Spring3MVC and POI
本教程我们将通过Apache的 POI进行excel的导出和写入:
即把数据库的数据导出excel格式,
读取excel表报中的数据并写入数据库.
我们将会使用mysql进行数据的操作.
POI是什么?
也可以访问 Apache POI 官方网站
目前最新版本为3.8b2,此教程我们将采用3.7版本.
对于POI的基本用法可以观看官方的 quick-guide
下面是我们的应用程序文件夹结构:
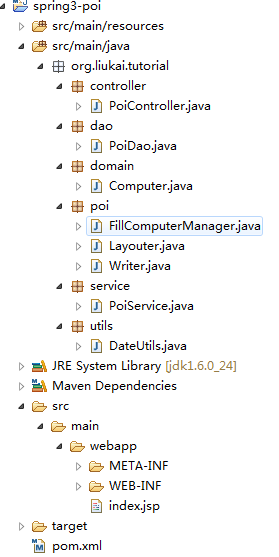
然后是pom.xml里添加的jar包:
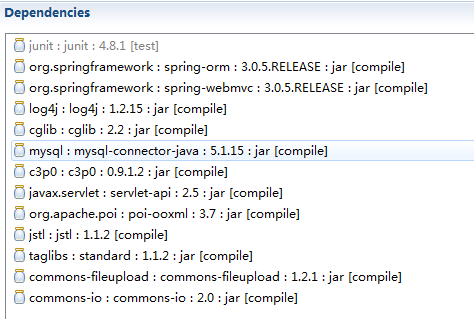
注意:poi的jar包一定要导入poi-ooxml
通过依赖顺便能导入poi.
如果直接导入poi后面的WebbookFactory将找不到jar包.
在数据库spring3db中创建一个表 computer
也可以直接把附件代码中src/main/resource/data下面的spring3db.sql导入数据库中.
导入后的数据库如下所示
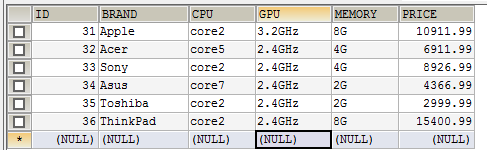
首先添加Spring MVC所必须的配置.
web.xml
在web.xml中我们定义servlet:spring.
按照惯例,我们必须声明一个spring-servle.xml
spring-servle.xml
这个XML配置声明一个视图解析器.在控制器中会根据JSP名映射到/ WEB-INF/jsp中相应的位置.
spring-servle.xml中的multipartResolver是Spring分段文件上传所必须的 ,用于检查请求中是否包含multipart.
更多的详情 对分段文件上传(multipart file upload)的支持
要进行数据库操作,一定需要一个数据库连接的配置.
jdbc.properties
application-dataSource.xml
该文件主要配置了:
1.启用了事务管理
2.声明了一个数据源
然后创建一个applicationContext.xml.
applicationContext.xml.
至此,基本的配置文件就完成了.
然后我们定义一个Computer对象
Computer.java
接下来就是POI来操作excel了.
需要注意的是POI里每个不同的模块代表了对不同格式档案的操作.如下:
HSSF - 提供读写Microsoft Excel XLS格式档案的功能。
XSSF - 提供读写Microsoft Excel OOXML XLSX格式档案的功能。
HWPF - 提供读写Microsoft Word DOC格式档案的功能。
HSLF - 提供读写Microsoft PowerPoint格式档案的功能。
HDGF - 提供读Microsoft Visio格式档案的功能。
HPBF - 提供读Microsoft Publisher格式档案的功能。
HSMF - 提供读Microsoft Outlook格式档案的功能。
在本教程中我们是实现对excel的操作.所以包含了HSSF和XLSX(开头在pom导入中强调了需要
导入ooxml的jar包,也包含了XSSF)
对导出的excel进行自定义格式:
Layouter.java
可以通过 POI单元格顔色设定了解更多的信息.
然后我们是填充数据的一个类:
FillComputerManager.java
报表写入类
Writer.java
这样对导出表报的格式基本设置完成.
接着我们完成一个对数据库进行操作的类.
PoiDao.java
该类我们实现了两个方法:查询所有的Computer对象并装入一个list的类 : getComputer
批量插入的类:insertComputer
前者用于报表的导出,后者用于报表的插入.
业务层中我们还是需要实现两个业务:导出和导入excel文件.
PoiService.java
此业务层实现了两个方法:
exportXLS:用于读取数据库并导出报表.
readReport:用于读取报表并插入数据库中.
untils包里的DateUtils.java只有一个类,用于格式化日期.
DateUtils.java
最后就是我们的controller层了
PoiController.java
到此,后台的代码基本完成了.
下面还有3个JSP页面.
index.jsp
report.jsp
addedReport.jsp
启动项目后输入:
http://localhost:8080/spring3-poi/report
点击 Export Report我们会得到一个excel文件.
打开后
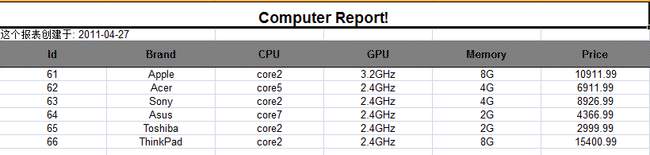
如此我们通过读取数据库得到了一个excel的文件.
点击"浏览",选择需要导入的excel报表.
注:强烈建议选择我们刚导出的excel报表.因为选择其他的报表格式不同,肯定会报错.
本教程只是演示基本的POI操作.如果要用于生产环境中,请根据自己的状况进行改动和重构.
成功后会显示

这个时候查询数据库,就会发现有2个相同的数据.说明我们导入成功.
总结
本教程中,我们成功的通过使用POI来进行了excel操作
大家可以根据本教程自定义excel的格式,输出的字段.
需要注意的是两点:
1.导入jar包一定要包含poi-ooxml.
2.别忘记关闭InputStream
BTW:附件为本次教程源码.你可以下载后直接在tomcat或其他web服务器启动.也可以自行添加
maven插件启动.
即把数据库的数据导出excel格式,
读取excel表报中的数据并写入数据库.
我们将会使用mysql进行数据的操作.
POI是什么?
引用
Apache POI是Apache软件基金会的开放源码函式库,POI提供API给Java程式对Microsoft Office格式档案读和写的功能。 .NET的开发人员则可以利用NPOI (POI for .NET) 来存取 POI 的功能。
也可以访问 Apache POI 官方网站
目前最新版本为3.8b2,此教程我们将采用3.7版本.
对于POI的基本用法可以观看官方的 quick-guide
下面是我们的应用程序文件夹结构:

然后是pom.xml里添加的jar包:

注意:poi的jar包一定要导入poi-ooxml
通过依赖顺便能导入poi.
如果直接导入poi后面的WebbookFactory将找不到jar包.
在数据库spring3db中创建一个表 computer
CREATE TABLE `computer` ( `ID` BIGINT(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `BRAND` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL, `CPU` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL, `GPU` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL, `MEMORY` VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL, `PRICE` DOUBLE DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`ID`) ) ENGINE=INNODB AUTO_INCREMENT=67 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
也可以直接把附件代码中src/main/resource/data下面的spring3db.sql导入数据库中.
导入后的数据库如下所示

首先添加Spring MVC所必须的配置.
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd"> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value> /WEB-INF/application-dataSource.xml /WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml </param-value> </context-param> <servlet> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> </web-app>
在web.xml中我们定义servlet:spring.
按照惯例,我们必须声明一个spring-servle.xml
spring-servle.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> <!-- 定义一个视图解析器 --> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" p:prefix="/WEB-INF/jsp/" p:suffix=".jsp" /> <!-- Spring分段文件上传所必须的 ,用于检查请求中是否包含multipart see: http://www.html.org.cn/books/springReference/ch13s08.html --> <bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver" p:maxUploadSize="5000000" /> </beans>
这个XML配置声明一个视图解析器.在控制器中会根据JSP名映射到/ WEB-INF/jsp中相应的位置.
spring-servle.xml中的multipartResolver是Spring分段文件上传所必须的 ,用于检查请求中是否包含multipart.
更多的详情 对分段文件上传(multipart file upload)的支持
要进行数据库操作,一定需要一个数据库连接的配置.
jdbc.properties
# database properties #spring3db is databaseName. app.jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver app.jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost/spring3db app.jdbc.username=root app.jdbc.password=root
application-dataSource.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd">
<description>dataSource配置</description>
<!-- 指定数据库配置文件地址. -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath*:/jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 启用注释管理事务注释风格. -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
<!--声明一个数据源.c3p0-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"
destroy-method="close"
p:driverClass="${app.jdbc.driverClassName}"
p:jdbcUrl="${app.jdbc.url}"
p:user="${app.jdbc.username}"
p:password="${app.jdbc.password}"
p:acquireIncrement="5"
p:idleConnectionTestPeriod="60"
p:maxPoolSize="100"
p:maxStatements="50"
p:minPoolSize="10"
p:maxIdleTime="25000"
/>
<!--声明一个事务管理器. -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"
p:dataSource-ref="dataSource" />
</beans>
该文件主要配置了:
1.启用了事务管理
2.声明了一个数据源
然后创建一个applicationContext.xml.
applicationContext.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.0.xsd"> <!-- 激活spring的注解. --> <context:annotation-config /> <!-- 扫描注解组件并且自动的注入spring beans中. 例如,他会扫描@Controller 和@Service下的文件.所以确保此base-package设置正确. --> <context:component-scan base-package="org.liukai.tutorial" /> <!-- 配置注解驱动的Spring MVC Controller 的编程模型.注:此标签只在 Servlet MVC工作! --> <mvc:annotation-driven /> </beans>
至此,基本的配置文件就完成了.
然后我们定义一个Computer对象
Computer.java
package org.liukai.tutorial.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Computer implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7955753961332480136L;
private Long id;
private String brand;
private String cpu;
private String gpu;
private String memory;
private Double price;
//getter&setter
}
接下来就是POI来操作excel了.
需要注意的是POI里每个不同的模块代表了对不同格式档案的操作.如下:
引用
HSSF - 提供读写Microsoft Excel XLS格式档案的功能。
XSSF - 提供读写Microsoft Excel OOXML XLSX格式档案的功能。
HWPF - 提供读写Microsoft Word DOC格式档案的功能。
HSLF - 提供读写Microsoft PowerPoint格式档案的功能。
HDGF - 提供读Microsoft Visio格式档案的功能。
HPBF - 提供读Microsoft Publisher格式档案的功能。
HSMF - 提供读Microsoft Outlook格式档案的功能。
在本教程中我们是实现对excel的操作.所以包含了HSSF和XLSX(开头在pom导入中强调了需要
导入ooxml的jar包,也包含了XSSF)
对导出的excel进行自定义格式:
Layouter.java
package org.liukai.tutorial.poi;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.util.CellRangeAddress;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.util.HSSFColor;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Font;
import org.liukai.tutorial.utils.DateUtils;
/**
* 更多单元格请查看http://justdoblogger.com/blog/200911/setfillforegroundcolor.html
*
* @author liukai
*
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class Layouter {
/**
* 创建报表
*/
public static void buildReport(HSSFSheet worksheet, int startRowIndex,
int startColIndex) {
// 设置列的宽度
worksheet.setColumnWidth(0, 5000);
worksheet.setColumnWidth(1, 5000);
worksheet.setColumnWidth(2, 5000);
worksheet.setColumnWidth(3, 5000);
worksheet.setColumnWidth(4, 5000);
worksheet.setColumnWidth(5, 5000);
buildTitle(worksheet, startRowIndex, startColIndex);
buildHeaders(worksheet, startRowIndex, startColIndex);
}
/**
* 创建报表标题和日期
*/
private static void buildTitle(HSSFSheet worksheet, int startRowIndex,
int startColIndex) {
// 设置报表标题字体
Font fontTitle = worksheet.getWorkbook().createFont();
fontTitle.setBoldweight(Font.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD);
fontTitle.setFontHeight((short) 280);
// 标题单元格样式
HSSFCellStyle cellStyleTitle = worksheet.getWorkbook()
.createCellStyle();
cellStyleTitle.setAlignment(CellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);
cellStyleTitle.setWrapText(true);
cellStyleTitle.setFont(fontTitle);
// 报表标题
HSSFRow rowTitle = worksheet.createRow((short) startRowIndex);
rowTitle.setHeight((short) 500);
HSSFCell cellTitle = rowTitle.createCell(startColIndex);
cellTitle.setCellValue("Computer Report!");
cellTitle.setCellStyle(cellStyleTitle);
// 合并区域内的报告标题
worksheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(0, 0, 0, 5));
// date header
HSSFRow dateTitle = worksheet.createRow((short) startRowIndex + 1);
HSSFCell cellDate = dateTitle.createCell(startColIndex);
cellDate.setCellValue("这个报表创建于: " + DateUtils.getNowTime());
}
/**
* 创建表头
*/
private static void buildHeaders(HSSFSheet worksheet, int startRowIndex,
int startColIndex) {
// Header字体
Font font = worksheet.getWorkbook().createFont();
font.setBoldweight(Font.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD);
// 单元格样式
HSSFCellStyle headerCellStyle = worksheet.getWorkbook()
.createCellStyle();
headerCellStyle.setFillBackgroundColor(HSSFColor.GREY_25_PERCENT.index);
headerCellStyle.setFillPattern(CellStyle.FINE_DOTS);
headerCellStyle.setAlignment(CellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);
headerCellStyle.setVerticalAlignment(CellStyle.VERTICAL_CENTER);
headerCellStyle.setWrapText(true);
headerCellStyle.setFont(font);
headerCellStyle.setBorderBottom(CellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
// 创建字段标题
HSSFRow rowHeader = worksheet.createRow((short) startRowIndex + 2);
rowHeader.setHeight((short) 500);
HSSFCell cell1 = rowHeader.createCell(startColIndex + 0);
cell1.setCellValue("Id");
cell1.setCellStyle(headerCellStyle);
HSSFCell cell2 = rowHeader.createCell(startColIndex + 1);
cell2.setCellValue("Brand");
cell2.setCellStyle(headerCellStyle);
HSSFCell cell3 = rowHeader.createCell(startColIndex + 2);
cell3.setCellValue("CPU");
cell3.setCellStyle(headerCellStyle);
HSSFCell cell4 = rowHeader.createCell(startColIndex + 3);
cell4.setCellValue("GPU");
cell4.setCellStyle(headerCellStyle);
HSSFCell cell5 = rowHeader.createCell(startColIndex + 4);
cell5.setCellValue("Memory");
cell5.setCellStyle(headerCellStyle);
HSSFCell cell6 = rowHeader.createCell(startColIndex + 5);
cell6.setCellValue("Price");
cell6.setCellStyle(headerCellStyle);
}
}
可以通过 POI单元格顔色设定了解更多的信息.
然后我们是填充数据的一个类:
FillComputerManager.java
package org.liukai.tutorial.poi;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.CellStyle;
import org.liukai.tutorial.domain.Computer;
public class FillComputerManager {
public static void fillReport(HSSFSheet worksheet, int startRowIndex,
int startColIndex, List<Computer> datasource) {
// Row offset
startRowIndex += 2;
// Create cell style for the body
HSSFCellStyle bodyCellStyle = worksheet.getWorkbook().createCellStyle();
bodyCellStyle.setAlignment(CellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);
bodyCellStyle.setWrapText(false); //是否自动换行.
// Create body
for (int i=startRowIndex; i+startRowIndex-2< datasource.size()+2; i++) {
// Create a new row
HSSFRow row = worksheet.createRow((short) i+1);
// Retrieve the id value
HSSFCell cell1 = row.createCell(startColIndex+0);
cell1.setCellValue(datasource.get(i-2).getId());
cell1.setCellStyle(bodyCellStyle);
// Retrieve the brand value
HSSFCell cell2 = row.createCell(startColIndex+1);
cell2.setCellValue(datasource.get(i-2).getBrand());
cell2.setCellStyle(bodyCellStyle);
// Retrieve the model value
HSSFCell cell3 = row.createCell(startColIndex+2);
cell3.setCellValue(datasource.get(i-2).getCpu());
cell3.setCellStyle(bodyCellStyle);
// Retrieve the maximum power value
HSSFCell cell4 = row.createCell(startColIndex+3);
cell4.setCellValue(datasource.get(i-2).getGpu());
cell4.setCellStyle(bodyCellStyle);
// Retrieve the price value
HSSFCell cell5 = row.createCell(startColIndex+4);
cell5.setCellValue(datasource.get(i-2).getMemory());
cell5.setCellStyle(bodyCellStyle);
// Retrieve the efficiency value
HSSFCell cell6 = row.createCell(startColIndex+5);
cell6.setCellValue(datasource.get(i-2).getPrice());
cell6.setCellStyle(bodyCellStyle);
}
}
}
报表写入类
Writer.java
package org.liukai.tutorial.poi;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
public class Writer {
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("service");
public static void write(HttpServletResponse response, HSSFSheet worksheet) {
logger.debug("Writing report to the stream");
try {
// Retrieve the output stream
ServletOutputStream outputStream = response.getOutputStream();
// Write to the output stream
worksheet.getWorkbook().write(outputStream);
// 清除缓存
outputStream.flush();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("报表输入失败!");
}
}
}
这样对导出表报的格式基本设置完成.
接着我们完成一个对数据库进行操作的类.
PoiDao.java
package org.liukai.tutorial.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.liukai.tutorial.domain.Computer;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSourceUtils;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.simple.SimpleJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("poiDao")
public class PoiDao {
private SimpleJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Resource(name = "dataSource")
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.jdbcTemplate = new SimpleJdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
public List<Computer> getComputer() {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM computer";
return jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Computer>(
Computer.class));
}
public int[] insertComputer(List<Computer> list) {
String sql = "INSERT INTO computer (BRAND,CPU,GPU,MEMORY,PRICE)VALUES(:brand,:cpu,:gpu,:memory,:price)";
SqlParameterSource[] batch = SqlParameterSourceUtils.createBatch(list
.toArray());
return jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batch);
}
}
该类我们实现了两个方法:查询所有的Computer对象并装入一个list的类 : getComputer
批量插入的类:insertComputer
前者用于报表的导出,后者用于报表的插入.
业务层中我们还是需要实现两个业务:导出和导入excel文件.
PoiService.java
package org.liukai.tutorial.service;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.openxml4j.exceptions.InvalidFormatException;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.DateUtil;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Workbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.WorkbookFactory;
import org.liukai.tutorial.dao.PoiDao;
import org.liukai.tutorial.domain.Computer;
import org.liukai.tutorial.poi.FillComputerManager;
import org.liukai.tutorial.poi.Layouter;
import org.liukai.tutorial.poi.Writer;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service("poiService")
@Transactional
public class PoiService {
@Resource(name = "poiDao")
private PoiDao dao;
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("service");
public void exportXLS(HttpServletResponse response) {
// 1.创建一个 workbook
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
// 2.创建一个 worksheet
HSSFSheet worksheet = workbook.createSheet("Computer");
// 3.定义起始行和列
int startRowIndex = 0;
int startColIndex = 0;
// 4.创建title,data,headers
Layouter.buildReport(worksheet, startRowIndex, startColIndex);
// 5.填充数据
FillComputerManager.fillReport(worksheet, startRowIndex, startColIndex,
getDatasource());
// 6.设置reponse参数
String fileName = "ComputersReport.xls";
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "inline; filename="
+ fileName);
// 确保发送的当前文本格式
response.setContentType("application/vnd.ms-excel");
// 7. 输出流
Writer.write(response, worksheet);
}
/**
* 读取报表
*/
public List<Computer> readReport(InputStream inp) {
List<Computer> computerList = new ArrayList<Computer>();
try {
String cellStr = null;
Workbook wb = WorkbookFactory.create(inp);
Sheet sheet = wb.getSheetAt(0);// 取得第一个sheets
//从第四行开始读取数据
for (int i = 3; i <= sheet.getLastRowNum(); i++) {
Computer computer = new Computer();
Computer addComputer = new Computer();
Row row = sheet.getRow(i); // 获取行(row)对象
if (row == null) {
// row为空的话,不处理
continue;
}
for (int j = 0; j < row.getLastCellNum(); j++) {
Cell cell = row.getCell(j); // 获得单元格(cell)对象
// 转换接收的单元格
cellStr = ConvertCellStr(cell, cellStr);
// 将单元格的数据添加至一个对象
addComputer = addingComputer(j, computer, cellStr);
}
// 将添加数据后的对象填充至list中
computerList.add(addComputer);
}
} catch (InvalidFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (inp != null) {
try {
inp.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
logger.info("没有数据流!");
}
}
return computerList;
}
/**
* 从数据库获得所有的Computer信息.
*/
private List<Computer> getDatasource() {
return dao.getComputer();
}
/**
* 读取报表的数据后批量插入
*/
public int[] insertComputer(List<Computer> list) {
return dao.insertComputer(list);
}
/**
* 获得单元格的数据添加至computer
*
* @param j
* 列数
* @param computer
* 添加对象
* @param cellStr
* 单元格数据
* @return
*/
private Computer addingComputer(int j, Computer computer, String cellStr) {
switch (j) {
case 0:
computer.setId(null);
break;
case 1:
computer.setBrand(cellStr);
break;
case 2:
computer.setCpu(cellStr);
break;
case 3:
computer.setGpu(cellStr);
break;
case 4:
computer.setMemory(cellStr);
break;
case 5:
computer.setPrice(new Double(cellStr).doubleValue());
break;
}
return computer;
}
/**
* 把单元格内的类型转换至String类型
*/
private String ConvertCellStr(Cell cell, String cellStr) {
switch (cell.getCellType()) {
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
// 读取String
cellStr = cell.getStringCellValue().toString();
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
// 得到Boolean对象的方法
cellStr = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
// 先看是否是日期格式
if (DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)) {
// 读取日期格式
cellStr = cell.getDateCellValue().toString();
} else {
// 读取数字
cellStr = String.valueOf(cell.getNumericCellValue());
}
break;
case Cell.CELL_TYPE_FORMULA:
// 读取公式
cellStr = cell.getCellFormula().toString();
break;
}
return cellStr;
}
}
此业务层实现了两个方法:
exportXLS:用于读取数据库并导出报表.
readReport:用于读取报表并插入数据库中.
untils包里的DateUtils.java只有一个类,用于格式化日期.
DateUtils.java
package org.liukai.tutorial.utils;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateUtils {
/**
* 获得yyyy-MM-dd格式的当前日期
*/
public static String getNowTime() {
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
return dateFormat.format(date);
}
}
最后就是我们的controller层了
PoiController.java
package org.liukai.tutorial.controller;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.liukai.tutorial.domain.Computer;
import org.liukai.tutorial.service.PoiService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/report")
public class PoiController {
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("controller");
@Resource(name = "poiService")
private PoiService service;
/**
* 跳转到主页.
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getIndex() {
logger.info("index!");
return "report";
}
/**
* 导出excel报表
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/export", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void getXLS(HttpServletResponse response) {
service.exportXLS(response);
}
/**
* 读取excel报表
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/read", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String getReadReport(@RequestParam MultipartFile file)
throws IOException {
List<Computer> list = service.readReport(file.getInputStream());
service.insertComputer(list);
return "addedReport";
}
}
到此,后台的代码基本完成了.
下面还有3个JSP页面.
index.jsp
<% response.sendRedirect("/report"); %>
report.jsp
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="spring" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="form" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<title>Report</title>
</head>
<body>
<c:url var="exportUrl" value="/report/export" />
<c:url var="readUrl" value="/report/read" />
<h3><a href="${exportUrl }">Export Report</a></h3>
<br />
<form id="readReportForm" action="${readUrl }" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data" >
<label for="file">File</label>
<input id="file" type="file" name="file" />
<p><button type="submit">Read</button></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
addedReport.jsp
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>导入成功!</h1>
<a href="/spring3-poi/report">返回</a>
</body>
</html>
启动项目后输入:
http://localhost:8080/spring3-poi/report

点击 Export Report我们会得到一个excel文件.
打开后

如此我们通过读取数据库得到了一个excel的文件.
点击"浏览",选择需要导入的excel报表.
注:强烈建议选择我们刚导出的excel报表.因为选择其他的报表格式不同,肯定会报错.
本教程只是演示基本的POI操作.如果要用于生产环境中,请根据自己的状况进行改动和重构.
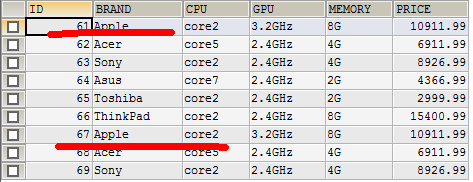
成功后会显示

这个时候查询数据库,就会发现有2个相同的数据.说明我们导入成功.

总结
本教程中,我们成功的通过使用POI来进行了excel操作
大家可以根据本教程自定义excel的格式,输出的字段.
需要注意的是两点:
1.导入jar包一定要包含poi-ooxml.
2.别忘记关闭InputStream
BTW:附件为本次教程源码.你可以下载后直接在tomcat或其他web服务器启动.也可以自行添加
maven插件启动.