【javascript继承】之——原型链继承和类式继承
什么是继承啊?答:别人白给你的过程就叫继承。
为什么要用继承呢?答:捡现成的呗。
好吧,既然大家都想捡现成的,那就要学会怎么继承!
在了解之前,你需要先了解构造函数、对象、原型链等概念......
JS里常用的两种继承方式:
- 原型链继承(对象间的继承)
- 类式继承(构造函数间的继承)
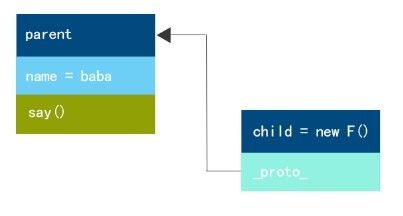
原型链继承:
//要继承的对象 var parent={ name : "baba" say : function(){ alert("I am baba"); } } //新对象 var child = proInherit(parent); //测试 alert(child.name); //"baba" child.say(); //"I am baba"
利用proInherit(obj)方法,传入对象,就能实现对象的属性及方法的继承,这个方法不是内置方法,所以要自己定义,非常简单:
function proInherit(obj){ function F () {} F.prototype = obj; return new F(); }
其中F()为一个临时的空的构造函数,然后将F()的原型设置为父对象,但是同时它又通过受益于_proto_链接而具有其父亲对象的全部功能。
链式图解:
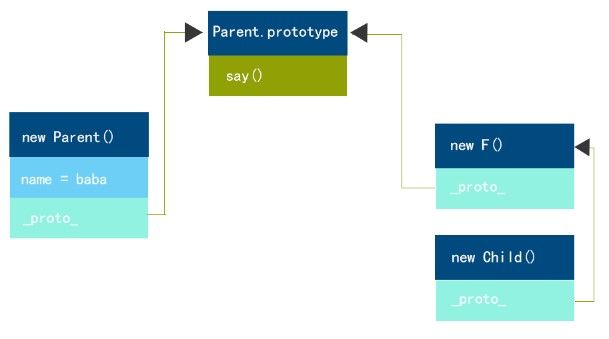
类式继承:
//父类构造函数 function Parent() { this.name = "baba"; } //父类原型方法 Parent.prototype.getName = function () { return this.name; } //子类构造函数 function Child() { this.name = "cc"; } //类式继承 classInherit(Parent, Child); //实例 var child = new Child(); alert(child.getName()) //“baba”
下面我们来看看这个继承的关键方法:classInherit(Parent,Child)
var classInherit = (function () { var F = function () { } return function (P, C) { F.prototype = P.prototype; C.prototype = new F(); C.prototype.constructor = C; } }());
分析一下这个方法:
- 首先创建一个空的构造函数F(),用其实例的_proto_属性来构建父类与子类的原型链。起到一个代理的作用,目的是为了防止C.prototype = P.prototype,这样会在子类实例化后修改属性或方法时候,连同父类一起修改。
- 整体采用即时函数并且在闭包中存储F(),防止多次继承时候创建大量的空的构造函数,从而减少消耗内存。
- 最后一行的意思是,由于原型链的关系,C的实例对象的constructor会指向P,所以重新设置。
链式图解:
这种方式虽然在实例的时候继承了原型方法,但是父类的属性无法继承,下面介绍一种复制继承,算是对类式继承的补充。
复制继承:
//复制继承 function copyInherit(p, c) { var i, toStr = Object.prototype.toString, astr = "[object Array]"; c = c || {}; for (i in p) { if (p.hasOwnProperty(i)) { if (typeof p[i] === "object") { c[i] = toStr.call(p[i]) == astr ? [] : {}; c[i] = copyInherit(p[i], c[i]); } else { c[i] = p[i]; } } } return c; } //重写Parent function Parent() { this.name = "pp"; this.obj= {a:1,b:2}; this.arr= [1, 2] } //实例 var child = new Child(); var parent = new Parent(); copyInherit(parent, child); alert(child.name) //"baba" alert(child.arr) //1,2 alert(child.obj.a) //1
分析下copyInherit(p,c)
当一个值赋予一个变量时候,分为传值和传引用两种方式,当你父对象内属性包含数组类型或是对象类型时候, c[i] = toStr.call(p[i]) == astr ? [] : {};这一句会避免修改子对象属性而引起的父对象属性被篡改。
总结:
类式继承比较普遍,因为大家都比较熟悉这种构造函数方式,但是内存占用比较大。而原型式继承,占用内存比较小,但是包含数组,或者对象类型的克隆比较麻烦。复制继承简单,而且应用广泛。