JBPM3中文用户手册——第三章:教程(1)
[译:liuu 对应版本: 3.3.1/3.2.3 ]
3 教程
本教程将为你展示使用jpdl的基本流程构建和管理运行时执行的API用法。
教程的形式是解说一组示例,每个示例关注特定的主题并包含丰富的注释。这些示例可以在下载包目录src/java.examples下找到。
最佳的学习方式,是基于已提供的例子,新建一个项目,边修改,边试验。
Eclipse用户开始步骤如下:
1、 下载jbpm分发包,并解压
2、 “文件”à“导入”à选择“现有项目到工作空间”,点击“下一步”,然后浏览选中jbpm的根目录,点“完成”。现在,在你的工作空间里,有了一个jbpm3项目。
3、 你可以在“src/java.examples/...”目录下,找到本教程的示例。打开这些例子后,你可以通过“运行”à“运行为”à“JUnit Test”运行它们。
jBPM包含一个图形化设计器工具,用于编辑示例中展示的那些XML。你可以在2.1可用下载概览一节中,找到这个工具的下载指导。不过,你并不必须要这个图形化设计器,来完成这个教程。
3.1 Hello World示例
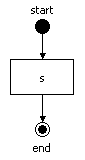
一个流程定义是一张有向图,由节点和迁移组成。HelloWorld流程有3个节点。为了看清这些零零散散的东西,是如何放到一起的工作,我们将从一个简单的流程开始,而且也不使用流程设计工具。下图是HelloWorld流程的图示:
图表 3.1 Hello World流程图
| public void testHelloWorldProcess() { // This method shows a process definition and one execution // of the process definition. The process definition has // 3 nodes: an unnamed start-state, a state 's' and an // end-state named 'end'. // The next line parses a piece of xml text into a // ProcessDefinition. A ProcessDefinition is the formal // description of a process represented as a java object. ProcessDefinition processDefinition = ProcessDefinition.parseXmlString( "<process-definition>" + " <start-state>" + " <transition to='s' />" + " </start-state>" + " <state name='s'>" + " <transition to='end' />" + " </state>" + " <end-state name='end' />" + "</process-definition>" );
// The next line creates one execution of the process definition. // After construction, the process execution has one main path // of execution (=the root token) that is positioned in the // start-state. ProcessInstance processInstance = new ProcessInstance(processDefinition);
// After construction, the process execution has one main path // of execution (=the root token). Token token = processInstance.getRootToken();
// Also after construction, the main path of execution is positioned // in the start-state of the process definition. assertSame(processDefinition.getStartState(), token.getNode());
// Let's start the process execution, leaving the start-state // over its default transition. token.signal(); // The signal method will block until the process execution // enters a wait state.
// The process execution will have entered the first wait state // in state 's'. So the main path of execution is now // positioned in state 's' assertSame(processDefinition.getNode("s"), token.getNode());
// Let's send another signal. This will resume execution by // leaving the state 's' over its default transition. token.signal(); // Now the signal method returned because the process instance // has arrived in the end-state.
assertSame(processDefinition.getNode("end"), token.getNode()); } |