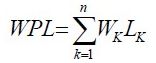在介绍哈弗曼树之前首先介绍有关哈夫曼树的概念:
路径:树中一个节点到另一个节点的分支构成这两各节点的路径。
如图:根到a节点经过 1、2。1、2就是根到a的一条路径。
权值:通常是指每个叶子节点出现的次数。如上图:a的权值为1,b的权值为2,c的权值为3,d的权值为4。
节点的带权路径长度:在一棵树中,如果其节点附带一个权值,把该节点的路径长度与该节点的权值之积称为该节点的带权路径长度。
树的带权路径长度:所有节点的带权路径长度之和为树的带权路径长度。
n为带权值的叶子节点的个数,Wk为第k个叶子节点的权值,Lk为该节点的路径长度。
上图树的带权路径长度为WPL=1*2+2*2+3*2+4*2=20;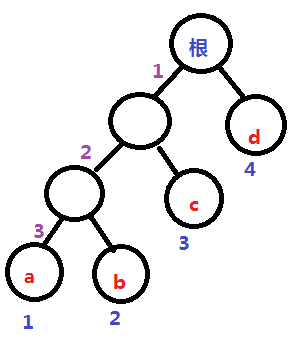
此树的带权路径长度WPL=1*3+2*3+3*2+4*1=19;
综上可得,每棵树的结构不同,树的带权路径长度可能不同。
哈夫曼树:树的带权路径长度最小的树称为哈夫曼树。
构造哈弗曼的方法:
从n个带权的节点中,每次选两个最小的,作为左右孩子节点,构造一棵树,树的根的权值为这两个孩子节点权值的和。同时将这两个节点从n各节点中删除,将他们的双亲节点添加到n-2个节点中,称为有n-1带权的节点。重复以上步骤,直至只有一个节点时,作为此树的根节点。

创建好哈夫曼树后,要构建哈弗曼编码。某节点若为哈夫曼树的左孩子则为0(或1),若为右孩子则为1(或0),从根到叶子节点得到的一组编码,即为哈弗曼编码。
上图a的编码:0;b的编码:01;c的编码:001;d的编码:000;
哈弗曼树的两个重要应用:可以实现对数据的压缩和加密。
下面的java程序实现了哈弗曼的创建、编码、根据某一文件的字符串翻译出对应的哈弗曼树的01串,将结果输出到另一文件中。
1.统计次数。在创建哈弗曼之前要对每个字符(以字节的形式)出现次数,即权值排序。排序用到java自带的类PriorityQueue,他需要一个指定的迭代器MyComparator,规定排序是按照何种方式排序(例如根据人的年龄、身高、还是体重)。
2.构造哈夫曼树。将排好序的权值(保存在HashMap<Byte,Integer>中,Byte字符(以字节的形式),Integer权值),每次从中选出两个,作为左右孩子,构造树,并移除这两个节点。用poll()方法可以实现。最后返回树的根节点。
3.构造哈弗曼编码。构造树的过程中规定左孩子为0,有孩子为1.遍历叶子节点得到每个字符的编码。
4.得到01串。对应文件中的字符翻译出对应的01串。每翻译100个01串,就写到文件中。再将字符串清0,继续翻译。
package Dream.hafuman0719;
/**
* 定义二叉树的节点
* @author Dream
* @Date 2014年7月20日
*/
public class TreeNode {
int obj;
//默认的Byte为null,默认的byte为0
Byte b;
int flag=-1; //哈弗曼每个节点的编码,左为0,右为1,根节点设为-1
TreeNode parent; //某节点的父亲节点
TreeNode leftChild; //某节点的左儿子节点
TreeNode rightChild; //某节点的右儿子节点
public TreeNode(int obj,Byte b){
this.obj=obj;
this.b=b;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return obj+"";
}
}
package Dream.hafuman0719;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 哈夫曼树的创建
*
* @author Dream
* @Date 2014年7月19日
*/
public class HufumanTree {
String str="E:\\a.txt";
File file =new File(str);
public static void main(String[] args) {
HufumanTree tree = new HufumanTree();
HashMap<Byte,Integer> map=tree.countNum("E:\\abc.txt");
//得到创建好的哈弗曼的根节点
TreeNode root=tree.Hufuman(map);
//得到哈弗曼编码
HashMap<Byte,String> mapCode=tree.HafumanCode(root);
String str=tree.printString(mapCode, "E:\\abc.txt");
}
/**
* 1.统计文件中每个字节出现的次数
* @param path 要统计的文件的路径
* @return 返回
*/
public HashMap<Byte,Integer> countNum(String path){
HashMap<Byte,Integer> map=new HashMap<Byte,Integer>();
try{
FileInputStream fis =new FileInputStream(path);
//将文件打包成缓冲流
BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis);
//读取一个字节
int t=bis.read();
//如果没有读到文件末尾
while(t!=-1){
byte bt=(byte)t;
//判断这个字节是否出现过
if(map.containsKey(bt)){
//根据key得到对应的value
int count=map.get(bt);
count++;
//用新的value替换旧的value
map.put(bt, count);
}
else{
//第一次出现将它放到map中,出现的次数为1
map.put(bt, 1);
}
//读取下一个字节
t=bis.read();
}
bis.close();
}catch(Exception ef){
ef.printStackTrace();
}
return map;
}
/**
* 2.构造哈夫曼树 步骤一:将给出的每个权值,构造对应的节点,按权值大小进行排序
* 步骤二:创建哈夫曼树
*
*/
public TreeNode Hufuman(HashMap<Byte,Integer> map) {
//步骤一
PriorityQueue<TreeNode> nodeList =sort(map);
//步骤一的结果作为步骤二的条件
//步骤二
TreeNode root = creatHafumanTree(nodeList);
return root;
}
// ********************************************************************
/**
* 排序
*
* @param map
* <字节,次数>奖次数作为权值,进行排序
* @return 返回排好序的哈弗曼节点
*/
public PriorityQueue<TreeNode> sort(HashMap<Byte,Integer> map) {
// 按照自然顺序或指定规则将元素排序的队列,队列的默认长度为11
//使用指定的初始容量创建一个 PriorityQueue,并根据指定的比较器对元素进行排序。
PriorityQueue<TreeNode> nodeList = new PriorityQueue<TreeNode>(11,
new MyComparator());
//得到value
Set<Byte> bt=map.keySet();
// 将元素添加到队列中
for (byte b:bt) {
int value=map.get(b);
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(value,b);
nodeList.add(node);
}
return nodeList;
}
// ********************************************************************
public TreeNode creatHafumanTree(PriorityQueue<TreeNode> nodeList) {
//如果队列中只有一个元素则作为根节点返回,如果队列中开始时就没有元素则返回root为null
while (nodeList.size() > 1) {
//从队列中取出两个权值较小的构造哈夫曼树
TreeNode n1 = nodeList.poll();
TreeNode n2 = nodeList.poll();
//将两个节点的权值和作为新的节点插到队列中
TreeNode n3 = new TreeNode(n1.obj + n2.obj,null);
nodeList.add(n3);
//构造哈夫曼树节点之间的关系
n3.leftChild = n1;
n3.rightChild = n2;
n1.flag=0;
n2.flag=1;
n1.parent = n3;
n2.parent = n3;
}
//得到最后一个节点作为根节点
TreeNode root = nodeList.poll();
return root;
}
//哈弗曼编码
public HashMap<Byte,String> HafumanCode(TreeNode root){
HashMap<Byte,String> map=new HashMap<Byte,String>();
getHafumanCode(root,null,map,"");
return map;
}
/**
* 得到哈弗曼编码
* @param root 哈夫曼树的根节点
* @param parent 每个节点的双亲节点
* @param map 将得到的哈弗曼编码保存到映射map中
* @param s 得到的每个节点的编码字符串
*/
public void getHafumanCode(TreeNode root,TreeNode parent,HashMap<Byte,String>map,String s){
if(root!=null){
//每个节点的编码
if(root.flag!=-1){
s+=root.flag;
}
TreeNode left=root.leftChild;
getHafumanCode(left,root,map,s);
TreeNode right=root.rightChild;
getHafumanCode(right,root,map,s);
}
//得到了叶子节点的孩子
else{
map.put(parent.b, s);
//System.out.println(parent.obj);
}
}
//得到哈弗曼编码的方法二(根据叶子节点倒推编码)
public void getHafumanCode2(TreeNode root,TreeNode parent,HashMap<Byte,String>map){
if(root!=null){
TreeNode left=root.leftChild;
getHafumanCode2(left,root,map);
TreeNode right=root.rightChild;
getHafumanCode2(right,root,map);
}
//得到了叶子节点的孩子
else{
String s=""+parent.flag;
TreeNode node=parent.parent;
while(node!=null && node.flag!=-1){
//注意区分node.flag+s和s+node.flag的区别
s=node.flag+s;
node=node.parent;
}
map.put(parent.b, s);
//System.out.println(parent.obj);
}
}
/**
* 5.输出01串
* @param map Byte为文件中的字节表示 String为每个字节对应的编码
* @param path 文件的路径,文件中保存的是字节
* @return 返回文件中所有字节对应的01串
*/
public String printString(HashMap<Byte,String> map,String path){
//01串
String s="";
//遍历文件得到字节,根据字节翻译得到01串
try{
//输入流
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream(path);
//缓冲流
InputStreamReader bis=new InputStreamReader(fis);
//读入一个字节
int t=bis.read();
while(t!=-1){
byte bt=(byte)t;
if(s.length()>5){
writeString(file,s);
s="";
}
s+=map.get(bt);
t=bis.read();
}
bis.close();
}catch(Exception ef){
ef.printStackTrace();
}
return s;
}
public void writeString(File file,String s){
try{
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(file,true);
OutputStreamWriter bos=new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
char c=s.charAt(i);
bos.write(c);
}
bos.flush();
bos.close();
}catch(Exception ef){
ef.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 前序遍历二叉树
public void printTree(TreeNode tn) {
if (tn != null) {
System.out.println(tn.obj);
// 遍历左子树
TreeNode leftNode = tn.leftChild;
printTree(leftNode);
// 遍历右子树
TreeNode rightNode = tn.rightChild;
printTree(rightNode);
}
}
//PriorityQueue根据MyComparator的排序规则自动给PriorityQueue中的元素排序
//指定的迭代器
class MyComparator implements Comparator<TreeNode> {
@Override
//根据第一个参数小于、等于、大于第二个参数分别返回负数、零、正整数
public int compare(TreeNode o1, TreeNode o2) {
int num = o1.obj - o2.obj;
return num;
}
}
}