分型终章之 L—system
恶心人的众多考试终于完了,我也有时间整理一下前面所做的东西,今天借着L—system对分型做一个总结。
L-System是什么:
一定要下一个定义的话,我做不到,因为不学语文好多年了,其实也没什么意义,我的理解就是,给定一个字符串,根据特定的规则,进行取点,画线,旋转,最终实现一个分型的图形。
L-System需要什么:
根据我个人的理解,一个L-System,有2个要素:
(1)母串和子串:给定一个母串,用递归的方法,将母串中的字符替换成子串,最终形成一
个字符串。
(2)方向:图形需要旋转,旋转需要方向,在这里可以定义两个方向,+:表示顺时针旋转
的方向,-:表示逆时针旋转的方向。
L-System的流程:
(1)根据给定的母串和子串,用递归的方法,得到最终的字符串——F:向前走一个单位,
+:顺时针旋转一个度数;-:逆时针旋转一个度数;
(2)设定一个初始坐标和初始方向,根据最终的字符串,得到所有点的坐标,保存起来
(3)根据坐标画线,得到最终的图形
L-System的难点:
如何把图形在正中显示
我一共写了四个类,具体代码如下:
第一个类:DrawBoard,显示图形的面板,上面有一些输入框
第二个类:Word类,由母串得到子串
第三个类:GetPoint类,这个类根据字符串得到所有的坐标点,并且将其存放起来
第四个类:Listener,该类的作用是将三个类整合,从Word类得到一个字符串,将字符串传入GetPoint类,得到所有点的坐标,最终画出图形
最终效果:
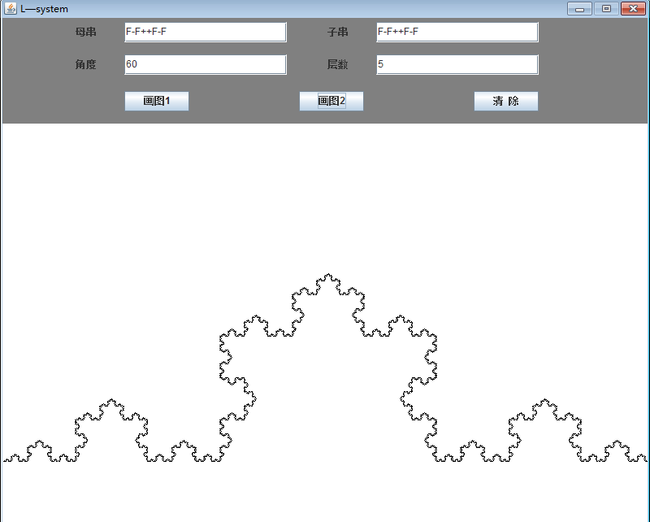

L-System是什么:
一定要下一个定义的话,我做不到,因为不学语文好多年了,其实也没什么意义,我的理解就是,给定一个字符串,根据特定的规则,进行取点,画线,旋转,最终实现一个分型的图形。
L-System需要什么:
根据我个人的理解,一个L-System,有2个要素:
(1)母串和子串:给定一个母串,用递归的方法,将母串中的字符替换成子串,最终形成一
个字符串。
(2)方向:图形需要旋转,旋转需要方向,在这里可以定义两个方向,+:表示顺时针旋转
的方向,-:表示逆时针旋转的方向。
L-System的流程:
(1)根据给定的母串和子串,用递归的方法,得到最终的字符串——F:向前走一个单位,
+:顺时针旋转一个度数;-:逆时针旋转一个度数;
(2)设定一个初始坐标和初始方向,根据最终的字符串,得到所有点的坐标,保存起来
(3)根据坐标画线,得到最终的图形
L-System的难点:
如何把图形在正中显示
我一共写了四个类,具体代码如下:
第一个类:DrawBoard,显示图形的面板,上面有一些输入框
package source;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JLabel;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
public class DrawBoard extends JFrame{
Graphics g;
public static void main(String [] args){
DrawBoard db = new DrawBoard();
db.createBoard();
}
/**
* 创建窗体
*/
public void createBoard(){
//设置窗体的基本属性
this.setTitle("L—system");
this.setSize(800,800);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(3);
this.setResizable(false);
this.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
this.setLayout(new BorderLayout());//设置窗体的布局管理器为边框布局管理器
//控制面板
JPanel jp1 = new JPanel();
jp1.setLayout(null);
jp1.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(10,130));
jp1.setBackground(Color.GRAY);
this.add(jp1,BorderLayout.NORTH);
//画板
JPanel jp2 = new JPanel();
jp2.setPreferredSize(new Dimension());
jp2.setBackground(Color.WHITE);
this.add(jp2);
//控件
JLabel jl1 = new JLabel("母串");
JLabel jl2 = new JLabel("子串");
JLabel jl3 = new JLabel("角度");
JLabel jl4 = new JLabel("层数");
jl1.setBounds(90,5,150,25);
jl2.setBounds(400,5,150,25);
jl3.setBounds(90,45,150,25);
jl4.setBounds(400,45,150,25);
JTextField jtf1 = new JTextField(10);
JTextField jtf2 = new JTextField(10);
JTextField jtf3 = new JTextField(10);
JTextField jtf4 = new JTextField(10);
JButton jb1 = new JButton("画图1");
JButton jb2 = new JButton("画图2");
JButton jb3 = new JButton("清 除");
jp1.add(jl1);
jp1.add(jtf1);
jtf1.setBounds(150,5,200,25);
jp1.add(jl2);
jp1.add(jtf2);
jtf2.setBounds(460,5,200,25);
jp1.add(jl3);
jp1.add(jtf3);
jtf3.setBounds(150,45,200,25);
jp1.add(jl4);
jp1.add(jtf4);
jtf4.setBounds(460,45,200,25);
jp1.add(jb1);
jb1.setBounds(150,90,80,25);
jp1.add(jb2);
jb2.setBounds(365,90,80,25);
jp1.add(jb3);
jb3.setBounds(580,90,80,25);
this.setVisible(true);
//得到画布
g=jp2.getGraphics();
//加监听器
Listener lis = new Listener(g,jtf1,jtf2,jtf3,jtf4);
jb1.addActionListener(lis);
jb2.addActionListener(lis);
jb3.addActionListener(lis);
}
}
第二个类:Word类,由母串得到子串
package source;
/**
* 根据母串得到子串
* @author 朱正直
*
*/
public class Word {
private String parent;//定义母串
private String child;//定义子串
//在创建对象时传入母串和子串
public Word(String parent,String child){
this.parent=parent;
this.child=child;
}
//根据母串和子串生成最终字符串
public String createWord(int depth){
if (depth == 0 ) return parent;
String sequence = parent;
for(int i=0;i<depth;i++){
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer();//用StringBuffer类存储字符串,这个类是一个可变长度的字符串类,最后在调用这个类的toString方法,转化成String类
for(int j=0;j<sequence.length();j++){
if(sequence.charAt(j)=='F') str.append(child);
else str.append(sequence.charAt(j));
}
sequence=str.toString();
}
return sequence;
}
}
第三个类:GetPoint类,这个类根据字符串得到所有的坐标点,并且将其存放起来
package source;
import java.awt.Point;
/**
* 得到所有点的坐标
* @author 朱正直
*
*/
public class GetPoint {
private String sequence;
private double ra;
private double rb;
public GetPoint(String str,int a,int b){
this.sequence=str;
ra=a*Math.PI/180;
rb=b*Math.PI/180;
}
public Point[] getPt(int W,int H){
double len = 10.0;//定义初始步长(两点之间线的长度)
double x0=1.0,y0=0;//定义初始方向
double x1=0,y1=0;//定义初始点的坐标
double min_x,max_x,min_y,max_y;
min_x=max_x=x1;
min_y=max_y=y1;
for(int i=0;i<sequence.length();i++){
if(sequence.charAt(i)=='F'){
double _x1=x1+len*x0;
double _y1=y1+len*y0;
x1=_x1;
y1=_y1;
if(x1<min_x) min_x=x1;
if(x1>max_x) max_x=x1;
if(y1<min_y) min_y=y1;
if(y1>max_y) max_y=y1;
}
else if(sequence.charAt(i)=='+'){
double _x0=x0*Math.cos(ra)-y0*Math.sin(ra);
double _y0=x0*Math.sin(ra)+y0*Math.cos(ra);
x0=_x0;
y0=_y0;
}
else if(sequence.charAt(i)=='-'){
double _x0=x0*Math.cos(-rb)-y0*Math.sin(-rb);
double _y0=x0*Math.sin(-rb)+y0*Math.cos(-rb);
x0=_x0;
y0=_y0;
}
}
/**
* 接下来调整初始位置和步长
*/
double r=Math.min(W/(max_x-min_x),H/(max_y-min_y));
len*=r;
double mid_x=(min_x+max_x)*0.5,mid_y=(min_y+max_y)*0.5;
x1=W*0.5-mid_x*r;
y1=H*0.5-mid_y*r;
x0=1.0;
y0=0;
int n=1;
for(int i=0;i<sequence.length();i++)
if(sequence.charAt(i)=='F') ++n;
Point [] points = new Point[n];
points[0]= new Point((int)x1,(int)y1);
int index=1;
for(int i=0;i<sequence.length();i++){
if(sequence.charAt(i)=='F'){
double _x1=x1+len*x0;
double _y1=y1+len*y0;
x1=_x1;
y1=_y1;
points[index++]=new Point((int)x1,(int)y1);
}else if(sequence.charAt(i)=='+'){
double _x0=x0*Math.cos(ra)-y0*Math.sin(ra);
double _y0=x0*Math.sin(ra)+y0*Math.cos(ra);
x0=_x0;
y0=_y0;
}else if(sequence.charAt(i)=='-'){
double _x0=x0*Math.cos(-rb)-y0*Math.sin(-rb);
double _y0=x0*Math.sin(-rb)+y0*Math.cos(-rb);
x0=_x0;
y0=_y0;
}
}
return points;
}
}
第四个类:Listener,该类的作用是将三个类整合,从Word类得到一个字符串,将字符串传入GetPoint类,得到所有点的坐标,最终画出图形
package source;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Point;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
public class Listener implements ActionListener{
Graphics g;
JTextField jtf1;
JTextField jtf2;
JTextField jtf3;
JTextField jtf4;
public Listener(Graphics g1,JTextField jtf11,JTextField jtf21,JTextField jtf31,JTextField jtf41){
g=g1;
jtf1=jtf11;
jtf2=jtf21;
jtf3=jtf31;
jtf4=jtf41;
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String str = e.getActionCommand();
if(str.equals("画图1")){
draw1(g);
}
if(str.equals("画图2")){
draw2(g);
}
if(str.equals("清 除")){
// g.clearRect(0,155,800,600);
g.clearRect(0,0,800,800);
}
}
/*
* 将所有存入的点连起来
*/
public void draw1(Graphics g){
String s1=jtf1.getText();
String s2=jtf2.getText();
int s3=Integer.parseInt(jtf3.getText());
int s4=Integer.parseInt(jtf4.getText());
Word wd = new Word(s1,s2);
String sequence=wd.createWord(s4);
GetPoint gp = new GetPoint(sequence,s3,s3);
Point [] point = gp.getPt(800,600);
for(int i=0;i<point.length-1;i++){
g.drawLine((int)point[i].getX(),(int)point[i].getY(),(int)point[i+1].getX(),(int)point[i+1].getY());
}
}
public void draw2(Graphics g){
String s1=jtf1.getText();
String s2=jtf2.getText();
int s3=Integer.parseInt(jtf3.getText());
int s4=Integer.parseInt(jtf4.getText());
Word wd = new Word(s1,s2);
String sequence=wd.createWord(s4);
GetPoint gp = new GetPoint(sequence,s3,s3);
Point [] point = gp.getPt(800,600);
for(int i=0;i<point.length-1;i++){
double xa = point[i].getX();
double ya = point[i].getY();
double xb = point[i+1].getX();
double yb = point[i+1].getY();
xa=800-xa;
xb=800-xb;
g.drawLine((int)xa,(int)ya,(int)xb,(int)yb);
}
}
}
最终效果:

