Draw2D学习(一)
我们可以将Draw2d理解为SWT的“Java2d”,在它出现之前,SWT的图形处理一直是不太令人满意的。
Draw2d是SWT的轻量级组件系统,Draw2d的实例由SWT组件、LightweightSystem和Draw2d的IFigure实例集合组成。
有一张很经典的用来分析Draw2d结构的图,用来阐述各个部分之间的关系,如下:
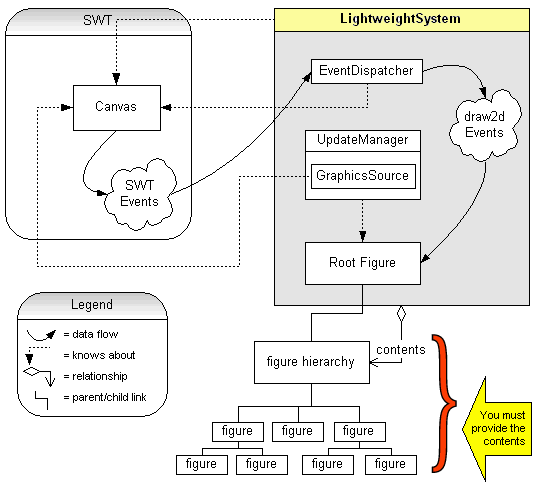
它们三者之间的关系是:LightweightSystem是桥梁,将IFigure实例连接到SWT组件上,通常是Canvas画布,或者它的子类Shell和某个Editor的Control,我们在界面上不能看到LightweightSystem,但是界面上所有能看到的组件都是直接或者间接放在它内部由它管理的,其内的组件按照树状结构排列。
LightweightSystem包含三个主要组成部分:RootFigure是LightweightSystem中所有图形的根,也就是说其他图形都是直接或间接放在RootFigure里的;EventDispatcher把Canvas上的各种事件分派给RootFigure,这些事件最终会被分派给适当的图形,请注意这个RootFigure和你应用程序中最顶层的IFigure不是同一个对象,前者是看不见的被LightweightSystem内部使用的,而后者通常会是一个可见的画布,它是直接放在前者中的;UpdateManager用来重绘图形,当Canvas被要求重绘时,LWS会调用它的performUpdate()方法。
接下来我们看一个简单的HelloWorld例子,初步接触Draw2D。
效果很简单,一个窗体中包含了一个“Hello World”字符串。
由上面的简单例子我们可以知道,一个典型的Draw2d程序,有明显的流程:
1、创建一个画布,用于作为所有figure的顶头容器
2、创建LightweightSystem的实例
3、将画布setContents到LightweightSystem
4、创建自己需要的IFigure组件,并将其组合成为自己想实现的图形。
5、将创建好的图形添加到画布之上。
其中红色部分就是我们重点要实现的部分。
接下来我们来实现一个复杂一点的,其重点是了解Draw2d的一些Figure
实现的是一个温度计,实现了温度上下限的控制,实现了温度水银柱的高度可调节,实现了精度的调节。
包括三个类,背景类,组件类,测试类,分别如下:
在测试类里面,我们给温度计加上了一个线程,每次将温度升高一点。这样温度计就可以“动”起来了。
实现效果如下图:

其实Draw2d还远不止这些知识,在接下来的几篇文章中,将会更深入Draw2d的Figure中,看看Draw2d的内置形状,连线,实现几个更精细的图形。
希望对刚接触Draw2d的同行们会有点帮助。
Draw2d是SWT的轻量级组件系统,Draw2d的实例由SWT组件、LightweightSystem和Draw2d的IFigure实例集合组成。
有一张很经典的用来分析Draw2d结构的图,用来阐述各个部分之间的关系,如下:

它们三者之间的关系是:LightweightSystem是桥梁,将IFigure实例连接到SWT组件上,通常是Canvas画布,或者它的子类Shell和某个Editor的Control,我们在界面上不能看到LightweightSystem,但是界面上所有能看到的组件都是直接或者间接放在它内部由它管理的,其内的组件按照树状结构排列。
LightweightSystem包含三个主要组成部分:RootFigure是LightweightSystem中所有图形的根,也就是说其他图形都是直接或间接放在RootFigure里的;EventDispatcher把Canvas上的各种事件分派给RootFigure,这些事件最终会被分派给适当的图形,请注意这个RootFigure和你应用程序中最顶层的IFigure不是同一个对象,前者是看不见的被LightweightSystem内部使用的,而后者通常会是一个可见的画布,它是直接放在前者中的;UpdateManager用来重绘图形,当Canvas被要求重绘时,LWS会调用它的performUpdate()方法。
接下来我们看一个简单的HelloWorld例子,初步接触Draw2D。
import org.eclipse.draw2d.IFigure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Label;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.LightweightSystem;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
/**
* 一个简单的Draw2d实例,由Canvas、LightweightSystem和IFigure组成
*/
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//新建Shell,Shell是Canvas的子类
Shell shell = new Shell();
shell.setText("Hello World");
//添加LightweihtSystem实例
LightweightSystem lws = new LightweightSystem(shell);
//添加IFigure实例
IFigure label = new Label("Hello World");
//把IFigure添加到LightweightSystem中
lws.setContents(label);
shell.open();
Display display = Display.getDefault();
while(!shell.isDisposed()){
if(!display.readAndDispatch()){
display.sleep();
}
}
}
}
效果很简单,一个窗体中包含了一个“Hello World”字符串。
由上面的简单例子我们可以知道,一个典型的Draw2d程序,有明显的流程:
1、创建一个画布,用于作为所有figure的顶头容器
2、创建LightweightSystem的实例
3、将画布setContents到LightweightSystem
4、创建自己需要的IFigure组件,并将其组合成为自己想实现的图形。
5、将创建好的图形添加到画布之上。
其中红色部分就是我们重点要实现的部分。
接下来我们来实现一个复杂一点的,其重点是了解Draw2d的一些Figure
实现的是一个温度计,实现了温度上下限的控制,实现了温度水银柱的高度可调节,实现了精度的调节。
包括三个类,背景类,组件类,测试类,分别如下:
package cn.zoomtech.irving.swt.temprature;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.*;
/**
* Background
* @author Irving.Sun
*
*/
public class BackgroundFigure extends FreeformLayeredPane
{
public BackgroundFigure()
{
setLayoutManager(new FreeformLayout());
// setBackgroundColor(ColorConstants.white);
setBorder(new LineBorder(ColorConstants.cyan));
setOpaque(true);
}
}
package cn.zoomtech.irving.swt.mytemprature;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.ColorConstants;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Ellipse;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Figure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.Label;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.LineBorder;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.PositionConstants;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.RectangleFigure;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.geometry.Rectangle;
import org.eclipse.swt.graphics.Color;
/**
* create the figures
* @author Irving.Sun
*
*/
public class MyTempratureFigure extends Figure {
// 温度颜色
private Color tempratrueColor = ColorConstants.red;
// 温度计边框颜色
private Color recOuterColor = ColorConstants.darkGreen;
// 立体效果颜色
private Color solidColor = ColorConstants.white;
// 温度计内部颜色
private Color recInnerColor = ColorConstants.gray;
// 水银柱区域
private RectangleFigure tempratureArea;
// 水银柱底端部分
private RectangleFigure bottomTempratureArea;
// 水银柱显示温度部分
private RectangleFigure showTempratureArea;
// 温度计底部
private Ellipse bottomArea;
// 显示温度信息的区域
private Label infoLabel;
// 当前温度值
private int currentTemprature;
// 显示刻度的区域
private Label mark;
// 用于显示温度的水银高度
private int showHeight;
// 温度计宽度
private int width = 12;
// 温度计高度
private int height = 200;
// 最低温度
private int min = 0;
// 最高温度
private int max = 100;
private List<Integer> standardPrecision = Arrays.asList(0, 1, 2, 5, 10);
// 精确度
// 提供0.5 ,1.0 ,5.0 ,10.0 五种精度选择
private double precision = 1.0;
// 水银部分与顶端的间距
private int marginTop = 15;
// 水银部分内顶间距
private int paddingTop = 5;
private String warningInfo = "";
private Label warningLabel;
/**
* 构造函数
*
* @param width
* @param min
* @param max
* @param precision
*/
public MyTempratureFigure(int width, int min, int max, double precision) {
if (width > 0) {
this.width = width;
}
if (min > 0) {
this.min = min;
}
if (max > 0 && min < max) {
this.max = max;
}
if (precision > 0) {
this.precision = precision;
}
}
public MyTempratureFigure() {
}
/**
* 创建图像
*/
public void createFigure() {
// 获取图像位置
Rectangle location = bounds;
int realPercision = parsePrecision();
// 底端半径默认和水银柱的宽度相等
int bottomRadius = width;
int tempratureHeight = paddingTop + height + bottomRadius;
// 温度跨度
int totalTemrature = max - min;
// 总的标度数
int totalScale = (realPercision == 0.5) ? totalTemrature * 2
: (totalTemrature % realPercision == 0 ? totalTemrature
/ realPercision : totalTemrature / realPercision + 1);
// 每个标度占的像素值
int eachScale = height / totalScale;
// 画温度计水银部分
tempratureArea = new RectangleFigure();
int x = (location.x + location.width / 2) - width / 2;
int y = (location.y + marginTop);
tempratureArea.setBounds(new Rectangle(x, y, width, tempratureHeight));
// 填充灰色
tempratureArea.setBackgroundColor(recInnerColor);
tempratureArea.setBorder(new LineBorder(recOuterColor));
tempratureArea.setOpaque(true);
add(tempratureArea);
// 显示温度的部分
if (currentTemprature < max && currentTemprature > min) {
int tempCurrentTemprature = currentTemprature - min;
if (tempCurrentTemprature > 0) {
showHeight = (tempCurrentTemprature / realPercision)
* eachScale + (tempCurrentTemprature % realPercision)
* (eachScale / realPercision);
}
showTempratureArea = new RectangleFigure();
int showTempratureAreaX = x;
int showTempratureAreaY = height + y - showHeight + paddingTop;
showTempratureArea.setBounds(new Rectangle(showTempratureAreaX,
showTempratureAreaY, width, showHeight));
// 填充红色
showTempratureArea.setBackgroundColor(tempratrueColor);
showTempratureArea.setBorder(new LineBorder(tempratrueColor));
add(showTempratureArea);
warningInfo = "";
} else {
warningInfo = "温度值不在显示范围之内!";
}
// 画温度计下半部分球
bottomArea = new Ellipse();
int bottomX = x - width / 2;
int bottomY = y + tempratureHeight - bottomRadius;
bottomArea.setBounds(new Rectangle(bottomX, bottomY, 2 * bottomRadius,
2 * bottomRadius));
bottomArea.setBackgroundColor(tempratrueColor);
// bottomArea.setBorder(new);
add(bottomArea);
// 温度计底端部分
bottomTempratureArea = new RectangleFigure();
int bottomTempratureAreaX = x;
int bottomTempratureAreaY = y + tempratureHeight - bottomRadius - 1
+ paddingTop - paddingTop;
bottomTempratureArea.setBounds(new Rectangle(bottomTempratureAreaX,
bottomTempratureAreaY, width, bottomRadius + 1 + paddingTop));
// 填充红色
bottomTempratureArea.setBackgroundColor(tempratrueColor);
bottomTempratureArea.setBorder(new LineBorder(tempratrueColor));
add(bottomTempratureArea);
// 添加刻度显示的label
mark = new Label();
int markX = x + width;
int markY = y + this.paddingTop;
int markWidth = 30;
int markHeight = height;
mark.setBounds(new Rectangle(markX, markY, markWidth, markHeight));
add(mark);
// 画刻度的位置
int cursor = markY + markHeight;
int tempTemprature = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < totalScale + 1; i++) {
tempTemprature = min + i * realPercision;
RectangleFigure tempRec = new RectangleFigure();
tempRec.setBounds(new Rectangle(markX, cursor, i % 10 == 0 ? 8 : 5,
1));
if (i % 10 == 0) {
Label tag = new Label(tempTemprature + "°");
tag.setLabelAlignment(PositionConstants.LEFT);
tag.setBounds(new Rectangle(markX + 8, cursor - 8, 50, 15));
add(tag);
}
add(tempRec);
cursor -= eachScale;
}
// 设置立体效果
RectangleFigure solidFigure = new RectangleFigure();
solidFigure.setBounds(new Rectangle(x + (2 * width / 3), y, 1,
tempratureHeight - bottomRadius - 1));
solidFigure.setBorder(new LineBorder(solidColor));
solidFigure.setBackgroundColor(solidColor);
add(solidFigure);
// 显示温度和信息的Label
int infoLabelX = location.x;
int infoLabelY = bottomY + 2 * bottomRadius + 2;
infoLabel = new Label();
infoLabel.setBounds(new Rectangle(infoLabelX, infoLabelY,
location.width, 25));
add(infoLabel);
infoLabel.setLabelAlignment(PositionConstants.CENTER);
String info = "当前温度为: " + currentTemprature + "°\n精确到: "
+ realPercision + "°";
infoLabel.setText(info);
// 显示警告信息的label
warningLabel = new Label(warningInfo);
warningLabel.setForegroundColor(tempratrueColor);
warningLabel.setBounds(new Rectangle(infoLabel.getBounds().x, infoLabel
.getBounds().y + 27, location.width, 25));
warningLabel.setLabelAlignment(PositionConstants.CENTER);
add(warningLabel);
}
/**
* 获取精度 ,如果四舍五入的值在内置精度范围之内,则返回内置精度范围 如果不在,则返回1
*
* @return
*/
private int parsePrecision() {
int realPrecision = new Long(Math.round(precision)).intValue();
if (standardPrecision.contains(realPrecision)) {
return realPrecision;
}
return 1;
}
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(int width) {
this.width = width;
repaint();
}
public int getMin() {
return min;
}
public void setMin(int min) {
this.min = min;
repaint();
}
public int getMax() {
return max;
}
public void setMax(int max) {
this.max = max;
repaint();
}
public double getPrecision() {
return precision;
}
public void setPrecision(double precision) {
this.precision = precision;
repaint();
}
public int getCurrentTemprature() {
return currentTemprature;
}
public void setCurrentTemprature(int currentTemprature) {
this.currentTemprature = currentTemprature;
repaint();
}
/**
* 刷新界面
*/
public void repaint() {
removeAll();
createFigure();
super.repaint();
}
}
在测试类里面,我们给温度计加上了一个线程,每次将温度升高一点。这样温度计就可以“动”起来了。
package cn.zoomtech.irving.swt.temprature;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.LightweightSystem;
import org.eclipse.draw2d.geometry.Rectangle;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display;
import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell;
import cn.zoomtech.irving.swt.mytemprature.MyTempratureFigure;
public class TestTemprature {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Shell shell = new Shell();
shell.setSize(200, 400);
shell.open();
shell.setText("测试图形");
LightweightSystem lws = new LightweightSystem(shell);
final BackgroundFigure backgroundChart = new BackgroundFigure();
backgroundChart.setBounds(new Rectangle(20, 20,
shell.getSize().x - 20 * 2, shell.getSize().y - 20 * 2));
lws.setContents(backgroundChart);
final MyTempratureFigure temp = new MyTempratureFigure();
temp.setBounds(backgroundChart.getBounds());
temp.setMin(10);
// temp.setMax(1000);
temp.setCurrentTemprature(40);
temp.setPrecision(2);
temp.createFigure();
backgroundChart.add(temp);
temp.setCurrentTemprature(20);
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
int oldTemprature = temp.getCurrentTemprature();
temp
.setCurrentTemprature(oldTemprature <= temp.getMax() ? oldTemprature + 1
: 0);
Display.getDefault().timerExec(100, this);
}
};
Display.getDefault().timerExec(1000, runnable);
Display display = Display.getDefault();
while (!shell.isDisposed()) {
if (!display.readAndDispatch())
display.sleep();
}
}
}
实现效果如下图:

其实Draw2d还远不止这些知识,在接下来的几篇文章中,将会更深入Draw2d的Figure中,看看Draw2d的内置形状,连线,实现几个更精细的图形。
希望对刚接触Draw2d的同行们会有点帮助。