jxls官方网站http://jxls.sourceforge.net/
jxls采用基于excel模板的方式来导出excel,支持
支持写sql语句导数据
简单属性访问
强大的表达式
报表导出
报表标签使用
列隐藏
动态样式
jdbc resultset导出
在一个单元格上使用多个bean的属性
合并单元格
动态分组
等等,底层采用的poi来操作excel,所以要下载poi,下列表是依赖包
* POI (3.5 or later)
* Commons BeanUtils
* Commons Collections
* Commons JEXL
* Commons Logging
* Commons Digester
使用模板的直接好处就是减少了设置excel相应单元格样式,复杂表格不好编码,手动填充数据,减少编码出错率等诸多不便之处。
简单的使用就不用做例子了,直接上一个难一点的。该功能最终的导出效果图如下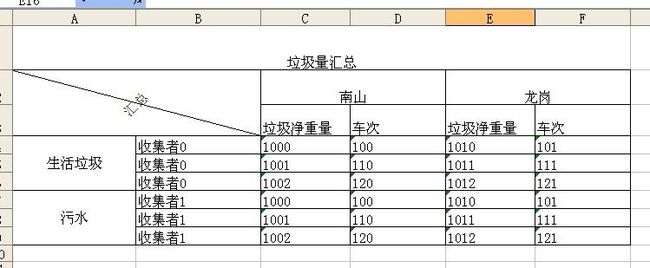
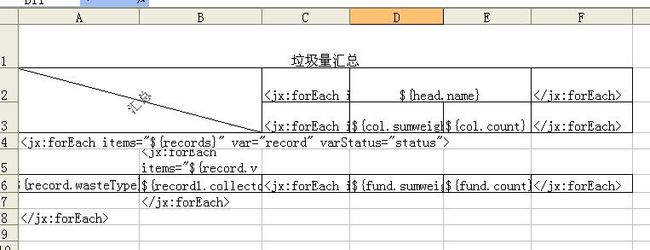
要求:1.导出的excel的表头是动态的且支持单元格合并,2.支持分组,通过设置合并单元格的属性,能自动将相同数据纵向合并单元格
所操作excel的模板图如下
测试用例所使用的简单bean
public class ExcelColumn {
private String value;
private int row;
private int col;
public ExcelColumn(String value, int row, int col) {
super();
this.value = value;
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
//getter/setter
}
public class Column {
private String sumweight;
private String count;
//getter/setter
}
public class FundsVO {
private String sumweight;
private String count;
//getter/setter
}
public class Head {
private String name;
//getter/setter
}
public class Record {
private String wasteType;
private Collection<ValueBean> valuebeans;
//getter/setter
}
public class ValueBean {
private String collector;
private Collection<FundsVO> fund;
//getter/setter
}
测试用例主体方法
@Test
public void dymicColumnTest() throws ParsePropertyException, InvalidFormatException, IOException {
List<Head> heads = new ArrayList<Head>();
Head col1 = new Head("南山");
Head col2 = new Head("龙岗");
heads.add(col1);
heads.add(col2);
List<Column> cols = new ArrayList<Column>();
Column co1 = new Column();
co1.setSumweight("垃圾净重量");
co1.setCount("车次");
cols.add(co1);
cols.add(co1);
List<Collection<ValueBean>> data = new ArrayList<Collection<ValueBean>>();
data.add(new ArrayList<ValueBean>());
data.add(new ArrayList<ValueBean>());
for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
ValueBean con1 = new ValueBean();
con1.setCollector("收集者" + k);
Collection<FundsVO> fund = new ArrayList<FundsVO>();
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
FundsVO f1 = new FundsVO();
f1.setCount("1" + i + j);
f1.setSumweight("10" + j + i);
fund.add(f1);
}
con1.setFund(fund);
data.get(k).add(con1);
}
}
Collection<Record> records = new ArrayList<Record>();
Record r1 = new Record();
r1.setWasteType("生活垃圾");
r1.setValuebeans(data.get(0));
records.add(r1);
Record r2 = new Record();
r2.setWasteType("污水");
r2.setValuebeans(data.get(1));
records.add(r2);
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("records", records);
map.put("heads", heads);
map.put("cols", cols);
String templateFileName = "D:\\workspace\\jxlsdemo\\src\\hi\\magicdetective\\dynmiccolumn\\dynmic.xls";
String destFileName = "D:\\workspace\\jxlsdemo\\src\\hi\\magicdetective\\dynmiccolumn\\dynmic_output.xls";
XLSTransformer transformer = new XLSTransformer();
//注册自定义合并单元格转换器
transformer.registerCellProcessor(new MultPropertyCellProcessor(new String[] { "record.wasteType" }));
transformer.transformXLS(templateFileName, map, destFileName);
}
package hi.magicdetective.dynmiccolumn;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import net.sf.jxls.parser.Cell;
import net.sf.jxls.processor.CellProcessor;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Sheet;
import org.apache.poi.ss.util.CellRangeAddress;
/**
* 多属性合并单元格转换器
* @author ydw
*
*/
public class MultPropertyCellProcessor implements CellProcessor {
/**
* 合并属性集
*/
private String[] keys;
/**
* 合并数据集
*/
private Map<String, List<ExcelColumn>> mergedMap = new HashMap<String, List<ExcelColumn>>();
/**
* 合并属性的起始行列
*/
private Map<String, ExcelColumn> first = new HashMap<String, ExcelColumn>();
public MultPropertyCellProcessor(String[] keys) {
this.keys = keys;
}
/**
* 刚开始不明白这个Map namedCells参数的含义,通过跟踪源代码发现是下面类调用的
* SimpleRowTransformer
* private void applyCellProcessors(Sheet sheet, Cell cell) {
for (int i = 0; i < cellProcessors.size(); i++) {
CellProcessor cellProcessor = (CellProcessor) cellProcessors.get(i);
cellProcessor.processCell(cell, sheet.getNamedCells());
}
}
*/
@Override
public void processCell(Cell cell, Map namedCells) {
for (String key : keys) {
if (cell.getStringCellValue().contains(key)) {
first.put(key,
new ExcelColumn(key, cell.getPoiCell().getRowIndex(), cell.getPoiCell().getColumnIndex()));
}
}
//同行列,实际数据,不是表达式值
for (String key : keys) {
int firstRow = first.get(key) == null ? -1 : first.get(key).getRow();
int firstCol = first.get(key) == null ? -1 : first.get(key).getCol();
if (cell.getPoiCell().getRowIndex() == firstRow && cell.getPoiCell().getColumnIndex() == firstCol
&& !cell.getStringCellValue().contains(key)) {
String value = cell.getStringCellValue();
//由属性+值构成键
String tmpKey = key + "_" + value;
if (mergedMap.containsKey(tmpKey)) {
mergedMap.get(tmpKey).add(new ExcelColumn(value, firstRow, firstCol));
} else {
List<ExcelColumn> list = new ArrayList<ExcelColumn>();
list.add(new ExcelColumn(value, firstRow, firstCol));
mergedMap.put(tmpKey, list);
}
}
merged(cell.getPoiCell().getSheet(), mergedMap);
}
}
private void merged(Sheet sheet, Map<String, List<ExcelColumn>> map) {
Set<Entry<String, List<ExcelColumn>>> set = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, List<ExcelColumn>> entry : set) {
String tmpKey = entry.getKey();
int firstRow = 9999;
int lastRow = -1;
int colindex = 0;
for (ExcelColumn col : map.get(tmpKey)) {
colindex = col.getCol();
if (col.getRow() < firstRow)
firstRow = col.getRow();
if (col.getRow() > lastRow)
lastRow = col.getRow();
}
CellRangeAddress range = new CellRangeAddress(firstRow, lastRow, colindex, colindex);
sheet.addMergedRegion(range);
}
}
}