在web项目中,对数据的导入导出是非常实用和常见的,而excel文件则是十分常见的格式。
Excel导入——解析已存在的excel文件,并把里面的数据一一对应,插入到数据库表中,同时在页面上显示出来。(通常数据库里面会有一张字段与该excel表头一一对应的表);
Excel导出——把数据库中的表的数据导出,保存在excel文件中。
poi相对于jxl,是更为成熟的excel解析技术。这段时间折腾了几天,终于弄清楚了过程,特此记录。
一些主要的基本概念:poi-3.8-x.jar
HSSFWokbook——对应excel文件的工作薄
HSSFSheet——对应excel文件的表空间
HSSFRow——对应excel文件的表的行
HSSFCell——对应excel文件的表单元格
HSSFCellStyle——对应excel文件的表单元格样式
一、Excel导入(需上传已存在的excel文件)
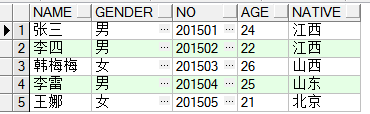
已经存在的excel文件:
jsp页面:
<form name="" class="k-form col3" id="M2100F004">
<label class="k-field-label">文件导入:</label>
<input class="form-control k-field-file" data-allowblank="false" type="file" id="file" name="excelFile" />
<button type="button" class="xxx" type="SUBMIT" onclick="importExcel">导入</button>
</form>
上传的js:
$.ajaxFileUpload({
url : "demo/demo-importExcel.json",
//dataType : 'json',
secureuri : false,
fileElementId : 'file',
success : function(res, status) { //服务器成功响应处理函数
if (status) {
//some code
},
error : function(res, status, e) {//服务器响应失败处理函数
alert("导入数据异常:文件导入过程异常。");
}
});
}else{
alert("导入数据异常:系统只支持Excel模板文件导入,请选择正确的模板文件.");
return;
}
}
对应的后台:
@RequestMapping(value = "/demo/demo-importExcel.json")
@ResponseBody
public String importExcel( @RequestParam(value = "excelFile") MultipartFile excelFile,HttpServletRequest request) throws BiffException, IOException, KPromptException{
if (null == excelFile) {
result = "模板文件为空,请选择文件";
return result;
}
// String path = request.getSession().getServletContext().getRealPath("demo2");
String path = "E:\\demo";
//容错处理
File dir = new File(path);
if(!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
String fileName = excelFile.getOriginalFilename();//report.xls
String fileName2 = excelFile.getName();//excelFile
InputStream fis = excelFile.getInputStream();
List<Map<String, Stirng>> data = ExcelImportUtil..parseExcel(fis);
//解析到的数据就可以做一些数据库的插入操作了……
return "success";
}
重点来了,excel导入我把它封装成了一个工具方法:
public class ExcelImportUtil {
public static List<Map<String, String>> parseExcel(InputStream fis) {
List<Map<String, String>> data = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();;
try {
HSSFWorkbook book = new HSSFWorkbook(fis);
HSSFSheet sheet = book.getSheetAt(0);
int firstRow = sheet.getFirstRowNum();
int lastRow = sheet.getLastRowNum();
//除去表头和第一行
// ComnDao dao = SysBeans.getComnDao();
for(int i = firstRow + 1; i<lastRow+1; i++) {
Map map = new HashMap();
HSSFRow row = sheet.getRow(i);
int firstCell = row.getFirstCellNum();
int lastCell = row.getLastCellNum();
for(int j=firstCell; j<lastCell; j++) {
HSSFCell cell2 = sheet.getRow(firstRow + 1).getCell(j);
String key = cell2.getStringCellValue();
HSSFCell cell = row.getCell(j);
if(cell.getCellType() == HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC) {
cell.setCellType(HSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING);
}
String val = cell.getStringCellValue();
// System.out.println(val);
if(i == firstRow + 1) {
break;
}else{
map.put(key, val);
}
// System.out.println(map);
}
if(i != firstRow + 1) {
data.add(map);
System.out.println(map);
}
}
System.out.println(data);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return data;
}
}
可看到数据库中的结果:
注意:
1)poi的api读取excel文件时,最常见的两种cell的数据格式是Numeric和String,所以当是数字格式的时候,需要把它的cell type转成String,否则会出现Cannot get a numeric value from a text cell的错误。对应的,设计相应数据库表最好都是Varchar2格式的。
2)需注意需要解析的只是表的数据,所以表的标题应该不在解析范围内;但表头需要解析,他们对应数据库表里的字段;row和cell的位置都是从0开始,
二、Excel导出(这里用到了spring的AbstractExcelView)
首先页面:
<a href="demo/demo-exportExcel.json" data-descript="导出测试">导出</a>
<!-- 或者抽离出一个js-->
var exportExcel = function(){
var url = "demo/demo-exportExcel.json";
window.open(url);
}
对应的后台:
第一步:excel导出的主要工具类:
public class ExcelExportUtil {
public static HSSFWorkbook generateExcel(List<Map<String, String>> list, String title) {
HSSFWorkbook book = new HSSFWorkbook();
try{
File desFile = new File("d:\\人员表.xls");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(desFile);
//样式设置
HSSFCellStyle style = book.createCellStyle();
style.setFillForegroundColor(HSSFColor.SKY_BLUE.index);
style.setFillPattern(HSSFCellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
style.setBorderBottom(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setBorderLeft(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setBorderRight(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setBorderTop(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);
// 生成一个字体
HSSFFont font = book.createFont();
font.setColor(HSSFColor.VIOLET.index);
font.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12);
font.setBoldweight(HSSFFont.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD);
// 把字体应用到当前的样式
style.setFont(font);
HSSFCellStyle style2 = book.createCellStyle();
style2.setFillPattern(HSSFCellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND);
//设置上下左右边框
style2.setBorderBottom(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style2.setBorderLeft(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style2.setBorderRight(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style2.setBorderTop(HSSFCellStyle.BORDER_THIN);
style2.setAlignment(HSSFCellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER);
//填充表头标题
int colSize = list.get(0).entrySet().size();
System.out.println("size:" + colSize);
//合并单元格供标题使用(表名)
sheet.addMergedRegion(new CellRangeAddress(0, 0, 0, colSize-1));
HSSFRow firstRow = sheet.createRow(0);//第几行(从0开始)
HSSFCell firstCell = firstRow.createCell(0);
firstCell.setCellValue(title);
firstCell.setCellStyle(style);
//填充表头header
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(1);
Set<Entry<String, String>> set = list.get(0).entrySet();
List<Entry<String, String>> l = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String,String>>(set);
System.out.println("l:" + l.size());
for(int i=0; i< l.size(); i++) {
String key = l.get(i).getKey();
System.out.println(key);
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(key);
cell.setCellStyle(style2);
}
//填充表格内容
System.out.println("list:" + list.size());
for(int i=0; i<list.size(); i++) {
HSSFRow row2 = sheet.createRow(i+2);//index:第几行
Map<String, String> map = list.get(i);
Set<Entry<String, String>> set2 = map.entrySet();
List<Entry<String, String>> ll = new ArrayList(set2);
for(int j=0; j<ll.size(); j++) {
String val = ll.get(j).getValue();
HSSFCell cell = row2.createCell(j);//第几列:从0开始
cell.setCellValue(val);
cell.setCellStyle(style2);
}
}
// book.write(fos);
// fos.close();
} catch(Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return book;
}
}
注意:
1)合并单元格的语法,这里new CellRangeAddress(0, 0, 0, colSize-1)底层为:
public CellRangeAddress(int firstRow, int lastRow, int firstCol, int lastCol)
{
super(firstRow, lastRow, firstCol, lastCol);
}
因此表示合并第一行第0-colSize-1列,这常常用于放置表的标题。
2)createRow(int rownum)和createCell(int cellnum)表示创建第几行或第几列,都是从0开始。
第二步,在第一步得到HSSFWorkbook的基础上,得到excel文件:涉及的jar包:spring-webmvc-4.x.jar
public class ViewExcel extends AbstractExcelView {
@Override
protected void buildExcelDocument(Map<String, Object> map,
HSSFWorkbook book, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception {
// String filename = "人员信息.xls";//设置下载时客户端Excel的名称
// filename = encodeFilename(filename, request);//处理中文文件名
response.setContentType("application/vnd.ms-excel");
response.setHeader("Content-disposition", "attachment;filename=" + filename);
OutputStream ouputStream = response.getOutputStream();
book.write(ouputStream);
ouputStream.flush();
ouputStream.close();
}
}
第三步,控制层:
@RequestMapping(value = "/demo/demo-exportExcel.json")
@ResponseBody
public ModelAndView report(ModelMap model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
ViewExcel viewExcel = new ViewExcel();
Map obj = null;
System.out.println("response:" + response);
//获取数据库表生成的workbook
Map condition = new HashMap();
//这里是从数据库里查数据并组装成我们想要的数据结构的过程,略。。
List<Map<String, String>> data = dao.xxxx;
HSSFWorkbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.generateExcel(data, "人员信息表");
try {
viewExcel.buildExcelDocument(obj, workbook, request, response);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return new ModelAndView(viewExcel, model);
}
需注意:下载时是否弹出下载选择框是由浏览器的下载选项设置决定的,并不是代码决定的——特没有节操,害我折腾了N久!!
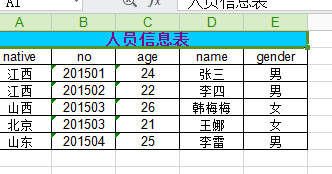
成果:
顺便提一下,做的过程遇到的一些j2se的语法问题:
List<String>转换为String[]的方法:
String[] strs = list.toArray(new String[list.size()])即需指定String[]类型的参数,如果直接这样:String[] strs = (String[]) list.toArray();会出现类型转换的异常:
[Ljava.lang.Object; cannot be cast to [Ljava.lang.String;