hopfield网络联想记忆实现方法
Hopfield联想记忆实现原理
设计方法
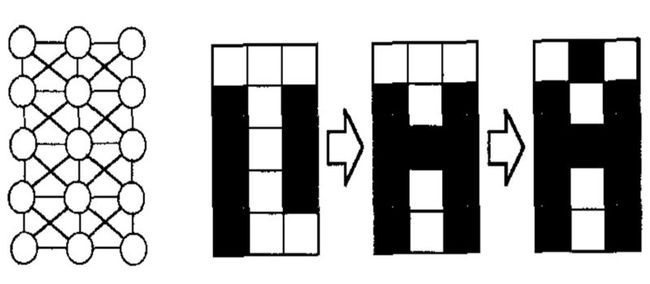
利用H网想起字母“A”
代码如下
结果如下
目标状态
-1 1 -1
1 -1 1
1 1 1
1 -1 1
1 -1 1
初始状态
-1 -1 -1
1 -1 1
1 -1 1
1 -1 1
1 -1 -1
运行后状态
-1 1 -1
1 -1 1
1 1 1
1 -1 1
1 -1 1
将结果矩阵中1连起来,就是一个字母A
- H网的E能量函数,平稳点——谷,这些谷与要记忆的内容对应。
- 设法把所需记忆的模式设计成某个确定网络状态的一个稳定平衡点。
- 当网络从与记忆模式较靠近的某个初始状态(即发生某些变形或含有某些噪声的记忆模式)出发后,网络按H网工作运行规则进行状态更新;
- 最后网络的状态将稳定在能量函数的极小点,即记忆模式所对应的状态。
- 这样,就完成了由部分信息(含躁声的记忆模式)到全部信息(记忆模式)的联想过程。
设计方法
- 学习模式——决定权重 想要记忆的模式,用-1和1的2值表示模式:-1,-1,1,-1,1,1,...
- 想起模式 神经元输出值的初始化
P:模式的总数
ap(s):第p个模式的第s个要素(-1或1)
wij:第j个神经元与第i个神经元间的权重
任意两个神经元j、i间的权重:
wij=∑ap(i)ap(j),p=1…p;
i = j时,wij=0,即各神经元的输出不直接返回自身。
想起时,一般是未知的输入。设xi(0)为未知模式的第i个要素(-1或1)
将xi(0)作为相对应的神经元的初始值,其中,0意味t=0。
反复部分:对各神经元,计算:
xi (t+1) = f (∑wijxj(t)-θi),j=1…n, j≠i
n—神经元总数;f()--Sgn(); θi—神经元i发火阈值
反复进行,直到各个神经元的输出不再变化。
利用H网想起字母“A”

代码如下
public class HopfieldMemory {
int patternNumber=1 ;
int column=3;
int row=5;
static int [][] objectArray={{-1,1,-1},{1,-1,1},{1,1,1},{1,-1,1},{1,-1,1}};
static int [][] initArray={{-1,-1,-1},{1,-1,1},{1,-1,1},{1,-1,1},{1,-1,-1}};
int [][] w=new int[15][15];
int [] temp=new int[15];
static int [] temp2=new int [15];
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
HopfieldMemory hm=new HopfieldMemory();
hm.init();
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
hm.calculate();
}
System.out.println("目标状态");
for(int i=0;i<objectArray.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<objectArray[0].length;j++){
if(objectArray[i][j]!=-1)
System.out.print(" "+objectArray[i][j]+" ");
else
System.out.print(objectArray[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("初始状态");
for(int i=0;i<initArray.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<initArray[0].length;j++){
if(initArray[i][j]!=-1)
System.out.print(" "+initArray[i][j]+" ");
else
System.out.print(initArray[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("运行后状态");
for(int i=0;i<temp2.length;i++){
if(temp2[i]!=-1)
System.out.print(" "+temp2[i]+" ");
else
System.out.print(temp2[i]+" ");
if(i==2||i==5||i==8||i==11)
System.out.println();
}
}
public void init(){
int count=0;
for(int i=0;i<objectArray.length;i++)
for(int j=0;j<objectArray[0].length;j++){
temp[count++]=objectArray[i][j];
}
int count2=0;
for(int i=0;i<initArray.length;i++)
for(int j=0;j<initArray[0].length;j++){
temp2[count2++]=initArray[i][j];
}
for(int m=0;m<w.length;m++)
for(int n=0;n<m;n++){
w[m][n]=w[n][m]=temp[m]*temp[n];
}
}
public void calculate(){
for(int i=0;i<temp2.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<temp2.length;j++)
{
temp2[i] +=w[i][j]*temp2[j];
}
if(temp2[i]>=0)
temp2[i]=1;
else
temp2[i]=-1;
}
}
}
结果如下
目标状态
-1 1 -1
1 -1 1
1 1 1
1 -1 1
1 -1 1
初始状态
-1 -1 -1
1 -1 1
1 -1 1
1 -1 1
1 -1 -1
运行后状态
-1 1 -1
1 -1 1
1 1 1
1 -1 1
1 -1 1
将结果矩阵中1连起来,就是一个字母A