深入JVM系列(二)之GC机制、收集器与GC调优
一、回顾JVM内存分配
需要了解更多内存模式与内存分配的,请看深入JVM系列(一)之内存模型与内存分配
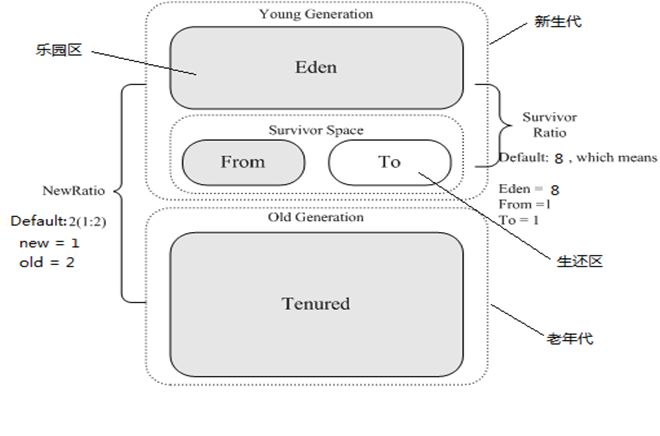
1.1、内存分配:
1、对象优先在EDEN分配2、大对象直接进入老年代
3、长期存活的对象将进入老年代
4、适龄对象也可能进入老年代:动态对象年龄判断
动态对象年龄判断:
虚拟机并不总是要求对象的年龄必须达到MaxTenuringThreshold才能晋升到老年代,当Survivor空间的相同年龄的所有对象大小总和大于Survivor空间的一半,年龄大于或等于该年龄的对象就可以直接进入老年代,无需等到MaxTenuringThreshold中指定的年龄
1.2、总结一下:
2、大对象(占内存大)、老对象(使用频繁)
3、Survivor无法容纳的对象,将进入老年代,Full GC的主要清理该处
二、JVM的GC机制
JVM有2个GC线程
第二个线程在Heap不足时,遍历Heap,将Young 区升级为Older区
Older区的大小等于-Xmx减去-Xmn,不能将-Xms的值设的过大,因为第二个线程被迫运行会降低JVM的性能。
2.1、堆内存GC
2.2、非堆内存不GC
GC不会在主程序运行期对PermGen Space进行清理,所以如果你的应用中有很多CLASS(特别是动态生成类,当然permgen space存放的内容不仅限于类)的话,就很可能出现PermGen Space错误。
2.3、内存申请、对象衰老过程
2.3.1、内存申请过程
- JVM会试图为相关Java对象在Eden中初始化一块内存区域;
- 当Eden空间足够时,内存申请结束。否则到下一步;
- JVM试图释放在Eden中所有不活跃的对象(minor collection),释放后若Eden空间仍然不足以放入新对象,则试图将部分Eden中活跃对象放入Survivor区;
- Survivor区被用来作为Eden及old的中间交换区域,当OLD区空间足够时,Survivor区的对象会被移到Old区,否则会被保留在Survivor区;
- 当old区空间不够时,JVM会在old区进行major collection;
- 完全垃圾收集后,若Survivor及old区仍然无法存放从Eden复制过来的部分对象,导致JVM无法在Eden区为新对象创建内存区域,则出现"Out of memory错误";
2.3.2、对象衰老过程
- 新创建的对象的内存都分配自eden。Minor collection的过程就是将eden和在用survivor space中的活对象copy到空闲survivor space中。对象在young generation里经历了一定次数(可以通过参数配置)的minor collection后,就会被移到old generation中,称为tenuring。
GC触发条件
| GC类型 | 触发条件 | 触发时发生了什么 | 注意 | 查看方式 |
| YGC | eden空间不足 | 清空Eden+from survivor中所有no ref的对象占用的内存 重新调整Eden 和from的大小(parallel GC会触发此项) |
全过程暂停应用 是否为多线程处理由具体的GC决定 |
jstat –gcutil gc log |
| FGC | old空间不足 perm空间不足 显示调用System.GC, RMI等的定时触发 YGC时的悲观策略 dump live的内存信息时(jmap –dump:live) |
清空heap中no ref的对象 permgen中已经被卸载的classloader中加载的class信息 如配置了CollectGenOFirst,则先触发YGC(针对serial GC) 如配置了ScavengeBeforeFullGC,则先触发YGC(针对serial GC) |
全过程暂停应用 是否为多线程处理由具体的GC决定 是否压缩需要看配置的具体GC |
jstat –gcutil gc log |
permanent generation空间不足会引发Full GC,仍然不够会引发PermGen Space错误。
三、GC监视、收集器与GC调优
3.1、监视JVM GC
首先说一下如何监视JVM GC,可以用JDK中的jstat工具,也可以在java程序启动的opt里加上如下几个参数(注:这两个参数只针对SUN的HotSpotVM):
-XX:-PrintGCPrintmessagesatgarbagecollection.Manageable. -XX:-PrintGCDetailsPrintmoredetailsatgarbagecollection.Manageable.(Introducedin1.4.0.) -XX:-PrintGCTimeStampsPrinttimestampsatgarbagecollection.Manageable(Introducedin1.4.0.)
当把-XX:-PrintGCDetails加入到javaopt里以后可以看见如下输出:
[GC[DefNew:34538K->2311K(36352K),0.0232439secs]45898K->15874K(520320K),0.0233874secs]
[FullGC[Tenured:13563K->15402K(483968K),0.2368177secs]21163K->15402K(520320K),[Perm:28671K->28635K(28672K)],0.2371537secs]
他们分别显示了JVM GC的过程,清理出了多少空间。第一行GC使用的是‘普通GC’(MinorCollections),第二行使用的是‘全GC’(MajorCollections)。他们的区别很大,在第一行最后我们可以看见他的时间是0.0233874秒,而第二行的FullGC的时间是0.2371537秒。第二行的时间是第一行的接近10倍,也就是我们这次调优的重点,减少FullGC的次数,以为FullGC会暂停程序比较长的时间,如果FullGC的次数比较多。程序就会经常性的假死。
注:
GC信息的格式
[GC [<collector>: <starting occupancy1> -> <ending occupancy1>, <pause time1> secs] <starting occupancy3> -> <ending occupancy3>, <pause time3> secs]
<collector> GC为minor收集过程中使用的垃圾收集器起的内部名称.
<starting occupancy1> young generation 在进行垃圾收集前被对象使用的存储空间.
<ending occupancy1> young generation 在进行垃圾收集后被对象使用的存储空间
<pause time1> minor收集使应用暂停的时间长短(秒)
<starting occupancy3> 整个堆(Heap Size)在进行垃圾收集前被对象使用的存储空间
<ending occupancy3> 整个堆(Heap Size)在进行垃圾收集后被对象使用的存储空间
<pause time3> 整个垃圾收集使应用暂停的时间长短(秒),包括major收集使应用暂停的时间(如果发生了major收集).
GC信息的选项
-XX:+PrintGCDetails 显示GC的详细信息
-XX:+PrintGCApplicationConcurrentTime 打印应用执行的时间
-XX:+PrintGCApplicationStoppedTime 打印应用被暂停的时间
3.2、collector收集器的种类
GC在 HotSpot VM 5.0里有四种:
incremental (sometimes called train) low pause collector已被废弃,不在介绍.
| 类别 | serial collector | parallel collector (throughput collector) |
concurrent collector (concurrent low pause collector) |
| 介绍 | 单线程收集器 使用单线程去完成所有的gc工作,没有线程间的通信,这种方式会相对高效 |
并行收集器 使用多线程的方式,利用多CUP来提高GC的效率 主要以到达一定的吞吐量为目标 |
并发收集器 使用多线程的方式,利用多CUP来提高GC的效率 并发完成大部分工作,使得gc pause短 |
| 试用场景 | 单处理器机器且没有pause time的要求 | 适用于科学技术和后台处理 有中规模/大规模数据集大小的应用且运行在多处理器上,关注吞吐量(throughput) |
适合中规模/大规模数据集大小的应用,应用服务器,电信领域 关注response time,而不是throughput |
| 使用 | Client模式下默认 可使用 可用-XX:+UseSerialGC强制使用 优点:对server应用没什么优点 缺点:慢,不能充分发挥硬件资源 |
Server模式下默认 --YGC:PS FGC:Parallel MSC 可用-XX:+UseParallelGC或-XX:+UseParallelOldGC强制指定 --ParallelGC代表FGC为Parallel MSC --ParallelOldGC代表FGC为Parallel Compacting 优点:高效 缺点:当heap变大后,造成的暂停时间会变得比较长 |
可用-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC强制指定 优点: 对old进行回收时,对应用造成的暂停时间非常端,适合对latency要求比较高的应用 缺点: 1.内存碎片和浮动垃圾 2.old去的内存分配效率低 3.回收的整个耗时比较长 4.和应用争抢CPU |
| 内存回收触发 | YGC eden空间不足 FGC old空间不足 perm空间不足 显示调用System.gc() ,包括RMI等的定时触发 YGC时的悲观策略 dump live的内存信息时(jmap –dump:live) |
YGC eden空间不足 FGC old空间不足 perm空间不足 显示调用System.gc() ,包括RMI等的定时触发 YGC时的悲观策略--YGC前&YGC后 dump live的内存信息时(jmap –dump:live) |
YGC eden空间不足 CMS GC 1.old Gen的使用率大的一定的比率 默认为92% 2.配置了CMSClassUnloadingEnabled,且Perm Gen的使用达到一定的比率 默认为92% 3.Hotspot自己根据估计决定是否要触法 4.在配置了ExplictGCInvokesConcurrent的情况下显示调用了System.gc. Full GC(Serial MSC) promotion failed 或 concurrent Mode Failure时; |
| 内存回收触发时发生了什么 | YGC eden空间不足 FGC old空间不足 perm空间不足 显示调用System.gc() ,包括RMI等的定时触发 YGC时的悲观策略 dump live的内存信息时(jmap –dump:live) |
YGC 同serial动作基本相同,不同点: 1.多线程处理 2.YGC的最后不仅重新计算Tenuring Threshold,还会重新调整Eden和From的大小 FGC 1.如配置了ScavengeBeforeFullGC(默认),则先触发YGC(??) 2.MSC:清空heap中的no ref对象,permgen中已经被卸载的classloader中加载的class信息,并进行压缩 3.Compacting:清空heap中部分no ref的对象,permgen中已经被卸载的classloader中加载的class信息,并进行部分压缩 多线程做以上动作. |
YGC 同serial动作基本相同,不同点: 1.多线程处理 CMSGC: 1.old gen到达比率时只清除old gen中no ref的对象所占用的空间 2.perm gen到达比率时只清除已被清除的classloader加载的class信息 FGC 同serial |
| 细节参数 | 可用-XX:+UseSerialGC强制使用 -XX:SurvivorRatio=x,控制eden/s0/s1的大小 -XX:MaxTenuringThreshold,用于控制对象在新生代存活的最大次数 -XX:PretenureSizeThreshold=x,控制超过多大的字节的对象就在old分配. |
-XX:SurvivorRatio=x,控制eden/s0/s1的大小 -XX:MaxTenuringThreshold,用于控制对象在新生代存活的最大次数 -XX:UseAdaptiveSizePolicy 去掉YGC后动态调整eden from已经tenuringthreshold的动作 -XX:ParallelGCThreads 设置并行的线程数 |
-XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction 设置old gen使用到达多少比率时触发 -XX:CMSInitiatingPermOccupancyFraction,设置Perm Gen使用到达多少比率时触发 -XX:+UseCMSInitiatingOccupancyOnly禁止hostspot自行触发CMS GC |
注:
- throughput collector与concurrent low pause collector的区别是throughput collector只在young area使用使用多线程,而concurrent low pause collector则在tenured generation也使用多线程。
- 根据官方文档,他们俩个需要在多CPU的情况下,才能发挥作用。在一个CPU的情况下,会不如默认的serial collector,因为线程管理需要耗费CPU资源。而在两个CPU的情况下,也提高不大。只是在更多CPU的情况下,才会有所提高。当然 concurrent low pause collector有一种模式可以在CPU较少的机器上,提供尽可能少的停顿的模式,见CMS GC Incremental mode。
- 当要使用throughput collector时,在java opt里加上-XX:+UseParallelGC,启动throughput collector收集。也可加上-XX:ParallelGCThreads=<desired number>来改变线程数。还有两个参数 -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=<nnn>和 -XX:GCTimeRatio=<nnn>,MaxGCPauseMillis=<nnn>用来控制最大暂停时间,而-XX: GCTimeRatio可以提高GC说占CPU的比,以最大话的减小heap。
附注SUN的官方说明:
1. The throughput collector: this collector uses a parallel version of the young generation collector. It is used if the -XX:+UseParallelGC option is passed on the command line. The tenured generation collector is the same as the serial collector. 2. The concurrent low pause collector: this collector is used if the -Xincgc™ or -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC is passed on the command line. The concurrent collector is used to collect the tenured generation and does most of the collection concurrently with the execution of the application. The application is paused for short periods during the collection. A parallel version of the young generation copying collector is used with the concurrent collector. The concurrent low pause collector is used if the option -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC is passed on the command line. 3. The incremental (sometimes called train) low pause collector: this collector is used only if -XX:+UseTrainGC is passed on the command line. This collector has not changed since the J2SE Platform version 1.4.2 and is currently not under active development. It will not be supported in future releases. Please see the 1.4.2 GC Tuning Document for information on this collector.
CMS GC Incremental mode
当要使用 concurrent low pause collector时,在java的opt里加上 -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC。concurrent low pause collector还有一种为CPU少的机器准备的模式,叫Incremental mode。这种模式使用一个CPU来在程序运行的过程中GC,只用很少的时间暂停程序,检查对象存活。
在Incremental mode里,每个收集过程中,会暂停两次,第二次略长。第一次用来,简单从root查询存活对象。第二次用来,详细检查存活对象。整个过程如下:
* stop all application threads; do the initial mark; resume all application threads(第一次暂停,初始话标记) * do the concurrent mark (uses one procesor for the concurrent work)(运行是标记) * do the concurrent pre-clean (uses one processor for the concurrent work)(准备清理) * stop all application threads; do the remark; resume all application threads(第二次暂停,标记,检查) * do the concurrent sweep (uses one processor for the concurrent work)(运行过程中清理) * do the concurrent reset (uses one processor for the concurrent work)(复原)
当要使用Incremental mode时,需要使用以下几个变量:
-XX:+CMSIncrementalMode default: disabled 启动i-CMS模式(must with -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC) -XX:+CMSIncrementalPacing default: disabled 提供自动校正功能 -XX:CMSIncrementalDutyCycle=<N> default: 50 启动CMS的上线 -XX:CMSIncrementalDutyCycleMin=<N> default: 10 启动CMS的下线 -XX:CMSIncrementalSafetyFactor=<N> default: 10 用来计算循环次数 -XX:CMSIncrementalOffset=<N> default: 0 最小循环次数(This is the percentage (0-100) by which the incremental mode duty cycle is shifted to the right within the period between minor collections.) -XX:CMSExpAvgFactor=<N> default: 25 提供一个指导收集数
-XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC \ -XX:+CMSIncrementalMode \ -XX:+CMSIncrementalPacing \ -XX:CMSIncrementalDutyCycleMin=0 \ -XX:CMSIncrementalDutyCycle=10 \ -XX:+PrintGC Details \ -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps \ -XX:-TraceClassUnloading
3.3、如何选择collector
- app运行在单处理器机器上且没有pause time的要求,让vm选择UseSerialGC.
- 重点考虑peak application performance(高性能),没有pause time太严格要求,让vm选择或者UseParallelGC+UseParallelOldGC(optionally).
- 重点考虑response time,pause time要小,UseConcMarkSweepGC.
Garbage Collctor – Future
Garbage First(G1) jdk1.6 update 14 or jdk7 few flags need to set -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=100 -XX:GCPauseIntervalMillis=6000
还没尝试过使用…
Summary
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class SummaryCase { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { List<Object> caches = new ArrayList<Object>(); for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) { caches.add(new byte[1024 * 1024 * 3]); Thread.sleep(1000); } caches.clear(); for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { caches.add(new byte[1024 * 1024 * 3]); Thread.sleep(1000); } } }
}
2.062: [GC Desired survivor size 1310720 bytes, new threshold 7 (max 15) 6467K->6312K(29440K), 0.0038214 secs] 4.066: [GC Desired survivor size 1310720 bytes, new threshold 7 (max 15) 12536K->12440K(29440K), 0.0036804 secs] 6.070: [GC Desired survivor size 1310720 bytes, new threshold 7 (max 15) 18637K->18584K(29440K), 0.0040175 secs] 6.074: [Full GC 18584K->18570K(29440K), 0.0031329 secs] 8.078: [Full GC 24749K->3210K(29440K), 0.0045590 secs]
(具体分析见 http://rdc.taobao.com/team/jm/archives/440 )
2.047: [GC Desired survivor size 524288 bytes, new threshold 15 (max 15) - age 1: 142024 bytes, 142024 total 6472K->6282K(29696K), 0.0048686 secs] 4.053: [GC Desired survivor size 524288 bytes, new threshold 15 (max 15) - age 2: 141880 bytes, 141880 total 12512K->12426K(29696K), 0.0047334 secs] 6.058: [GC Desired survivor size 524288 bytes, new threshold 15 (max 15) - age 3: 141880 bytes, 141880 total 18627K->18570K(29696K), 0.0049135 secs] 8.063: [Full GC 24752K->3210K(29696K), 0.0077895 secs](具体分析见 http://rdc.taobao.com/team/jm/archives/458 )
四、GC调优的小例子
例1:Heap size 设置
JVM 堆的设置是指java程序运行过程中JVM可以调配使用的内存空间的设置.JVM在启动的时候会自动设置Heap size的值,其初始空间(即-Xms)是物理内存的1/64,最大空间(-Xmx)是物理内存的1/4。可以利用JVM提供的-Xmn -Xms -Xmx等选项可进行设置。
Heap size 的大小是Young Generation 和Tenured Generaion 之和。
当在JAVA_HOME下demo/jfc/SwingSet2/目录下执行下面的命令。
java -jar -Xmn4m -Xms16m -Xmx16m SwingSet2.jar
系统输出为:
Exception in thread "Image Fetcher 0" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space Exception in thread "Image Fetcher 3" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space Exception in thread "Image Fetcher 1" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space Exception in thread "Image Fetcher 2" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
除了这些异常信息外,还会发现程序的响应速度变慢了。这说明Heap size 设置偏小,GC占用了更多的时间,而应用分配到的执行时间较少。
提示:在JVM中如果98%的时间是用于GC且可用的Heap size 不足2%的时候将抛出此异常信息。
将上面的命令换成以下命令执行则应用能够正常使用,且未抛出任何异常。
java -jar -Xmn4m -Xms16m -Xmx32m SwingSet2.jar
提示:Heap Size 最大不要超过可用物理内存的80%,一般的要将-Xms和-Xmx选项设置为相同,而-Xmn为1/4的-Xmx值。
例2:Young Generation(-Xmn)的设置
假设将Young generation 的大小设置为4M ,即执行java -jar -verbose:gc -Xmn4m -Xms32m -Xmx32m -XX:+PrintGCDetails SwingSet2.jar,
屏幕输出如下(节选)
[GC [DefNew: 3968K->64K(4032K), 0.0923407 secs] 3968K->2025K(32704K), 0.0931870 secs] [GC [DefNew: 4021K->64K(4032K), 0.0356847 secs] 5983K->2347K(32704K), 0.0365441 secs] [GC [DefNew: 3995K->39K(4032K), 0.0090603 secs] 6279K->2372K(32704K), 0.0093377 secs]
将程序体制并将Young Generation的大小设置为8M,即执行
java -jar -verbose:gc -Xmn8m -Xms32m -Xmx32m -XX:+PrintGCDetails SwingSet2.jar
屏幕输出如下(节选)
[GC [DefNew: 7808K->192K(8000K), 0.1016784 secs] 7808K->2357K(32576K), 0.1022834 secs] [GC [DefNew: 8000K->70K(8000K), 0.0149659 secs] 10165K->2413K(32576K), 0.0152557 secs] [GC [DefNew: 7853K->59K(8000K), 0.0069122 secs] 10196K->2403K(32576K), 0.0071843 secs] [GC [DefNew: 7867K->171K(8000K), 0.0075745 secs] 10211K->2681K(32576K), 0.0078376 secs] [GC [DefNew: 7970K->192K(8000K), 0.0201353 secs] 10480K->2923K(32576K), 0.0206867 secs] [GC [DefNew: 7979K->30K(8000K), 0.1787079 secs] 10735K->4824K(32576K), 0.1790065 secs]
那么根据GC输出的信息(这里取第一行)做一下Minor收集的比较。可以看出两次的Minor收集分别在Young generation中找回3904K(3968K->64K)和7616K(7808K->192K)而对于整个jvm则找回 1943K(3968K->2025)和5451K(7808K->2357K)。第一种情况下Minor收集了大约50%(1943/3904)的对象,而另外的50%的对象则被移到了tenured generation。在第二中情况下Minor收集了大约72%的对象,只有不到30%的对象被移到了Tenured Generation.这个例子说明此应用在的Young generation 设置为4m时显的偏小。
提示:一般的Young Generation的大小是整个Heap size的1/4。Young generation的minor收集率应一般在70%以上。当然在实际的应用中需要根据具体情况进行调整。
例3:Young Generation对应用响应的影响
java -jar -verbose:gc -Xmn4m -Xms32m -Xmx32m -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCApplicationConcurrentTime -XX:+PrintGCApplicationStoppedTime SwingSet2.jar
屏幕输出如下(节选)
Application time: 0.5114944 seconds [GC [DefNew: 3968K->64K(4032K), 0.0823952 secs] 3968K->2023K(32704K), 0.0827626 secs] Total time for which application threads were stopped: 0.0839428 seconds Application time: 0.9871271 seconds [GC [DefNew: 4020K->64K(4032K), 0.0412448 secs] 5979K->2374K(32704K), 0.0415248 secs] Total time for which application threads were stopped: 0.0464380 seconds
Young Generation 的Minor收集占用的时间可以计算如下:
应用线程被中断的总时常/(应用执行总时?L+应用线程被中断的总时常),那么在本例中垃圾收集占用的时?L约为系统的5%~14%。那么当垃圾收集占用的时间的比例越大的时候,系统的响应将越慢。
提示:对于互联网应用系统的响应稍微慢一些,用户是可以接受的,但是对于GUI类型的应用响应速度慢将会给用户带来非常不好的体验。
例4:如何决定Tenured Generation 的大小
java -verbose:gc -Xmn8m -Xmx32m-XX:+PririntGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps java类
命令行将提示(只提取了Major收集)
111.042: [GC 111.042: [DefNew: 8128K->8128K(8128K), 0.0000505 secs]111.042: [Tenured: 18154K->2311K(24576K), 0.1290354 secs] 26282K->2311K(32704K), 0.1293306 secs] 122.463: [GC 122.463: [DefNew: 8128K->8128K(8128K), 0.0000560 secs]122.463: [Tenured: 18630K->2366K(24576K), 0.1322560 secs] 26758K->2366K(32704K), 0.1325284 secs] 133.896: [GC 133.897: [DefNew: 8128K->8128K(8128K), 0.0000443 secs]133.897: [Tenured: 18240K->2573K(24576K), 0.1340199 secs] 26368K->2573K(32704K), 0.1343218 secs] 144.112: [GC 144.112: [DefNew: 8128K->8128K(8128K), 0.0000544 secs]144.112: [Tenured: 16564K->2304K(24576K), 0.1246831 secs] 24692K->2304K(32704K), 0.1249602 secs]
再执行
java -verbose:gc -Xmn8m -Xmx64m-XX:+PririntGCDetails -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps java类
命令行将提示(只提取了Major收集)
90.597: [GC 90.597: [DefNew: 8128K->8128K(8128K), 0.0000542 secs]90.597: [Tenured: 49841K->5141K(57344K), 0.2129882 secs] 57969K->5141K(65472K), 0.2133274 secs] 120.899: [GC 120.899: [DefNew: 8128K->8128K(8128K), 0.0000550 secs]120.899: [Tenured: 50384K->2430K(57344K), 0.2216590 secs] 58512K->2430K(65472K), 0.2219384 secs] 153.968: [GC 153.968: [DefNew: 8128K->8128K(8128K), 0.0000511 secs]153.968: [Tenured: 51164K->2309K(57344K), 0.2193906 secs] 59292K->2309K(65472K), 0.2196372 secs]
可以看出在Heap size 为32m的时候系统等候时间约为0.13秒左右,而设置为64m的时候等候时间则增大到0.22秒左右了。但是在32m的时候系统的Major收集间隔为 10秒左右,而Heap size 增加到64m的时候为30秒。那么应用在运行的时候是选择32m还是64m呢? 如果应用是web类型(即要求有大的吞吐量)的应用则使用64m(即 heapsize大一些)的比较好。对于要求实时响应要求较高的场合(例如GUI型的应用)则使用32m比较好一些。
注意:
1。因为在JVM5运行时已经对Heap-size进行了优化,所以在能确定java应用运行时不会超过默认的Heap size的情况下建议不要对这些值进行修改。
2。 Heap size的 -Xms -Xmn 设置不要超出物理内存的大小。否则会提示“Error occurred during initialization of VM Could not reserve enough space for object heap”。
例5:如何缩短minor收集的时间
java -jar -server -verbose:gc -Xmn8m -Xms32m -Xmx32m SwingSet2.jar
系统将输出如下信息(片段〕
[GC 7807K->2641K(32576K), 0.0676654 secs] [GC 10436K->3108K(32576K), 0.0245328 secs] [GC 10913K->3176K(32576K), 0.0072865 secs] [GC 10905K->4097K(32576K), 0.0223928 secs]
之后再执行
java -jar -server -verbose:gc -XX:+UseParNewGC -Xmn8m -Xms32m -Xmx32m SwingSet2.jar
系统将输出如下信息(片段〕
[ParNew 7808K->2656K(32576K), 0.0447687 secs] [ParNew 10441K->3143K(32576K), 0.0179422 secs] [ParNew 10951K->3177K(32576K), 0.0031914 secs] [ParNew 10985K->3867K(32576K), 0.0154991 secs]
很显然使用了-XX:+UseParNewGC选项的minor收集的时间要比不使用的时候优。
例6:如何缩短major收集的时间
java -jar -verbose:gc -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC -XX:+UseParNewGC -Xmn64m -Xms256m -Xmx256m SwingSet2.jar
系统将输出如下信息(片段〕
[Full GC 22972K->18690K(262080K), 0.2326676 secs] [Full GC 18690K->18690K(262080K), 0.1701866 secs
之后再执行
java -jar -verbose:gc -XX:+UseParNewGC -Xmn64m -Xms256m -Xmx256m SwingSet2.jar
系统将输出如下信息(片段〕
[Full GC 56048K->18869K(260224K), 0.3104852 secs]
提示:此选项在Heap Size 比较大而且Major收集时间较长的情况下使用更合适。
例7:关于-server选项
在JVM中将运行中的类认定为server-class的时候使用此选项。SUN 的Hot Spot JVM5 如果判断到系统的配置满足如下条件则自动将运行的类认定为server-class,并且会自动设置jvm的选项(当没有手工设置这选项的时候〕而且 HOTSPOT JVM5提供了自动调优的功能,他会根据JVM的运行情况进行调整。如果没有特别的需要是不需要太多的人工干预的。SUN形象的称这个机制为“人体工学 ”(Ergonomics〕。具体可以参考http://java.sun.com/docs/hotspot/gc5.0/ergo5.html
*.具有2个或更多个物理的处理器
*.具有2G或者更多的物理内存
提示:此选项要放在所有选项的前面。例如:java -server 其他选项 java类