1. As the time evolves, many logging techniques emerged.
1) java.util.logging (JUL) is provided by SUN along with JDK.
2) org.apache.log4j (Log4j) is provided by ASF.
-> Log4j-1.X and Log4j-2.X
-> But most projects are using Log4j-1.X
3) logback
4) org.apache.commons.logging (JakartaCommonsLogging) is provided by ASF
5) org.slf4j (SLF4J) is provided by SimpleLoggingFacade
2. Why do we use log and not System.out.println()?
1) SYSOUT is not controlable.
--> What if we want to output these information into file or other position?
--> What if we don't want all of these information to be printed?
--> What if we want the information to be partially printed according to theirs severe level?
2) SYSOUT is not tracable
--> If you are writing a java application server then only way to know what your server is doing is by seeing log file of your server. suppose you don't write anything in your java log file then no body knows what your sever is doing, it becomes increasingly important if your application is connected to upstream and downstream like in many stock trading systems or electronic trading system and get input from upstream , transforms and normalize it and send down to downstream. In case of any issue without java logs you won't be able to figure out what went wrong. That’s why logging in java is most important while writing any java server application. Logging in Java is not by choice it’s must to understand
3) So logging techniques have emerged to solve these problems.
--> They provide different severe level when output.
--> They provide different handlers/appenders for the position of information.
--> They are tracable.
3. Brief Comparasion of these techniques
1) Both Log4j, JUL and Logback are concrete implementations for logging.
--> But Log4j is more effecient and more functional than JUL .
2) Both commons-logging and slf4j are interfaces for logging.
--> The core target of these interfaces is to provide a simple and common standard for logging.
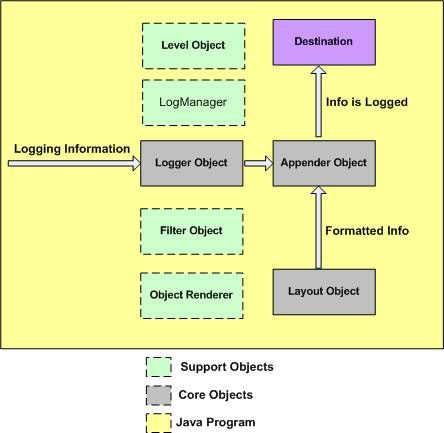
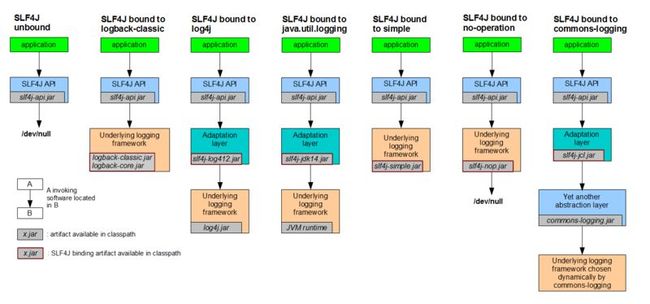
3) Diagrams in details
4. Brief Introduction to JUL and Log4j
1) JUL
1) Provided along with JDK.
2) Core function is provided with LogManager
3) Below is the detailed work flow of JUL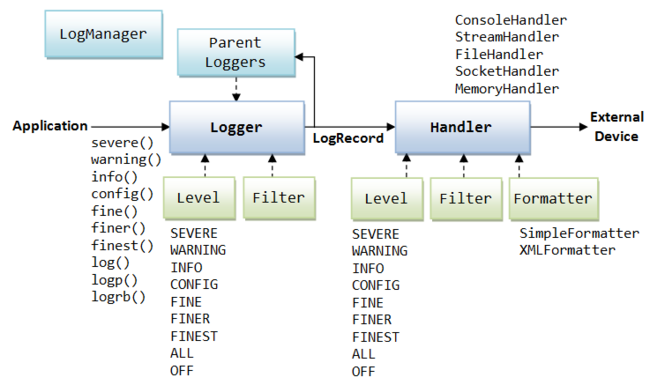
2) Log4j
1) Provided by ASF and has a long history.
2) The simple work flow of Log4j is as below
5. Brief Introduction to JCL and SLF4J
0) The benefits of using logging-frameworks:
--> Frameworks themselves didn't provide concrete logging function. They provided interfaces instead.
--> The real logging function is based on Log4j or JUL.
--> The deployer can decide which logging system to use, Log4j or JUL or others.
--> The deployer can easily change the logging system without change the code as the interface stays the same.
1) JCL
6. Summary:
1) By convention, many projects don't use JUL.
2) They are using Log4j and JCL as combination.
3) Or we can use Log4j and SLF4J as combination.
3) The new trend is using Logback and SLF4J as combination.
Reference Links:
2) http://www.tutorialspoint.com/log4j/log4j_architecture.htm
3) http://aofengblog.blog.163.com/blog/static/631702120113249403464/
4) http://webx.taobao.org/docs/logging.html
5) http://javarevisited.blogspot.hk/2011/05/top-10-tips-on-logging-in-java.html