WS-Security
WS-Security provides the means to secure your services beyond transport level protocols such as
HTTPS. Through a number of standards such as XML-Encryption, and headers defined in the WS-Security standard, it allows you to:
-
Pass authentication tokens between services.
-
Encrypt messages or parts of messages.
-
Sign messages.
-
Timestamp messages.
Currently, CXF implements WS-Security by integrating
WSS4J. To use the integration, you'll need to configure these interceptors and add them to your service or client respectively.
10.1. Overview of Encryption and Signing
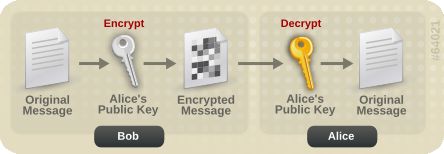
WS-Security makes heavy use of public and private key cryptography. It is helpful to understand these basics to really understand how to configure WS-Security. With public key cryptography, a user has a pair of public and private keys. These are generated using a large prime number and a key function.
The keys are related mathematically, but cannot be derived from one another. With these keys we can encrypt messages. For example, if Bob wants to send a message to Alice, he can encrypt a message using her public key. Alice can then decrypt this message using her private key. Only Alice can decrypt this message as she is the only one with the private key.
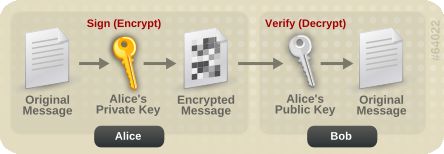
Messages can also be signed. This allows you to ensure the authenticity of the message. If Alice wants to send a message to Bob, and Bob wants to be sure that it is from Alice, Alice can sign the message using her private key. Bob can then verify that the message is from Alice by using her public key.
Chapter 11. WSS4J security on JBoss
Here is a brief chapter on how to use
Chapter 10, WS-Security
on JBossWS-CXF. Here you'll find some explanations on how to create a simple application and what you need to do to leverage WSS4J security on JBoss.
11.1. Creating the web service endpoint
First of all you need to create the web service endpoint or client using JAX-WS. This can be achieved in many ways. For instance you might want to:
-
Write your endpoint implementation, then run the
wsprovideJBoss commandline tool which generates the service contract. -
Run the
wsconsumeJBoss commandline tool to get the client artifacts from the service contract (top-down approach). -
Write your client plementation.
11.2. Turn on WS-Security
WSS4J security is triggered through interceptors that are added to the service and client individually or as required. These interceptors allow you to perform the most common WS-Security related processes:-
Pass authentication tokens between services.
-
Encrypt messages or parts of messages.
-
Sign messages.
-
Timestamp messages.
Interceptors can be added either programmatically or through the Spring xml configuration of endpoints. For instance, on server side, you can configure signature and encryption in thejboss-cxf.xmlfile this way:<beans xmlns='http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans' xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xmlns:beans='http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans' xmlns:jaxws='http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws' xsi:schemaLocation='http://cxf.apache.org/core http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/core.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd'> <bean id="Sign_Request" class="org.apache.cxf.ws.security.wss4j.WSS4JInInterceptor"> <constructor-arg> <map> <entry key="action" value="Timestamp Signature Encrypt"/> <entry key="signaturePropFile" value="bob.properties"/> <entry key="decryptionPropFile" value="bob.properties"/> <entry key="passwordCallbackClass" value="org.jboss.test.ws.jaxws.samples.wsse.KeystorePasswordCallback"/> </map> </constructor-arg> </bean> <bean id="Sign_Response" class="org.apache.cxf.ws.security.wss4j.WSS4JOutInterceptor"> <constructor-arg> <map> <entry key="action" value="Timestamp Signature Encrypt"/> <entry key="user" value="bob"/> <entry key="signaturePropFile" value="bob.properties"/> <entry key="encryptionPropFile" value="bob.properties"/> <entry key="encryptionUser" value="Alice"/> <entry key="signatureKeyIdentifier" value="DirectReference"/> <entry key="passwordCallbackClass" value="org.jboss.test.ws.jaxws.samples.wsse.KeystorePasswordCallback"/> <entry key="signatureParts" value="{Element}{http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecurity-utility-1.0.xsd}Timestamp;{Element}{http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/}Body"/> <entry key="encryptionParts" value="{Element}{http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#}Signature;{Content}{http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/}Body"/> <entry key="encryptionKeyTransportAlgorithm" value="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#rsa-1_5"/> <entry key="encryptionSymAlgorithm" value="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#tripledes-cbc"/> </map> </constructor-arg> </bean> <jaxws:endpoint id='ServiceImpl' address='http://@jboss.bind.address@:8080/jaxws-samples-wsse-sign-encrypt' implementor='org.jboss.test.ws.jaxws.samples.wsse.ServiceImpl'> <jaxws:invoker> <bean class='org.jboss.wsf.stack.cxf.InvokerJSE'/> </jaxws:invoker> <jaxws:outInterceptors> <bean class="org.apache.cxf.binding.soap.saaj.SAAJOutInterceptor"/> <ref bean="Sign_Response"/> </jaxws:outInterceptors> <jaxws:inInterceptors> <ref bean="Sign_Request"/> <bean class="org.apache.cxf.binding.soap.saaj.SAAJInInterceptor"/> </jaxws:inInterceptors> </jaxws:endpoint> </beans>This specifies the whole security configuration (including algorithms and elements to be signed or encrypted); moreover it references a properties file (bob.properties) providing the keystore-related information:org.apache.ws.security.crypto.provider=org.apache.ws.security.components.crypto.Merlin org.apache.ws.security.crypto.merlin.keystore.type=jks org.apache.ws.security.crypto.merlin.keystore.password=password org.apache.ws.security.crypto.merlin.keystore.alias=bob org.apache.ws.security.crypto.merlin.file=bob.jks
As you can see in thejbossws-cxf.xmlfile above, a keystore password callback handler is also configured; while the properties file has the password for the keystore, this callback handler is used to set password for each key (it has to match the one used when each key was imported in the store). Here is an example:package org.jboss.test.ws.jaxws.samples.wsse; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import javax.security.auth.callback.Callback; import javax.security.auth.callback.CallbackHandler; import javax.security.auth.callback.UnsupportedCallbackException; import org.apache.ws.security.WSPasswordCallback; public class KeystorePasswordCallback implements CallbackHandler { private Map<String, String> passwords = new HashMap<String, String>(); public KeystorePasswordCallback() { passwords.put("alice", "password"); passwords.put("bob", "password"); } public void handle(Callback[] callbacks) throws IOException, UnsupportedCallbackException { for (int i = 0; i < callbacks.length; i++) { WSPasswordCallback pc = (WSPasswordCallback)callbacks[i]; String pass = passwords.get(pc.getIdentifer()); if (pass != null) { pc.setPassword(pass); return; } } } public void setAliasPassword(String alias, String password) { passwords.put(alias, password); } }On the client side, you can similarly setup the interceptors programmatically; here is an excerpt of the client for the above described endpoint:Endpoint cxfEndpoint = client.getEndpoint(); Map<String,Object> outProps = new HashMap<String,Object>(); outProps.put("action", "Timestamp Signature Encrypt"); outProps.put("user", "alice"); outProps.put("signaturePropFile", "META-INF/alice.properties"); outProps.put("signatureKeyIdentifier", "DirectReference"); outProps.put("passwordCallbackClass", "org.jboss.test.ws.jaxws.samples.wsse.KeystorePasswordCallback"); outProps.put("signatureParts", "{Element}{http://docs.oasis-open.org/wss/2004/01/oasis-200401-wss-wssecurity-utility-1.0.xsd}Timestamp;{Element}{http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/}Body"); outProps.put("encryptionPropFile", "META-INF/alice.properties"); outProps.put("encryptionUser", "Bob"); outProps.put("encryptionParts", "{Element}{http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#}Signature;{Content}{http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/}Body"); outProps.put("encryptionSymAlgorithm", "http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#tripledes-cbc"); outProps.put("encryptionKeyTransportAlgorithm", "http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#rsa-1_5"); WSS4JOutInterceptor wssOut = new WSS4JOutInterceptor(outProps); //request cxfEndpoint.getOutInterceptors().add(wssOut); cxfEndpoint.getOutInterceptors().add(new SAAJOutInterceptor()); Map<String,Object> inProps= new HashMap<String,Object>(); inProps.put("action", "Timestamp Signature Encrypt"); inProps.put("signaturePropFile", "META-INF/alice.properties"); inProps.put("passwordCallbackClass", "org.jboss.test.ws.jaxws.samples.wsse.KeystorePasswordCallback"); inProps.put("decryptionPropFile", "META-INF/alice.properties"); WSS4JInInterceptor wssIn = new WSS4JInInterceptor(inProps); //response cxfEndpoint.getInInterceptors().add(wssIn); cxfEndpoint.getInInterceptors().add(new SAAJInInterceptor());11.2.1. Package and deploy
To deploy your web service endpoint, you need to package the following files along with your service implementation and WSDL contract:-
The
jbossws-cxf.xmldescriptor. -
The properties file.
-
The keystore file (if required for signature/encryption).
-
The keystore password callback handler class.
For instance, here are the archive contents for the signature and encryption sample ( POJO endpoint) mentioned before:[cxf-tests]$ jar -tvf target/test-libs/jaxws-samples-wsse-sign-encrypt.war 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:26 CEST 2008 META-INF/ 106 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 META-INF/MANIFEST.MF 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:26 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/ 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:26 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/ 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/ 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/ 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ws/ 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ws/jaxws/ 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ws/jaxws/samples/ 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ws/jaxws/samples/wsse/ 1628 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ws/jaxws/samples/wsse/KeystorePasswordCallback.class 364 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ws/jaxws/samples/wsse/ServiceIface.class 859 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ws/jaxws/samples/wsse/ServiceImpl.class 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ws/jaxws/samples/wsse/jaxws/ 685 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ws/jaxws/samples/wsse/jaxws/SayHello.class 1049 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/org/jboss/test/ws/jaxws/samples/wsse/jaxws/SayHelloResponse.class 2847 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/jbossws-cxf.xml 0 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/wsdl/ 1575 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/wsdl/SecurityService.wsdl 641 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/wsdl/SecurityService_schema1.xsd 1820 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/bob.jks 311 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/classes/bob.properties 573 Tue Jun 03 19:41:24 CEST 2008 WEB-INF/web.xml
On client side, instead, you only need the properties and keystore files (assuming you set up the interceptors programmatically). You just need to deploy and test your WS-Security-enabled application.11.3. WS-Security Policies
JBossWS-CXF also includes CXF WS-Security Policy implementation, which can be used to configure WS-Security more easily. Instead of manually configuring interceptors in the client or through thejbossws-cxf.xmldescriptor, you simply provide the right policies in the WSDL contract.... <binding name="SecurityServicePortBinding" type="tns:ServiceIface"> <wsp:PolicyReference URI="#SecurityServiceSignPolicy"/> ... <wsp:Policy wsu:Id="SecurityServiceSignPolicy" xmlns:sp="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/07/securitypolicy"> <wsp:ExactlyOne> <wsp:All> <sp:AsymmetricBinding xmlns:sp='http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/07/securitypolicy'> <wsp:Policy> <sp:InitiatorToken> <wsp:Policy> <sp:X509Token sp:IncludeToken='http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/07/securitypolicy/IncludeToken/AlwaysToRecipient'> <wsp:Policy> <sp:WssX509V3Token10 /> </wsp:Policy> </sp:X509Token> </wsp:Policy> </sp:InitiatorToken> <sp:RecipientToken> <wsp:Policy> <sp:X509Token sp:IncludeToken='http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/07/securitypolicy/IncludeToken/Always'> <wsp:Policy> <sp:WssX509V3Token10 /> </wsp:Policy> </sp:X509Token> </wsp:Policy> </sp:RecipientToken> <sp:AlgorithmSuite> <wsp:Policy> <sp:Basic256 /> </wsp:Policy> </sp:AlgorithmSuite> <sp:Layout> <wsp:Policy> <sp:Strict /> </wsp:Policy> </sp:Layout> <sp:OnlySignEntireHeadersAndBody /> </wsp:Policy> </sp:AsymmetricBinding> <sp:Wss10 xmlns:sp='http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/07/securitypolicy'> <wsp:Policy> <sp:MustSupportRefEmbeddedToken /> </wsp:Policy> </sp:Wss10> <sp:SignedParts xmlns:sp='http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/07/securitypolicy'> <sp:Body /> </sp:SignedParts> </wsp:All> </wsp:ExactlyOne> </wsp:Policy> ...A few properties are also required to be set either in the message context or in thejbossws-cxf.xmldescriptor.-
((BindingProvider)proxy).getRequestContext().put(SecurityConstants.CALLBACK_HANDLER, new KeystorePasswordCallback());
-
((BindingProvider)proxy).getRequestContext().put(SecurityConstants.SIGNATURE_PROPERTIES, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("META-INF/alice.properties"));
-
((BindingProvider)proxy).getRequestContext().put(SecurityConstants.ENCRYPT_PROPERTIES, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("META-INF/alice.properties"));
<beans xmlns='http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans' xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xmlns:beans='http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans' xmlns:jaxws='http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws' xsi:schemaLocation='http://cxf.apache.org/core http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/core.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd'> <jaxws:endpoint id='ServiceImpl' address='http://@jboss.bind.address@:8080/jaxws-samples-wssePolicy-sign' implementor='org.jboss.test.ws.jaxws.samples.wssePolicy.ServiceImpl'> <jaxws:properties> <entry key="ws-security.signature.properties" value="bob.properties"/> <entry key="ws-security.encryption.properties" value="bob.properties"/> <entry key="ws-security.callback-handler" value="org.jboss.test.ws.jaxws.samples.wssePolicy.KeystorePasswordCallback"/> </jaxws:properties> </jaxws:endpoint> </beans>http://docs.redhat.com/docs/en-US/JBoss_Enterprise_Web_Platform/5/html/JBoss_WS_CXF_User_Guide/sect-Authentication.html
-