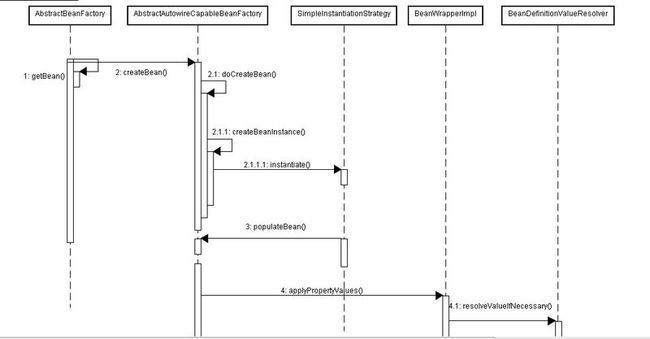
实例化bean和依赖注入是在AbstractBeanFactory的入口,但是实际还是在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory这个类中实现。bean实例化的时候有两种基本的方式,就是一用默认构造函数,一是在xml配置自己的可带参数的构造函数,这两种方式在spring中实例的流程是不一样的,对应的BeanDefinition的数据也是不同。所以这里就根据这两种实例化的方式来讲解这个至关重要的AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactor类。
- 默认构造函数实例化的方式
这里首先画出实例化的时序图:如下
- doCreateBean方法:通过上面的图可以看出在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的入口实例化bean是createBean方法。但是createBean方法其实并没有做些什么,唯一的工作判断是否可以实例化。重点还是在另外一个方法中。就是doCreateBean方法:我把这个方法细分为两大部分:一实例化bean,二属性依赖注入。可见下面标红的地方。
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
// Instantiate the bean.
if("org.springframework.aop.aspectj.AspectJPointcutAdvisor#0".equals(beanName)){
System.out.println(beanName);
}
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//这里为实例化bean的地方,还是调用本类的createBeanInstance方法
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
Class beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory() {
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//这里是设置bean的属性,也就是注入的发生
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
//这里也是一个重点,主要是调用BeanPostProcessor,在实例化前,同时AOP的实现也是跟这里有着莫大的关联。详细见下面的分析
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
}
// Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
}
return exposedObject;
}
- createBeanInstance方法:这里的createBeanInstance是实例化bean的地方。其中从时序图中看到会调用到 SimpleInstantiationStrategy类来实例化。而SimpleInstantiationStrategy这个是通过工厂方法得到的。其实本身通过工厂得到的是CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy,但是这个类继承了SimpleInstantiationStrategy。在SimpleInstantiationStrategy类中instantiate如下:其实就是通过BeanDefinition得到class,然后得到默认的构造函数,最后实例化。
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
if (mbd.getFactoryMethodName() != null) {
return instantiateUsingFactoryMethod(beanName, mbd, args);
}
// Shortcut when re-creating the same bean...
boolean resolved = false;
boolean autowireNecessary = false;
if (args == null) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
if (mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod != null) {
resolved = true;
autowireNecessary = mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved;
}
}
}
if (resolved) {
if (autowireNecessary) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, null, null);
}
else {
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
}
// Need to determine the constructor...
Constructor[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
//如果BeanDefinition中有constructorArgumentValues属性,则是调用相应的构造函数,而不是默认的构造函数。这里会在其他的地方详细解释
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
//调用本类的instantiateBean方法,其实就是用默认的无参数构造方法实例化bean
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
final BeanFactory parent = this;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
public Object run() {
//这里使用工厂方法得到实例化的策略,默认为CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy,并会调用到其父类SimpleInstantiationStrategy的instantiate方法,通过BeanDefinition得到class然后获得默认的无参构造方法实例化bean
//当然在SimpleInstantiationStrategy也可以使用CGLIB来实例化,有兴趣的可以自己查看
return getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, parent);
}
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
- populateBean方法:这个方法就是设置bean属性的,也就是依赖注入的过程。这个过程是相对比较复杂的。要知道spring最得人心的其中之一特性,肯定是不会那么简单的了。
protected void populateBean(String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
//通过BeanDefinition得到PropertyValues,PropertyValues是什么意思见另外一批解释
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
if (bw == null) {
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
//先判断BeanDefinition是否为合成的,用户配置xml的都是false。而这里是否有有初始化意识的BeanPostProcessor,其中AOP中AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator就是一个
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
//这里开始依赖注入,如果xml中设置了autowire为byName或者byType的话会调用下面的,如果没有设置为默认的则都不会调用,一般情况下不会这是自动装配,虽然很方便
//但是维护起来还是比较麻烦,再则没有使用一看xml配置文件就能够很方便
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
- autowireByName方法:按name自动装配。可以看到依赖注入的时候会检测配置的自动装入,如果发现不是默认的,而是byName或者byType的时候就会自动的装入了。这里的byName还是比较的简单,通过javabean的内省Introspector得到所有的PropertyDescriptor,然后通过PropertyDescriptor得到propertyName。这里的在CachedIntrospectionResults类中。读者如果有兴趣可自行查询。
protected void autowireByName(
String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
//得到BeanDefinition的所有propertyNames,这里得到propertyNames是通过javabean得到的的,有兴趣的可以自己查询
String[] propertyNames = unsatisfiedNonSimpleProperties(mbd, bw);
for (String propertyName : propertyNames) {
if (containsBean(propertyName)) {
Object bean = getBean(propertyName);
//通过propertyName向容器中拿到bean,然后添加到BeanDefinition的MutablePropertyValues中
pvs.add(propertyName, bean);
registerDependentBean(propertyName, beanName);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Added autowiring by name from bean name '" + beanName +
"' via property '" + propertyName + "' to bean named '" + propertyName + "'");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Not autowiring property '" + propertyName + "' of bean '" + beanName +
"' by name: no matching bean found");
}
}
}
}
- autowireByType方法:按类型自动装配。 如果自动装配是byType的话,就比较的麻烦。并且如果配置文件中有多个你设置的class怎么办呢?spring就会报错了。看源代码应该是有避免报错的方法。这里就先不说了。在resolveDependency方法的调用中会最后会调用到DefaultListableBeanFactory中的getBeanNamesForType,通过名称就可以看出意思就是通过class得到一批beannames。如果刚好只有一个,然后有是通过调用getBean来得到bean然后注入的。
protected void autowireByType(
String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
if (converter == null) {
converter = bw;
}
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<String>(4);
String[] propertyNames = unsatisfiedNonSimpleProperties(mbd, bw);
for (String propertyName : propertyNames) {
try {
PropertyDescriptor pd = bw.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName);
// Don't try autowiring by type for type Object: never makes sense,
// even if it technically is a unsatisfied, non-simple property.
if (!Object.class.equals(pd.getPropertyType())) {
MethodParameter methodParam = BeanUtils.getWriteMethodParameter(pd);
// Do not allow eager init for type matching in case of a prioritized post-processor.
boolean eager = !PriorityOrdered.class.isAssignableFrom(bw.getWrappedClass());
DependencyDescriptor desc = new AutowireByTypeDependencyDescriptor(methodParam, eager);
Object autowiredArgument = resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, converter);
if (autowiredArgument != null) {
pvs.add(propertyName, autowiredArgument);
}
for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {
registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, beanName);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Autowiring by type from bean name '" + beanName + "' via property '" +
propertyName + "' to bean named '" + autowiredBeanName + "'");
}
}
autowiredBeanNames.clear();
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, propertyName, ex);
}
}
}
- applyPropertyValues:这里做的大部分工作就是依赖的准备工作。其中上面还只是讲了像BeanDefinition中的MutablePropertyValues添加属性,并且解析xml的时候也会忘BeanDefinition注入属性,但是这里的属性是需要转换的。因为即使你在xml中配置为<property name="addStmt" value="2" />,它对应的是TypedStringValue,如果配置的是list,实际的类型为ManagedList。而如果是<property name="book" ref="book" />的话则为RuntimeBeanNameReference,等等其他的类型也是要转换的,即使依赖注入的时候像上面属性添加的实际是Object类型了是最终的类型了,也要通过resolveValueIfNecessary转换一下。而在这个方法中如果是Object就原样返回。
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, BeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, PropertyValues pvs) { if (pvs == null || pvs.isEmpty()) { return; } MutablePropertyValues mpvs = null; List<PropertyValue> original; if (System.getSecurityManager()!= null) { if (bw instanceof BeanWrapperImpl) { ((BeanWrapperImpl) bw).setSecurityContext(getAccessControlContext()); } } if (pvs instanceof MutablePropertyValues) { mpvs = (MutablePropertyValues) pvs; if (mpvs.isConverted()) { // Shortcut: use the pre-converted values as-is. try { bw.setPropertyValues(mpvs); return; } catch (BeansException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex); } } original = mpvs.getPropertyValueList(); } else { original = Arrays.asList(pvs.getPropertyValues()); } TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter(); if (converter == null) { converter = bw; } BeanDefinitionValueResolver valueResolver = new BeanDefinitionValueResolver(this, beanName, mbd, converter); // Create a deep copy, resolving any references for values. List<PropertyValue> deepCopy = new ArrayList<PropertyValue>(original.size()); boolean resolveNecessary = false; for (PropertyValue pv : original) { if (pv.isConverted()) { deepCopy.add(pv); } else { String propertyName = pv.getName(); Object originalValue = pv.getValue(); //这里通过valueResolver得到值,因为spring中如果配置的是string,知己PropertyValue中的值为TypedStringValue的类型,如果配置的是list,实际的类型为ManagedList。所以还需转换一下。这里的流程也就到了时序图中的4.1 Object resolvedValue = valueResolver.resolveValueIfNecessary(pv, originalValue); Object convertedValue = resolvedValue; boolean convertible = bw.isWritableProperty(propertyName) && !PropertyAccessorUtils.isNestedOrIndexedProperty(propertyName); if (convertible) { convertedValue = convertForProperty(resolvedValue, propertyName, bw, converter); } // Possibly store converted value in merged bean definition, // in order to avoid re-conversion for every created bean instance. if (resolvedValue == originalValue) { if (convertible) { pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue); } deepCopy.add(pv); } else if (convertible && originalValue instanceof TypedStringValue && !((TypedStringValue) originalValue).isDynamic() && !(convertedValue instanceof Collection || ObjectUtils.isArray(convertedValue))) { pv.setConvertedValue(convertedValue); deepCopy.add(pv); } else { resolveNecessary = true; deepCopy.add(new PropertyValue(pv, convertedValue)); } } } if (mpvs != null && !resolveNecessary) { mpvs.setConverted(); } // Set our (possibly massaged) deep copy. try { bw.setPropertyValues(new MutablePropertyValues(deepCopy)); } catch (BeansException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Error setting property values", ex); } }
- resolveValueIfNecessary方法:在时序图4.1中。这个方法在BeanDefinitionValueResolver类中,它的工作就是转换。转换为实际的类型。通过这里之后所有的依赖准备工作都准备好了。
public Object resolveValueIfNecessary(Object argName, Object value) {
// We must check each value to see whether it requires a runtime reference
// to another bean to be resolved.
if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanReference) {
RuntimeBeanReference ref = (RuntimeBeanReference) value;
return resolveReference(argName, ref);
}
else if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanNameReference) {
String refName = ((RuntimeBeanNameReference) value).getBeanName();
refName = String.valueOf(evaluate(refName));
if (!this.beanFactory.containsBean(refName)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Invalid bean name '" + refName + "' in bean reference for " + argName);
}
return refName;
}
else if (value instanceof BeanDefinitionHolder) {
// Resolve BeanDefinitionHolder: contains BeanDefinition with name and aliases.
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = (BeanDefinitionHolder) value;
return resolveInnerBean(argName, bdHolder.getBeanName(), bdHolder.getBeanDefinition());
}
else if (value instanceof BeanDefinition) {
// Resolve plain BeanDefinition, without contained name: use dummy name.
BeanDefinition bd = (BeanDefinition) value;
return resolveInnerBean(argName, "(inner bean)", bd);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedArray) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
ManagedArray array = (ManagedArray) value;
Class elementType = array.resolvedElementType;
if (elementType == null) {
String elementTypeName = array.getElementTypeName();
if (StringUtils.hasText(elementTypeName)) {
try {
elementType = ClassUtils.forName(elementTypeName, this.beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader());
array.resolvedElementType = elementType;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Improve the message by showing the context.
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Error resolving array type for " + argName, ex);
}
}
else {
elementType = Object.class;
}
}
return resolveManagedArray(argName, (List<?>) value, elementType);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedList) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
return resolveManagedList(argName, (List<?>) value);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedSet) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
return resolveManagedSet(argName, (Set<?>) value);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedMap) {
// May need to resolve contained runtime references.
return resolveManagedMap(argName, (Map<?, ?>) value);
}
else if (value instanceof ManagedProperties) {
Properties original = (Properties) value;
Properties copy = new Properties();
for (Map.Entry propEntry : original.entrySet()) {
Object propKey = propEntry.getKey();
Object propValue = propEntry.getValue();
if (propKey instanceof TypedStringValue) {
propKey = evaluate((TypedStringValue) propKey);
}
if (propValue instanceof TypedStringValue) {
propValue = evaluate((TypedStringValue) propValue);
}
copy.put(propKey, propValue);
}
return copy;
}
else if (value instanceof TypedStringValue) {
// Convert value to target type here.
TypedStringValue typedStringValue = (TypedStringValue) value;
Object valueObject = evaluate(typedStringValue);
try {
Class<?> resolvedTargetType = resolveTargetType(typedStringValue);
if (resolvedTargetType != null) {
return this.typeConverter.convertIfNecessary(valueObject, resolvedTargetType);
}
else {
return valueObject;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Improve the message by showing the context.
throw new BeanCreationException(
this.beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), this.beanName,
"Error converting typed String value for " + argName, ex);
}
}
else {
return evaluate(value);
}
}
/**
* Evaluate the given value as an expression, if necessary.
* @param value the candidate value (may be an expression)
* @return the resolved value
*/
protected Object evaluate(TypedStringValue value) {
Object result = this.beanFactory.evaluateBeanDefinitionString(value.getValue(), this.beanDefinition);
if (result != value.getValue()) {
value.setDynamic();
}
return result;
}
- setPropertyValue:这里为BeanWrapperImpl中的方法。也是上面applyPropertyValues会调用的。这里就是依赖注入实现的地方。这里还是通过javabean的机制,通过PropertyDescriptor得到属性的writeMethod,也就是你类中的set方法。然后通过反正注入。
private void setPropertyValue(PropertyTokenHolder tokens, PropertyValue pv) throws BeansException {
String propertyName = tokens.canonicalName;
String actualName = tokens.actualName;
if (tokens.keys != null) {
// Apply indexes and map keys: fetch value for all keys but the last one.
PropertyTokenHolder getterTokens = new PropertyTokenHolder();
getterTokens.canonicalName = tokens.canonicalName;
getterTokens.actualName = tokens.actualName;
getterTokens.keys = new String[tokens.keys.length - 1];
System.arraycopy(tokens.keys, 0, getterTokens.keys, 0, tokens.keys.length - 1);
Object propValue;
try {
propValue = getPropertyValue(getterTokens);
}
catch (NotReadablePropertyException ex) {
throw new NotWritablePropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName,
"Cannot access indexed value in property referenced " +
"in indexed property path '" + propertyName + "'", ex);
}
// Set value for last key.
String key = tokens.keys[tokens.keys.length - 1];
if (propValue == null) {
throw new NullValueInNestedPathException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName,
"Cannot access indexed value in property referenced " +
"in indexed property path '" + propertyName + "': returned null");
}
else if (propValue.getClass().isArray()) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = getCachedIntrospectionResults().getPropertyDescriptor(actualName);
Class requiredType = propValue.getClass().getComponentType();
int arrayIndex = Integer.parseInt(key);
Object oldValue = null;
try {
if (isExtractOldValueForEditor()) {
oldValue = Array.get(propValue, arrayIndex);
}
Object convertedValue = convertIfNecessary(propertyName, oldValue, pv.getValue(), requiredType,
new PropertyTypeDescriptor(pd, new MethodParameter(pd.getReadMethod(), -1), requiredType));
Array.set(propValue, arrayIndex, convertedValue);
}
catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new InvalidPropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName,
"Invalid array index in property path '" + propertyName + "'", ex);
}
}
else if (propValue instanceof List) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = getCachedIntrospectionResults().getPropertyDescriptor(actualName);
Class requiredType = GenericCollectionTypeResolver.getCollectionReturnType(
pd.getReadMethod(), tokens.keys.length);
List list = (List) propValue;
int index = Integer.parseInt(key);
Object oldValue = null;
if (isExtractOldValueForEditor() && index < list.size()) {
oldValue = list.get(index);
}
Object convertedValue = convertIfNecessary(propertyName, oldValue, pv.getValue(), requiredType,
new PropertyTypeDescriptor(pd, new MethodParameter(pd.getReadMethod(), -1), requiredType));
if (index < list.size()) {
list.set(index, convertedValue);
}
else if (index >= list.size()) {
for (int i = list.size(); i < index; i++) {
try {
list.add(null);
}
catch (NullPointerException ex) {
throw new InvalidPropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName,
"Cannot set element with index " + index + " in List of size " +
list.size() + ", accessed using property path '" + propertyName +
"': List does not support filling up gaps with null elements");
}
}
list.add(convertedValue);
}
}
else if (propValue instanceof Map) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = getCachedIntrospectionResults().getPropertyDescriptor(actualName);
Class mapKeyType = GenericCollectionTypeResolver.getMapKeyReturnType(
pd.getReadMethod(), tokens.keys.length);
Class mapValueType = GenericCollectionTypeResolver.getMapValueReturnType(
pd.getReadMethod(), tokens.keys.length);
Map map = (Map) propValue;
// IMPORTANT: Do not pass full property name in here - property editors
// must not kick in for map keys but rather only for map values.
Object convertedMapKey = convertIfNecessary(null, null, key, mapKeyType,
new PropertyTypeDescriptor(pd, new MethodParameter(pd.getReadMethod(), -1), mapKeyType));
Object oldValue = null;
if (isExtractOldValueForEditor()) {
oldValue = map.get(convertedMapKey);
}
// Pass full property name and old value in here, since we want full
// conversion ability for map values.
Object convertedMapValue = convertIfNecessary(
propertyName, oldValue, pv.getValue(), mapValueType,
new TypeDescriptor(new MethodParameter(pd.getReadMethod(), -1, tokens.keys.length + 1)));
map.put(convertedMapKey, convertedMapValue);
}
else {
throw new InvalidPropertyException(getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName,
"Property referenced in indexed property path '" + propertyName +
"' is neither an array nor a List nor a Map; returned value was [" + pv.getValue() + "]");
}
}
else {
if("addStmt".equals(pv.getName())){
System.out.println("test setPropertyValues");
}
PropertyDescriptor pd = pv.resolvedDescriptor;
if (pd == null || !pd.getWriteMethod().getDeclaringClass().isInstance(this.object)) {
pd = getCachedIntrospectionResults().getPropertyDescriptor(actualName);
if (pd == null || pd.getWriteMethod() == null) {
if (pv.isOptional()) {
logger.debug("Ignoring optional value for property '" + actualName +
"' - property not found on bean class [" + getRootClass().getName() + "]");
return;
}
else {
PropertyMatches matches = PropertyMatches.forProperty(propertyName, getRootClass());
throw new NotWritablePropertyException(
getRootClass(), this.nestedPath + propertyName,
matches.buildErrorMessage(), matches.getPossibleMatches());
}
}
pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().resolvedDescriptor = pd;
}
Object oldValue = null;
try {
Object originalValue = pv.getValue();
Object valueToApply = originalValue;
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(pv.conversionNecessary)) {
if (pv.isConverted()) {
valueToApply = pv.getConvertedValue();
}
else {
if (isExtractOldValueForEditor() && pd.getReadMethod() != null) {
final Method readMethod = pd.getReadMethod();
if (!Modifier.isPublic(readMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers()) &&
!readMethod.isAccessible()) {
if (System.getSecurityManager()!= null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
public Object run() {
readMethod.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
else {
readMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
oldValue = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
public Object run() throws Exception {
return readMethod.invoke(object);
}
}, acc);
}
else {
oldValue = readMethod.invoke(object);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (ex instanceof PrivilegedActionException) {
ex = ((PrivilegedActionException) ex).getException();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not read previous value of property '" +
this.nestedPath + propertyName + "'", ex);
}
}
}
valueToApply = convertForProperty(propertyName, oldValue, originalValue, pd);
}
pv.getOriginalPropertyValue().conversionNecessary = (valueToApply != originalValue);
}
final Method writeMethod = (pd instanceof GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor ?
((GenericTypeAwarePropertyDescriptor) pd).getWriteMethodForActualAccess() :
pd.getWriteMethod());
if (!Modifier.isPublic(writeMethod.getDeclaringClass().getModifiers()) && !writeMethod.isAccessible()) {
if (System.getSecurityManager()!= null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
public Object run() {
writeMethod.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
else {
writeMethod.setAccessible(true);
}
}
final Object value = valueToApply;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
public Object run() throws Exception {
writeMethod.invoke(object, value);
return null;
}
}, acc);
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException ex) {
throw ex.getException();
}
}
else {
writeMethod.invoke(this.object, value);
}
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
PropertyChangeEvent propertyChangeEvent =
new PropertyChangeEvent(this.rootObject, this.nestedPath + propertyName, oldValue, pv.getValue());
if (ex.getTargetException() instanceof ClassCastException) {
throw new TypeMismatchException(propertyChangeEvent, pd.getPropertyType(), ex.getTargetException());
}
else {
throw new MethodInvocationException(propertyChangeEvent, ex.getTargetException());
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
PropertyChangeEvent pce =
new PropertyChangeEvent(this.rootObject, this.nestedPath + propertyName, oldValue, pv.getValue());
throw new MethodInvocationException(pce, ex);
}
}
}