Flash/Flex学习笔记(36):碰撞检测
碰撞检测基本上可能分为二类:对象与对象的碰撞检测、对象与点的碰撞检测
为了方便测试,先写一个box类(生成一个小矩形)
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
public class Box extends Sprite {
private var w:Number;
private var h:Number;
private var color:uint;
public var vx:Number=0;
public var vy:Number=0;
public function Box(width:Number=50, height:Number=50, color:uint=0xff0000) {
w=width;
h=height;
this.color=color;
init();
}
public function init():void {
graphics.beginFill(color);
graphics.drawRect(-w / 2, -h / 2, w, h);
graphics.endFill();
}
}
}
最基本的对象碰撞检测:hitTestObject
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.events.Event;
public class Boxes extends Sprite {
private var box:Box;
private var boxes:Array;
private var gravity:Number=0.1;
public function Boxes() {
init();
}
private function init():void {
boxes = new Array();
createBox();
addEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME, onEnterFrame);
}
private function onEnterFrame(event:Event):void {
box.vy+=gravity;
box.y+=box.vy;
//如果物体下落到了舞台(最下)边界,则再造一个出来往下掉
if (box.y+box.height/2>stage.stageHeight) {
box.y=stage.stageHeight-box.height/2;
createBox();
} else{
for (var i:uint = 0; i < boxes.length; i++) {
//每个正在下掉的物体与其它物体做(矩形)碰撞检测
if (box!=boxes[i]&&box.hitTestObject(boxes[i])) {
box.y=boxes[i].y-boxes[i].height/2-box.height/2;
//堆到顶了,则停止
if (box.y<=box.height/2){
removeEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME,onEnterFrame);
} else{
createBox();
}
}
}
}
}
private function createBox():void {
box=new Box(Math.random()*40+10,Math.random()*40+10,Math.random()*0xffffff);
box.x=Math.random()*stage.stageWidth;
addChild(box);
boxes.push(box);
}
}
}
如果把Box换成前面例子中的Ball,就是下面这个样子:
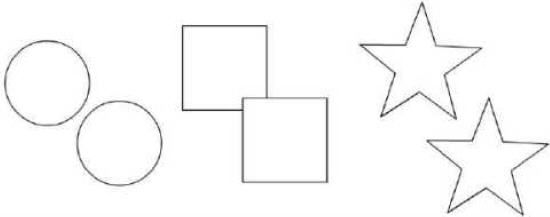
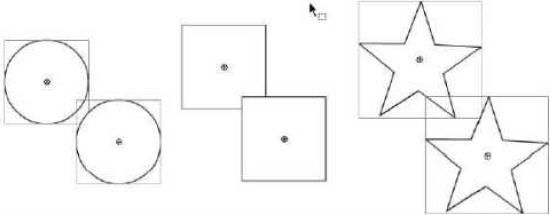
很明显:矩形换成球后,碰撞检测变得不精确了,有一些球似乎并没有真正撞到其它球也停下来了,这是为什么腻?
答案就在于:Flash对象碰撞检测默认采用“对象的矩形边界”做为检测依据。上面二张图演示了这一细节:第一张图虽然肉眼看上去只有二个矩形相交了,但是在Flash看来,其实每对图形都碰到了(第二张图),所以大家应该也能明白为啥换成球后,有些球会浮在空中了。
对象与点的碰撞检测:hitTestPoint
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.events.Event;
import flash.text.TextField;
public class PointHitTest extends Sprite {
private var ball:Ball;
private var box:Box;
private var txt:TextField = new TextField();
public function PointHitTest() {
init();
}
private function init():void {
ball=new Ball;
addChild(ball);
ball.x=stage.stageWidth/2;
ball.y=stage.stageHeight/2;
box = new Box(90,90);
addChild(box);
box.x = 100;
box.y = ball.y;
addEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME,EnterFrameHandler);
addChild(txt);
txt.selectable = false;
}
private function EnterFrameHandler(event:Event):void {
if (ball.hitTestPoint(mouseX,mouseY) || box.hitTestPoint(mouseX,mouseY)) {
txt.text = "碰到了!";
} else{
txt.text = "";
}
txt.x = mouseX + 15;
txt.y = mouseY;
}
}
}
用鼠标在二个物体上划过,会看到鼠标所在点与矩形及小球的碰撞检测结果,同样这里也存在一个问题:对于小球而言,默认也是采用矩形边界检测的,所以鼠标移到小球的边角时,虽然还没碰到球,也提示"碰到了",还好Flash提供了一个可选参数,以改进检测的精确度,只要把hitTestPoint第三个可选参数设置为true即可
if (ball.hitTestPoint(mouseX,mouseY) || box.hitTestPoint(mouseX,mouseY,true)) {
基于距离的检测:即检测二个物体的中心点距离是否低于最小距离
var ball_1:Ball=new Ball(70,0xff0000);
var ball_2:Ball=new Ball(70,0x0000ff);
ball_1.x=stage.stageWidth/2;
ball_1.y=stage.stageHeight/2;
ball_2.x=stage.stageWidth/2;
ball_2.y=stage.stageHeight/2;
ball_1.vx = Math.random()*20 - 20;
ball_1.vy = Math.random()*20 - 20;
ball_2.vx = Math.random()*20 - 20;
ball_2.vy = Math.random()*20 - 20;
addChild(ball_1);
addChild(ball_2);
addEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME,EnterFrameHandler);
function EnterFrameHandler(e:Event):void {
ball_1.x+=ball_1.vx;
ball_1.y+=ball_1.vy;
ball_2.x+=ball_2.vx;
ball_2.y+=ball_2.vy;
CheckBoundary(ball_1);
CheckBoundary(ball_2);
var dx:Number=ball_1.x-ball_2.x;
var dy:Number=ball_1.y-ball_2.y;
var dist:Number=Math.sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy);
if (dist<(ball_1.radius + ball_2.radius)) {
var angle:Number=Math.atan2(dy,dx);
ball_1.vx=dist*Math.cos(angle)*0.1;
ball_1.vy=dist*Math.sin(angle)*0.1;
ball_2.vx=dist*Math.cos(angle)*-0.1;
ball_2.vy=dist*Math.sin(angle)*-0.1;
}
}
function CheckBoundary(b:Ball) {
if (b.x>stage.stageWidth-b.width/2||b.x<=b.width/2) {
b.x-=b.vx;
b.vx*=-1;
}
if (b.y>stage.stageHeight-b.height/2||b.y<=b.height/2) {
b.y-=b.vy;
b.vy*=-1;
}
}
很明显,这种方法对于圆形物体是十分精确的,但对于非规则形状,只能近似检测.
如果结合上二篇提到的弹性运动,可以做出更复杂的动画:
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.events.Event;
public class Bubbles extends Sprite {
private var balls:Array;
private var numBalls:Number=10;
private var centerBall:Ball;
private var bounce:Number=-1;
private var spring:Number=0.2;
public function Bubbles() {
init();
}
private function init():void {
balls=new Array ;
centerBall=new Ball(100,0xcccccc);
addChild(centerBall);
centerBall.x=stage.stageWidth/2;
centerBall.y=stage.stageHeight/2;
for (var i:uint=0; i<numBalls; i++) {
var ball:Ball=new Ball(Math.random()*40+5,Math.random()*0xffffff);
ball.x=Math.random()*stage.stageWidth;
ball.y=Math.random()*stage.stageHeight;
ball.vx=(Math.random()*2-1)*10;
ball.vy=(Math.random()*2-1)*10;
addChild(ball);
balls.push(ball);
}
addEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME,onEnterFrame);
}
private function onEnterFrame(event:Event):void {
for (var i:uint=0; i<numBalls; i++) {
var ball:Ball=balls[i];
move(ball);
var dx:Number=ball.x-centerBall.x;
var dy:Number=ball.y-centerBall.y;
var dist:Number=Math.sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy);
var minDist:Number=ball.radius+centerBall.radius;
if (dist<minDist) {
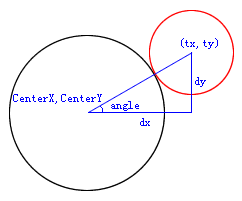
var angle:Number=Math.atan2(dy,dx);
var tx:Number=centerBall.x+Math.cos(angle)*minDist;//弹性运动的目标点x坐标
var ty:Number=centerBall.y+Math.sin(angle)*minDist;//弹性运动的目标点y坐标
ball.vx+=(tx-ball.x)*spring;
ball.vy+=(ty-ball.y)*spring;
}
}
}
private function move(ball:Ball):void {
ball.x+=ball.vx;
ball.y+=ball.vy;
if (ball.x+ball.radius>stage.stageWidth) {
ball.x=stage.stageWidth-ball.radius;
ball.vx*=bounce;
} else if (ball.x-ball.radius<0) {
ball.x=ball.radius;
ball.vx*=bounce;
}
if (ball.y+ball.radius>stage.stageHeight) {
ball.y=stage.stageHeight-ball.radius;
ball.vy*=bounce;
} else if (ball.y-ball.radius<0) {
ball.y=ball.radius;
ball.vy*=bounce;
}
}
}
}
原理图:
多物体基于距离的碰撞检测:
package {
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.events.Event;
public class Bubbles2 extends Sprite {
private var balls:Array;
private var numBalls:Number=20;
private var bounce:Number=-0.9;
private var spring:Number=0.2;
private var gravity:Number=1;
public function Bubbles2() {
init();
}
private function init():void {
balls = new Array();
for (var i:uint = 0; i < numBalls; i++) {
var ball:Ball=new Ball(Math.random()*30+20,Math.random()*0xffffff);
ball.x=Math.random()*stage.stageWidth;
ball.y=Math.random()*stage.stageHeight;
ball.vx=Math.random()*6-3;
ball.vy=Math.random()*6-3;
addChild(ball);
balls.push(ball);
}
addEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME, onEnterFrame);
}
private function onEnterFrame(event:Event):void {
for (var i:uint = 0; i < numBalls - 1; i++) {
var ball0:Ball=balls[i];
for (var j:uint = i + 1; j < numBalls; j++) {
var ball1:Ball=balls[j];
var dx:Number=ball1.x-ball0.x;
var dy:Number=ball1.y-ball0.y;
var dist:Number=Math.sqrt(dx*dx+dy*dy);
var minDist:Number=ball0.radius+ball1.radius;
if (dist<minDist) {
/*
var angle:Number=Math.atan2(dy,dx);
var tx:Number=ball0.x+Math.cos(angle)*minDist;
var ty:Number=ball0.y+Math.sin(angle)*minDist;
*/
var tx:Number=ball0.x + (dx/dist)*minDist;
var ty:Number=ball0.y + (dy/dist)*minDist;
var ax:Number = (tx - ball1.x) * spring;
var ay:Number = (ty - ball1.y) * spring;
ball0.vx-=ax;
ball0.vy-=ay;
ball1.vx+=ax;
ball1.vy+=ay;
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < numBalls; i++) {
var ball:Ball=balls[i];
move(ball);
}
}
private function move(ball:Ball):void {
ball.vy+=gravity;
ball.x+=ball.vx;
ball.y+=ball.vy;
if (ball.x+ball.radius>stage.stageWidth) {
ball.x=stage.stageWidth-ball.radius;
ball.vx*=bounce;
} else if (ball.x - ball.radius < 0) {
ball.x=ball.radius;
ball.vx*=bounce;
}
if (ball.y+ball.radius>stage.stageHeight) {
ball.y=stage.stageHeight-ball.radius;
ball.vy*=bounce;
} else if (ball.y - ball.radius < 0) {
ball.y=ball.radius;
ball.vy*=bounce;
}
}
}
}