官网地址
http://developer.android.com/training/basics/activity-lifecycle/index.html
Activity 可以说是Android最重要的概念之一,理解好它是我们学习android的必修课。
一、开始一个Activity
1.1 Activity的生命周期
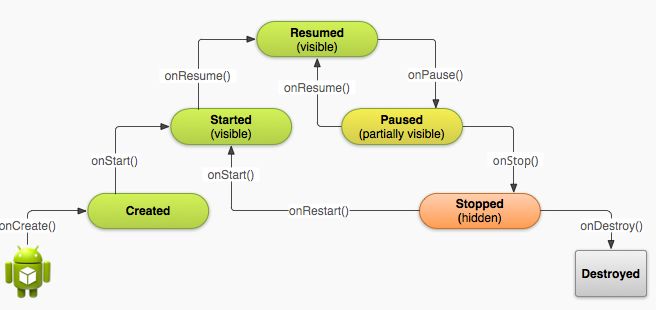
官网上有一张这样的图,很详细的说明了Activity 的周期和他们调用的方法。
1.2 指定启动的Activity
在文件AndroidManifest.xml中可以直接指定程序启动的时候运行哪一个Activity,如下:
<activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
1.3 创建一个Activity实例
通过上面的图,我们可以知道我们最先调用的是OnCreate方法来创建一个Activity实例,在类中通常这样调用Activity的onCreate() 方法。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
} 我们总是最先调用父类的onCreate方法。然后为这个Activity 添加界面(layout).
1.4 销毁一个Activity,我在IDE中重载了父类的方法,方面内容是这样的
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
}
二、暂停和唤醒一个Activity
没仔细看别人怎么翻译的,暂且这样叫吧,名字只是一个代号而已:)。
2.1 暂停一个Activity
官网如下解释:当系统调用onPause时,说明这个Activity仍然部分可见,用户准备离开这个Activity了,并且接下来会调用onStop()方法进入stop的状态。
我们通常使用onPause()方法做下面的事情。
1.停止动画或者其他消耗CPU的动作
2.提交未保存的修改,比如说一个email的草稿
3.释放系统资源,比如 broadcast receivers, handles to sensors (like GPS)
官网的上关于照相的例子
@Override
public void onPause() {
super.onPause(); // Always call the superclass method first
// Release the Camera because we don't need it when paused
// and other activities might need to use it.
if (mCamera != null) {
mCamera.release()
mCamera = null;
}
} 注:建议不要在onPause()方法中调用长时间占用cpu的操作,这样的操作应该放到onStop()方法中,因为会减缓图形可见和不可见的过渡。
2.2 唤醒你的Acitiviy
每次你的Activity来到前台展现时都会调用onResume()这个方法,所以你应该利用它来初始化你的组件,以及以前被onPause()方法释放的资源。
@Override
public void onResume() {
super.onResume(); // Always call the superclass method first
// Get the Camera instance as the activity achieves full user focus
if (mCamera == null) {
initializeCamera(); // Local method to handle camera init
}
}
三、停止和重启一个Activity
3.1 停止Acitivy
当调用onStop()方法来停止一个Activity时,表示它不再显示并且绝大部分的不适用的资源都会被回收,一旦你的Activity被停止了,当系统需要内存时,会直接销毁你的Activity实例,有时甚至不调用onDestroy()方法。所以在这个阶段处理内存中的资源特别的重要了。
尽管我们在onPause就已经释放一些资源了,但是和前者不同的时候,onStop()处理更加大的,更消耗CPU的操作,比如最后写点什么东西到数据库中保存。
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop(); // Always call the superclass method first
// Save the note's current draft, because the activity is stopping
// and we want to be sure the current note progress isn't lost.
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(NotePad.Notes.COLUMN_NAME_NOTE, getCurrentNoteText());
values.put(NotePad.Notes.COLUMN_NAME_TITLE, getCurrentNoteTitle());
getContentResolver().update(
mUri, // The URI for the note to update.
values, // The map of column names and new values to apply to them.
null, // No SELECT criteria are used.
null // No WHERE columns are used.
);
} 注:尽管系统可能在我们调用onStop()方法后销毁了我们的activity,但是我们依然保存了视图(view)的状态在Bundle中,如果用户在导航到这个Activity时,我们可能根绝这些状态重建一个Activity。
3.2 启动和重启一个Activity
当一个Activity从stoped状态回到前段界面时,会调用onRestart()方法。
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart(); // Always call the superclass method first
// The activity is either being restarted or started for the first time
// so this is where we should make sure that GPS is enabled
LocationManager locationManager =
(LocationManager) getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
boolean gpsEnabled = locationManager.isProviderEnabled(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER);
if (!gpsEnabled) {
// Create a dialog here that requests the user to enable GPS, and use an intent
// with the android.provider.Settings.ACTION_LOCATION_SOURCE_SETTINGS action
// to take the user to the Settings screen to enable GPS when they click "OK"
}
}
@Override
protected void onRestart() {
super.onRestart(); // Always call the superclass method first
// Activity being restarted from stopped state
}
四、重建Activity
前面说过,对于在stop状态的Activity,系统可能会直接销毁这个Activity,为什么会销毁是因为,系统感觉很久都不会有人用了,或者系统急需内存,而这些内存又被已经在stop状态的Activity占用了。
前面还说道,就算一个Activity被系统直接销毁了,依然可以通过一些状态来重建,而这些状态就是通过调用onSaveInstanceState() 和onRestoreInstanceState()来完成。
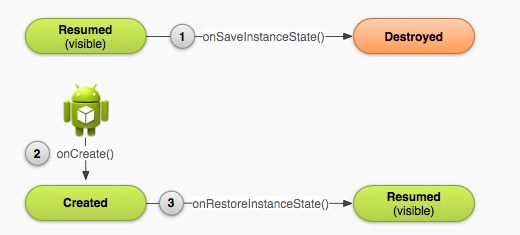
4.1 保存状态
比如要保存一个ListView 的滚动位置,或者EditText的文字,前面也讲过Bundle其实是一个Map
static final String STATE_SCORE = "playerScore";
static final String STATE_LEVEL = "playerLevel";
...
@Override
public void onSaveInstanceState(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Save the user's current game state
savedInstanceState.putInt(STATE_SCORE, mCurrentScore);
savedInstanceState.putInt(STATE_LEVEL, mCurrentLevel);
// Always call the superclass so it can save the view hierarchy state
super.onSaveInstanceState(savedInstanceState);
} 4.2 恢复Activity的状态
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); // Always call the superclass first
// Check whether we're recreating a previously destroyed instance
if (savedInstanceState != null) {
// Restore value of members from saved state
mCurrentScore = savedInstanceState.getInt(STATE_SCORE);
mCurrentLevel = savedInstanceState.getInt(STATE_LEVEL);
} else {
// Probably initialize members with default values for a new instance
}
...
} Activity的内容有很多,不同的动作都会让Activity进入不同的状态,如果想个更清楚一些,需要自己为每个阶段都写一段日志,然后各种操作这个Activity之后通过看日志的输出来帮助我们理解。
PS:阔别已久的这篇文章终于写完了,前段时间处理公司的事情去了。拿了公司的钱,公司的事情肯定是优先做的,但是一有时间我会接着把下面的完成的,呵呵。

