HBase的coprocessor分拆HRegion
引用
转载请注明出处,文章链接:http://blackwing.iteye.com/blog/1788647
之前通过修改TableInputFormatBase类实现了客户端分拆每个HRegion,从而实现一个region可以同时被多个map同时读取,原文:
http://blackwing.iteye.com/admin/blogs/1763961
但以上方法是把数据取回客户端进行,速度慢,现在改用coprocessor的endpoint方式,直接在server端计算好InputSplit后返回给客户端。
Hbase的coprocessor详解请参考:
https://blogs.apache.org/hbase/entry/coprocessor_introduction
coprocessor的开发还是很直观、简单的。
1.继承SplitRowProtocol
public interface SplitRowProtocol extends CoprocessorProtocol {
public List<InputSplit> getSplitRow(byte [] splitStart, byte [] splitEnd, byte [] tableName,String regionLocation, int mappersPerSplit) throws IOException;
}
把自己需要的函数、参数定义好。
2.实现刚才继承的接口、继承BaseEndpointCoprocessor
public class SplitRowEndPoint extends BaseEndpointCoprocessor implements
SplitRowProtocol {
@Override
public List<InputSplit> getSplitRow(byte[] splitStart, byte[] splitEnd,
byte[] tableName,String regionLocation,int mappersPerSplit) throws IOException {
RegionCoprocessorEnvironment environment = (RegionCoprocessorEnvironment) getEnvironment();
List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>();
HRegion region = environment.getRegion();
byte[] splitRow = region.checkSplit();
if (null != splitRow)
return splits;
try {
HTableInterface table = environment.getTable(tableName);
Scan scan = new Scan();
scan.setFilter(new FirstKeyOnlyFilter());
scan.setStartRow(splitStart);
scan.setStopRow(splitEnd);
scan.setBatch(300);
/*String regionLocation = table.getRegionLocation(splitStart,true)
.getHostname();*/
InternalScanner scanner = region.getScanner(scan);
List<String> rows = new ArrayList<String>();
try {
List<KeyValue> curVals = new ArrayList<KeyValue>();
boolean hasMore = false;
do {
curVals.clear();
hasMore = scanner.next(curVals);
KeyValue kv = curVals.get(0);
rows.add(Bytes.toString(curVals.get(0).getRow()));
} while (hasMore);
} finally {
scanner.close();
}
int splitSize = rows.size() / mappersPerSplit;
for (int j = 0; j < mappersPerSplit; j++) {
TableSplit tablesplit = null;
if (j == mappersPerSplit - 1)
tablesplit = new TableSplit(table.getTableName(), rows.get(
j * splitSize).getBytes(), rows
.get(rows.size() - 1).getBytes(), regionLocation);
else
tablesplit = new TableSplit(table.getTableName(), rows.get(
j * splitSize).getBytes(), rows.get(
j * splitSize + splitSize - 1).getBytes(),
regionLocation);
splits.add(tablesplit);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return splits;
}
}
3.为需要使用到该coprocessor的表加载coprocessor
加载coprocessor有3种方式
1)一种是通过配置文件,在hbase-site.xml中配置:
<property>
<name>hbase.coprocessor.region.classes</name>
<value>com.blackwing.util.hbase.coprocessor.SplitRowEndPoint</value>
</property>
这种方法缺点是,需要重启hbase。
2)通过hbase shell设置coprocessor
主要通过alter和table_att实现coprocessor的设置,之前需要disable表才能进行操作:
alter 'user_video_pref_t2',METHOD=>'table_att','coprocessor'=>'hdfs://myhadoop:8020/user/hadoop/coprocessor.jar|com.blackwing.util.hbase.coprocessor.SplitRowEndPoint|1073741823'
跟着enable表,再describe这个表,就能看到已经为该表添加了coprocessor。
3)java动态加载
动态加载,是通过java程序,实现某表的coprocessor设置,优点当然是无需重启hbase。
HBaseAdmin admin;
String[] truncatedTableInfo;
HTableDescriptor desc;
truncatedTableInfo = conf.getStrings("user_video_pref");
conf.addResource(propertyFileName);
try {
admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf);
desc = new HTableDescriptor(truncatedTableInfo[0]);
desc.setValue("VERSIONS", "1");
HColumnDescriptor coldef = new HColumnDescriptor(truncatedTableInfo[1]);
desc.addFamily(coldef);
int priority = 0;
if(conf.get("coprocessor.pref.priority").equals("USER"))
priority = Coprocessor.PRIORITY_USER;
else
priority = Coprocessor.PRIORITY_SYSTEM;
//2013-2-2 增加coprocessor
desc.setValue("COPROCESSOR$1", conf.get("coprocessor.pref.path")+"|"
+conf.get("coprocessor.pref.class")+
"|"+priority);
try {
if(admin.isTableAvailable(truncatedTableInfo[0]))
{
//清表
admin.disableTable(truncatedTableInfo[0]);
admin.deleteTable(truncatedTableInfo[0]);
if(admin.isTableAvailable(truncatedTableInfo[0]))
LOG.info("truncate table : user_video_pref fail !");
//建表
admin.createTable(desc);
}
if(admin.isTableAvailable(truncatedTableInfo[0]))
LOG.info("create table : user_video_pref done !");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} catch (MasterNotRunningException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ZooKeeperConnectionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
以上3种方法只是把coprocessor增加到某表,但因为hbase不会检查路径上的jar是否存在,类是否正确,所以要最终确认coprocessor是否真正添加成功,需要:
1)在hbase shell下,输入status 'detailed',看看对应表的属性中是否有:coprocessors=[SplitRowEndPoint]
或者:
2)在hbase的60010 web界面中,找到刚增加了coprocessor的表,点击进去其region server,查看该表的“Metrics”列,是否有:coprocessors=[SplitRowEndPoint]
如果有该属性,说明coprocessor已经添加成功,这样就能进行客户端的远程调用了。
客户端调用coprocessor也有两种方式,如下:
public <T extends CoprocessorProtocol> T coprocessorProxy(Class<T> protocol, Row row);
public <T extends CoprocessorProtocol, R> void coprocessorExec(
Class<T> protocol, List<? extends Row> rows,
BatchCall<T,R> callable, BatchCallback<R> callback);
public <T extends CoprocessorProtocol, R> voidcoprocessorExec(
Class<T> protocol, RowRange range,
BatchCall<T,R> callable, BatchCallback<R> callback);
一是使用coprocessorProxy方法,二是使用voidcoprocessorExec方法。二者的区别是
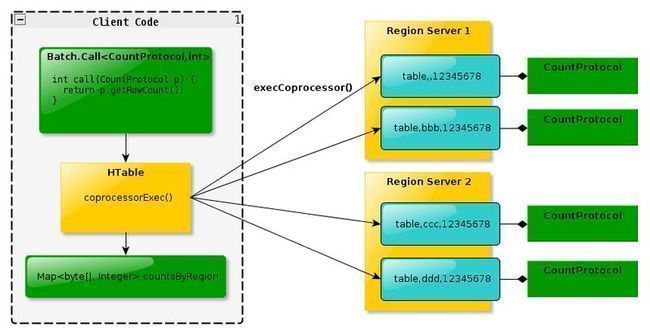
就是Exec方法是并行的,效率更高。
具体调用代码如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
conf.addResource("FilePath.xml");
String tableName="user_video_pref_t2";
try {
HTable table = new HTable(conf,tableName.getBytes());
Pair<byte[][], byte[][]> keys = table.getStartEndKeys();
for (int i = 0; i < keys.getFirst().length; i++) {
String regionLocation = table.getRegionLocation(keys.getFirst()[i],
true).getHostname();
Batch.Call call = Batch.forMethod(SplitRowProtocol.class,
"getSplitRow", f.getBytes(), e.getBytes(), tableName.getBytes(),regionLocation,1);
Map<byte[], List<InputSplit>> results = table
.coprocessorExec(SplitRowProtocol.class,
f.getBytes(), e.getBytes(), call);
// 2013-2-4 取得返回的所有InputSplit
for (List<InputSplit> list : results.values())
{
System.out.println("total input splits : " + list.size());
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
coprocessor的另外一种模式,oberser模式,类似于传统数据库的触发器,针对某个动作进行响应,例如preGet方法,就是在客户端get操作前触发执行,具体略过。