;
}
/** the list of nested activities.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made.
*/
public List<? extends Activity> getActivities() {
return activities;
}
/** the nested activities, keyed by activity name. If a activity with
* the same name occurs mutltiple times, the first in the list
* is included in the map.
* Activities with a null value for their name are not included
* in the map.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made.
*/
public Map<String, ? extends Activity> getActivitiesMap() {
if (activitiesMap == null) {
this.activitiesMap = ActivityImpl.getActivitiesMap(activities);
}
return activitiesMap;
}
/** indicates if this processDefinition has activities. */
public boolean hasActivities() {
return ((activities!= null) && (!activities.isEmpty()));
}
}
树叶构件角色:树叶构件角色由ActivityImpl来担当,ActivityImpl在没有子节点的时候,就是真正的树叶构件了。
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
protected ActivityBehaviour activityBehaviour;
protected boolean isActivityBehaviourStateful = false;
protected Descriptor activityBehaviourDescriptor;
protected List<TransitionImpl> outgoingTransitions = new ArrayList<TransitionImpl>();
protected List<TransitionImpl> incomingTransitions = new ArrayList<TransitionImpl>();
protected TransitionImpl defaultOutgoingTransition;
protected ActivityImpl parentActivity;
protected String type;
protected Continuation continuation = Continuation.SYNCHRONOUS;
protected ActivityCoordinatesImpl coordinates;
// Do not initialize. Caching is based on the nullity of this map
transient protected Map<String, TransitionImpl> outgoingTransitionsMap = null;
/**
* Use { @link ProcessDefinitionImpl#createActivity()} or { @link ActivityImpl#createActivity()} instead.
*/
public ActivityImpl() {
super();
}
// specialized activity containment methods //////////////////////////////////// /
public ActivityImpl addActivity(ActivityImpl activity) {
activity.setParentActivity( this);
super.addActivity(activity);
return activity;
}
public ActivityImpl findActivity(String activityName) {
if (activityName== null) {
if (name== null) {
return this;
}
} else if (activityName.equals(name)) {
return this;
}
return super.findActivity(activityName);
}
// outgoing transitions //////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/** creates an outgoing transition from this activity. */
public TransitionImpl createOutgoingTransition() {
// create a new transition
TransitionImpl transition = new TransitionImpl();
transition.setProcessDefinition(processDefinition);
// wire it between the source and destination
addOutgoingTransition(transition);
// if there is no default transition yet
if (defaultOutgoingTransition== null) {
// make this the default outgoing transition
defaultOutgoingTransition = transition;
}
return transition;
}
/**
* adds the given transition as a leaving transition to this activity.
* Also the source of the transition is set to this activity.
* Adding a transition that is already contained in the leaving
* transitions has no effect.
* @return the added transition.
* @throws NullPointerException if transition is null.
*/
public Transition addOutgoingTransition(TransitionImpl transition) {
if (! outgoingTransitions.contains(transition)) {
transition.setSource( this);
transition.setSourceIndex(outgoingTransitions.size());
outgoingTransitions.add(transition);
clearOutgoingTransitionsMap();
}
return transition;
}
/**
* removes the given transition from the leaving transitions.
* Also the transition's source will be nulled.
* This method will do nothing if the transition is null or if
* the given transition is not in the list of this activity's leaving
* transitions.
* In case this is the transition that was in the
* outgoingTransitionsMap and another transition exists with the same
* name, that transition (the first) will be put in the
* outgoingTransitionsMap as a replacement for the removed transition.
* If the transition is actually removed from the list of
* leaving transitions, the transition's source will be nulled.
*/
public boolean removeOutgoingTransition(TransitionImpl transition) {
if (transition!= null) {
boolean isRemoved = outgoingTransitions.remove(transition);
if (isRemoved) {
transition.setSource( null);
clearOutgoingTransitionsMap();
}
return isRemoved;
}
return false;
}
/** the first leaving transition with the given name or null of no
* such leaving transition exists.
*/
public TransitionImpl getOutgoingTransition(String transitionName) {
return (getOutgoingTransitionsMap()!= null ? outgoingTransitionsMap.get(transitionName) : null);
}
/** searches for the given transitionName in this activity and then up the
* parent chain. Returns null if no such transition is found. */
public TransitionImpl findOutgoingTransition(String transitionName) {
TransitionImpl transition = getOutgoingTransition(transitionName);
if (transition!= null) {
return transition;
}
if (parentActivity!= null) {
return parentActivity.findOutgoingTransition(transitionName);
}
return null;
}
/** searches for the default transition in this activity and then up the
* parent chain. Returns null if no such transition is found. */
public TransitionImpl findDefaultTransition() {
if (defaultOutgoingTransition!= null) {
return defaultOutgoingTransition;
}
if (parentActivity!= null) {
return parentActivity.findDefaultTransition();
}
return null;
}
/** the list of leaving transitions.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made.
*/
public List<? extends Transition> getOutgoingTransitions() {
return outgoingTransitions;
}
/** indicates if a leaving transition with the given transitionName exists. */
public boolean hasOutgoingTransition(String transitionName) {
return (getOutgoingTransition(transitionName)!= null);
}
/** indicates if this activity has leaving transitions */
public boolean hasOutgoingTransitions() {
return !outgoingTransitions.isEmpty();
}
/** sets the outgoingTransitions to the given list of outgoingTransitions.
* A copy of the collection is made. Also the outgoingTransitionsMap will
* be updated and the source of all the transitions in the given list will
* be set to this activity.
* In case there was a leaving transitions list present, these transition's
* source will be nulled.
*/
public void setOutgoingTransitions(List<TransitionImpl> outgoingTransitions) {
if (! this.outgoingTransitions.isEmpty()) {
List<TransitionImpl> removedTransitions = new ArrayList<TransitionImpl>(outgoingTransitions);
for (TransitionImpl removedTransition: removedTransitions) {
removeOutgoingTransition(removedTransition);
}
}
if (outgoingTransitions!= null) {
this.outgoingTransitions = new ArrayList<TransitionImpl>();
for (TransitionImpl addedTransition: outgoingTransitions) {
addOutgoingTransition(addedTransition);
}
} else {
this.outgoingTransitions = new ArrayList<TransitionImpl>();
}
clearOutgoingTransitionsMap();
}
// arriving transitions //////////////////////////////////////////////////// /
/**
* adds the given transition as an arriving transition to this activity.
* Also the source of the transition is set to this activity.
* @return the added transition.
* @throws NullPointerException if transition is null.
*/
public Transition addIncomingTransition(TransitionImpl transition) {
transition.setDestination( this);
incomingTransitions.add(transition);
return transition;
}
/** removes the given transition if it is contained in the arriving
* transitions of this activity. If this transition was actually removed,
* its destination pointer is nulled.
* @return true if a transition was removed.
*/
public boolean removeIncomingTransition(TransitionImpl transition) {
if ( (transition!= null) && (incomingTransitions.remove(transition))) {
transition.setDestination( null);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/** the list of arriving transitions.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made.
*/
public List<? extends Transition> getIncomingTransitions() {
return incomingTransitions;
}
/** indicates if this activity has arriving transitions */
public boolean hasIncomingTransitions() {
return !incomingTransitions.isEmpty();
}
/** sets the incomingTransitions to the given list of incomingTransitions.
* A copy of the collection is made. Also the destination of all the transitions
* in the given list will be set to this activity.
* In case there was an arriving transitions list present, these transition's
* destination will be nulled.
*/
public void setIncomingTransitions(List<TransitionImpl> incomingTransitions) {
if (! this.incomingTransitions.isEmpty()) {
for (TransitionImpl removedTransition: this.incomingTransitions) {
removedTransition.setDestination( null);
}
}
if (incomingTransitions!= null) {
this.incomingTransitions = new ArrayList<TransitionImpl>(incomingTransitions);
for (TransitionImpl addedTransition: incomingTransitions) {
addedTransition.setDestination( this);
}
} else {
this.incomingTransitions = null;
}
}
/** the leaving transitions, keyed by transition name. If a transition with
* the same name occurs mutltiple times, the first one is returned.
* Leaving transitions with a null value for their name are not included
* in the map.
* Beware: the actual member is returned. No copy is made.
*/
public Map<String, ? extends Transition> getOutgoingTransitionsMap() {
if(outgoingTransitionsMap == null){
outgoingTransitionsMap = new HashMap<String, TransitionImpl>();
for (TransitionImpl transition: outgoingTransitions) {
if (!outgoingTransitionsMap.containsKey(transition.getName())) {
outgoingTransitionsMap.put(transition.getName(), transition);
}
}
}
return outgoingTransitionsMap;
}
void clearOutgoingTransitionsMap() {
outgoingTransitionsMap = null;
}
// various helper methods ////////////////////////////////////////////////// /
static Map<String, ActivityImpl> getActivitiesMap(List<ActivityImpl> activities) {
Map<String, ActivityImpl> map = null;
if (activities!= null) {
map = new HashMap<String, ActivityImpl>();
for (ActivityImpl activity: activities) {
if (! map.containsKey(activity.getName())) {
map.put(activity.getName(), activity);
}
}
}
return map;
}
public String toString() {
if (name!= null) return "activity("+name+")";
if (dbid!=0) return "activity("+dbid+")";
return "activity("+System.identityHashCode( this)+")";
}
/** collects the full stack of parent in a list. This activity is the
* first element in the chain. The process definition will be the last element.
* the chain will never be null. */
public List<ObservableElementImpl> getParentChain() {
List<ObservableElementImpl> chain = new ArrayList<ObservableElementImpl>();
ObservableElementImpl processElement = this;
while (processElement!= null) {
chain.add(processElement);
processElement = processElement.getParent();
}
return chain;
}
public boolean isAsync() {
return ! (continuation==Continuation.SYNCHRONOUS);
}
public boolean contains(ActivityImpl activity) {
while (activity!= null) {
if (activity.getParent()== this) {
return true;
}
activity = activity.getParentActivity();
}
return false;
}
// customized getters and setters ////////////////////////////////////////// /
public ActivityBehaviour getActivityBehaviour() {
if (activityBehaviour!= null) {
return activityBehaviour;
}
if (activityBehaviourDescriptor!= null) {
ActivityBehaviour createdBehaviour = (ActivityBehaviour) ReflectUtil.instantiateUserCode(activityBehaviourDescriptor, processDefinition, null);
if (!isActivityBehaviourStateful) {
activityBehaviour = createdBehaviour;
}
return createdBehaviour;
}
return null;
}
// getters and setters //////////////////////////////////////////////////////
public ObservableElementImpl getParent() {
return (parentActivity!= null ? parentActivity : processDefinition);
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public TransitionImpl getDefaultOutgoingTransition() {
return defaultOutgoingTransition;
}
public void setDefaultOutgoingTransition(TransitionImpl defaultOutgoingTransition) {
this.defaultOutgoingTransition = defaultOutgoingTransition;
}
public ActivityImpl getParentActivity() {
return parentActivity;
}
public void setParentActivity(ActivityImpl parentActivity) {
this.parentActivity = parentActivity;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public ActivityCoordinatesImpl getCoordinates() {
return coordinates;
}
public void setCoordinates(ActivityCoordinatesImpl coordinates) {
this.coordinates = coordinates;
}
public Continuation getContinuation() {
return continuation;
}
public void setContinuation(Continuation continuation) {
this.continuation = continuation;
}
public void setActivityBehaviour(ActivityBehaviour activityBehaviour) {
this.activityBehaviour = activityBehaviour;
}
public Descriptor getActivityBehaviourDescriptor() {
return activityBehaviourDescriptor;
}
public void setActivityBehaviourDescriptor(Descriptor activityBehaviourDescriptor) {
this.activityBehaviourDescriptor = activityBehaviourDescriptor;
}
public boolean isActivityBehaviourStateful() {
return isActivityBehaviourStateful;
}
public void setActivityBehaviourStateful( boolean isActivityBehaviourStateful) {
this.isActivityBehaviourStateful = isActivityBehaviourStateful;
}
}
这里JBPM并没有严格按照模式的定义进行实现,而是根据业务进行了模型的分离。由于对子节点的管理是由流程引擎内部进行管理的,是不允许客户进行更改的;只需要向客户开放节点相关的业务接口;所以进行这样的实现还是符合业务实际场景的。
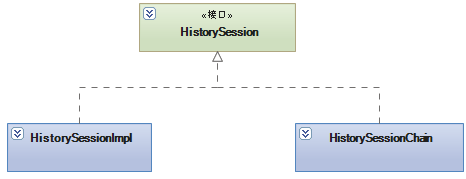
JBPM中的对多历史数据库支持的session模型具有安全组合模式的特征的。具体的结构如下图(1-8)所示
图 1-8
抽象构件角色:这里由HistorySession担当,其提供启动记录历史信息的接口。每个该类的实例都会对应一个独立的数据库。
void process(HistoryEvent historyEvent);
}
树叶构件角色:这里由HistorySessionImpl担当,其提供启动记录历史信息的具体实现。
public void process(HistoryEvent historyEvent) {
historyEvent.process();
}
}
树枝构件角色:这里由HistorySessionChain担当,其作为承载子对象的容器,可以承载代表不同历史库的HistorySession的对象。
protected List<HistorySession> historySessions = new ArrayList<HistorySession>();
public HistorySessionChain(List<HistorySession> historySessions) {
this.historySessions = historySessions;
}
public void process(HistoryEvent historyEvent) {
for (HistorySession historySession: historySessions) {
historySession.process(historyEvent);
}
}
}