学编程第一个肯定是hello world,Hadoop也不例外,它的hello world就是Wordcount,单词统计例子
1 package org.apache.hadoop.examples; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.util.StringTokenizer; 5 6 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 9 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 10 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 11 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 12 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 13 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 14 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 15 import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser; 16 17 public class WordCount { 18 19 public static class TokenizerMapper 20 extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>{ 21 22 private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); 23 private Text word = new Text(); 24 25 public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context 26 ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 27 StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); 28 while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) { 29 word.set(itr.nextToken()); 30 context.write(word, one); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 35 public static class IntSumReducer 36 extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> { 37 private IntWritable result = new IntWritable(); 38 39 public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, 40 Context context 41 ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 42 int sum = 0; 43 for (IntWritable val : values) { 44 sum += val.get(); 45 } 46 result.set(sum); 47 context.write(key, result); 48 } 49 } 50 51 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 52 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 53 String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args).getRemainingArgs(); 54 if (otherArgs.length != 2) { 55 System.err.println("Usage: wordcount <in> <out>"); 56 System.exit(2); 57 } 58 Job job = new Job(conf, "word count"); 59 job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class); 60 job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class); 61 job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class); 62 job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class); 63 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 64 job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); 65 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[0])); 66 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1])); 67 System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); 68 } 69 }
在Mapper中的map、以及Reducer中的reduce都有一个Context的类型
1 public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) 2 throws OException,InterruptedException{ 3 StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); 4 while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) { 5 word.set(itr.nextToken()); 6 context.write(word, one); 7 } 8 } 9 10 public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,Context context) 11 throws IOException, InterruptedException { 12 int sum = 0; 13 for (IntWritable val : values) { 14 sum += val.get(); 15 } 16 result.set(sum); 17 context.write(key, result); 18 }
这个Context究竟有何作用呢,按照翻译,它就是一个“上下文”,再由map中的
context.write(word, one);
以及reduce中的
context.write(key, result);
可以了解到,context应该是用来传递数据以及其他运行状态信息,map中的key、value写入context,让它传递给Reducer进行reduce,而reduce进行处理之后数据继续写入context,继续交给Hadoop写入hdfs系统。
那么Context究竟是怎样的呢。看一下它的继承实现结构。虽然Mapper与Reducer中都有一个Context类,但是它们并不是完全一样的。看一下Mapper与Reducer的源码。
1 public class Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> { 2 3 public class Context 4 extends MapContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> { 5 public Context(Configuration conf, TaskAttemptID taskid, 6 RecordReader<KEYIN,VALUEIN> reader, 7 RecordWriter<KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> writer, 8 OutputCommitter committer, 9 StatusReporter reporter, 10 InputSplit split) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 11 super(conf, taskid, reader, writer, committer, reporter, split); 12 } 13 } 14 15 /** 16 * Called once at the beginning of the task. 17 */ 18 protected void setup(Context context 19 ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 20 // NOTHING 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * Called once for each key/value pair in the input split. Most applications 25 * should override this, but the default is the identity function. 26 */ 27 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 28 protected void map(KEYIN key, VALUEIN value, 29 Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 30 context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value); 31 } 32 33 /** 34 * Called once at the end of the task. 35 */ 36 protected void cleanup(Context context 37 ) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 38 // NOTHING 39 } 40 41 /** 42 * Expert users can override this method for more complete control over the 43 * execution of the Mapper. 44 * @param context 45 * @throws IOException 46 */ 47 public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 48 setup(context); 49 try { 50 while (context.nextKeyValue()) { 51 map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context); 52 } 53 } finally { 54 cleanup(context); 55 } 56 } 57 }
可以看到原来Mapper与Reducer两个Context都是内部类的,Mapper的Context是通过继承MapContext,而Reducer的Context则是通过继承ReduceContext。
在Mapper.Context与Reducer.Context与继承前对比,没有增加成员以及方法,也没有重写方法,单纯把MapContext、ReduceContext重新封装,所以目标就是分析MapContext与ReduceContext
1 package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 6 7 8 public class MapContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> 9 extends TaskInputOutputContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> { 10 private RecordReader<KEYIN,VALUEIN> reader; 11 private InputSplit split; 12 13 public MapContext(Configuration conf, TaskAttemptID taskid, 14 RecordReader<KEYIN,VALUEIN> reader, 15 RecordWriter<KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> writer, 16 OutputCommitter committer, 17 StatusReporter reporter, 18 InputSplit split) { 19 super(conf, taskid, writer, committer, reporter); 20 this.reader = reader; 21 this.split = split; 22 } 23 24 25 public InputSplit getInputSplit() { 26 return split; 27 } 28 29 public KEYIN getCurrentKey() throws IOException, InterruptedException { 30 return reader.getCurrentKey(); 31 } 32 33 public VALUEIN getCurrentValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException { 34 return reader.getCurrentValue(); 35 } 36 37 public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException { 38 return reader.nextKeyValue(); 39 } 40 41 } 42 43 44 package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce; 45 46 import java.io.IOException; 47 import java.util.Iterator; 48 import java.util.NoSuchElementException; 49 50 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 51 import org.apache.hadoop.io.BytesWritable; 52 import org.apache.hadoop.io.DataInputBuffer; 53 import org.apache.hadoop.io.RawComparator; 54 import org.apache.hadoop.io.serializer.Deserializer; 55 import org.apache.hadoop.io.serializer.SerializationFactory; 56 import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.RawKeyValueIterator; 57 import org.apache.hadoop.util.Progressable; 58 59 60 public class ReduceContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> 61 extends TaskInputOutputContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> { 62 private RawKeyValueIterator input; 63 private Counter inputKeyCounter; 64 private Counter inputValueCounter; 65 private RawComparator<KEYIN> comparator; 66 private KEYIN key; // current key 67 private VALUEIN value; // current value 68 private boolean firstValue = false; // first value in key 69 private boolean nextKeyIsSame = false; // more w/ this key 70 private boolean hasMore; // more in file 71 protected Progressable reporter; 72 private Deserializer<KEYIN> keyDeserializer; 73 private Deserializer<VALUEIN> valueDeserializer; 74 private DataInputBuffer buffer = new DataInputBuffer(); 75 private BytesWritable currentRawKey = new BytesWritable(); 76 private ValueIterable iterable = new ValueIterable(); 77 78 public ReduceContext(Configuration conf, TaskAttemptID taskid, 79 RawKeyValueIterator input, 80 Counter inputKeyCounter, 81 Counter inputValueCounter, 82 RecordWriter<KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> output, 83 OutputCommitter committer, 84 StatusReporter reporter, 85 RawComparator<KEYIN> comparator, 86 Class<KEYIN> keyClass, 87 Class<VALUEIN> valueClass 88 ) throws InterruptedException, IOException{ 89 super(conf, taskid, output, committer, reporter); 90 this.input = input; 91 this.inputKeyCounter = inputKeyCounter; 92 this.inputValueCounter = inputValueCounter; 93 this.comparator = comparator; 94 SerializationFactory serializationFactory = new SerializationFactory(conf); 95 this.keyDeserializer = serializationFactory.getDeserializer(keyClass); 96 this.keyDeserializer.open(buffer); 97 this.valueDeserializer = serializationFactory.getDeserializer(valueClass); 98 this.valueDeserializer.open(buffer); 99 hasMore = input.next(); 100 } 101 102 /** Start processing next unique key. */ 103 public boolean nextKey() throws IOException,InterruptedException { 104 while (hasMore && nextKeyIsSame) { 105 nextKeyValue(); 106 } 107 if (hasMore) { 108 if (inputKeyCounter != null) { 109 inputKeyCounter.increment(1); 110 } 111 return nextKeyValue(); 112 } else { 113 return false; 114 } 115 } 116 117 118 public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException { 119 if (!hasMore) { 120 key = null; 121 value = null; 122 return false; 123 } 124 firstValue = !nextKeyIsSame; 125 DataInputBuffer next = input.getKey(); 126 currentRawKey.set(next.getData(), next.getPosition(), 127 next.getLength() - next.getPosition()); 128 buffer.reset(currentRawKey.getBytes(), 0, currentRawKey.getLength()); 129 key = keyDeserializer.deserialize(key); 130 next = input.getValue(); 131 buffer.reset(next.getData(), next.getPosition(), 132 next.getLength() - next.getPosition()); 133 value = valueDeserializer.deserialize(value); 134 hasMore = input.next(); 135 if (hasMore) { 136 next = input.getKey(); 137 nextKeyIsSame = comparator.compare(currentRawKey.getBytes(), 0, 138 currentRawKey.getLength(), 139 next.getData(), 140 next.getPosition(), 141 next.getLength() - next.getPosition() 142 ) == 0; 143 } else { 144 nextKeyIsSame = false; 145 } 146 inputValueCounter.increment(1); 147 return true; 148 } 149 150 public KEYIN getCurrentKey() { 151 return key; 152 } 153 154 public VALUEIN getCurrentValue() { 155 return value; 156 } 157 158 protected class ValueIterator implements Iterator<VALUEIN> { 159 160 public boolean hasNext() { 161 return firstValue || nextKeyIsSame; 162 } 163 164 @Override 165 public VALUEIN next() { 166 // if this is the first record, we don't need to advance 167 if (firstValue) { 168 firstValue = false; 169 return value; 170 } 171 // if this isn't the first record and the next key is different, they 172 // can't advance it here. 173 if (!nextKeyIsSame) { 174 throw new NoSuchElementException("iterate past last value"); 175 } 176 // otherwise, go to the next key/value pair 177 try { 178 nextKeyValue(); 179 return value; 180 } catch (IOException ie) { 181 throw new RuntimeException("next value iterator failed", ie); 182 } catch (InterruptedException ie) { 183 // this is bad, but we can't modify the exception list of java.util 184 throw new RuntimeException("next value iterator interrupted", ie); 185 } 186 } 187 188 public void remove() { 189 throw new UnsupportedOperationException("remove not implemented"); 190 } 191 192 } 193 194 protected class ValueIterable implements Iterable<VALUEIN> { 195 private ValueIterator iterator = new ValueIterator(); 196 @Override 197 public Iterator<VALUEIN> iterator() { 198 return iterator; 199 } 200 } 201 202 public 203 Iterable<VALUEIN> getValues() throws IOException, InterruptedException { 204 return iterable; 205 } 206 }
如下是这两的继承结构
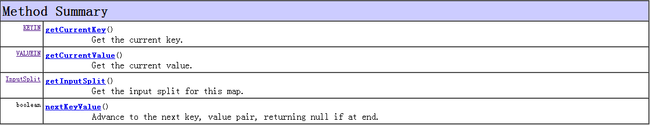
MapContext的方法汇总(不包括继承而来的,因为从继承结构可以看出MapContext与ReduceContext均继承TaskInputOutputContext,没有重写继承而来的方法,所以它们继承的都是一致的)
同理ReduceContext的方法汇总
上述的方法的用法都比较明显,不多说。
接下来就是看看共同继承的父类TaskInputOutputContext
有几个抽象方法:getCurrentKey() 、getCurrentValue() 、nextKeyValue() ,这是MapContext、ReduceContext共同的几个方法,务必需要MapContext与ReduceContext重新实现。write(KEYOUT key, VALUEOUT value) 则是把键值对写入DataOutput数据流中。在MapReduce编程过程中,不需要管理底层的数据流传输,write已经封装好了,直接调用即可写入流中。然后Hadoop会传输到下一步处理的环节。
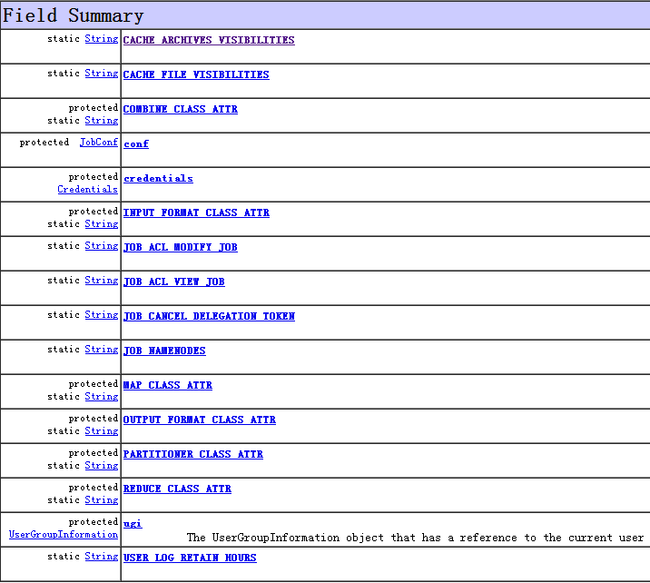
从前面Mapper.Context、 Reducer.Context、MapContext、ReduceContext、TaskInputOutputContext、TaskAttemptContext均没有添加任何成员变量,都是使用祖先JobContext的成员变量,而JobContext的成员变量汇总如下:
绝大部分的成员变量是static final 变量,有预先设定的值或者直接在构造函数中赋值。基本不需要再改变的,JobContext也提供了返回成员变量的函数,譬如诸多的get**.
至此已将Context的继承与实现讲完,其实也没有讲什么东西,只是把API与源码整理一下呗。