通向架构师的道路(第十八天)万能框架Spring(一)
一、前言
前一阵列刚换了个新的工作环境,然后自己的baby也刚出生,一直没有时间去做工作以后的其它事了,担搁了一段日子。
今天儿子满一周了,我内人她家帮着照顾着,总算我可以喘口气休息一下,因此决定将这个系列的博文继续下去,同时也将此篇献给我刚出生一周的儿子和幸苦了10个月的爱人。
二、基本概念
Spring,作为一个流行框架它给我们在日常工程中的框架搭建提供了太多的便利了,它就像一个骨架一样,你可以在上面自己去塑出肌肤与血肉并赋于它灵魂。
从今天开始我们将要连续几天基于Spring的基础上来讲软件开发框架,由于Spring被应用的太广泛太广泛了,因此此系列教程可以作为Spring开发的一套基础教程也可以称其为“典范或者公式化教程”吧.
此套教程会覆盖以下内容:
1) Spring+Struts1+jdbctemplate;
2) Spring+Struts1+Hibernate;
3) Spring+Struts2+ibatis;
4) Spring+Struts1、2+任意DAO层的Unit Test;
5)甚至还会讲到如何使用Spring来构建应用程序,对,你没听错使用Spring可以构建单独运行的java应
用程序,尤其在银行、保险业中有一种叫“批处理”的业务,就是应用程序,那么我们使用Spring会为
我们的批处理作业带来什么样的好处呢?敬请期待!
三、Spring+Struts+jdbctemplate
3.1 框架介绍
作为架构师,同时你也必须为“框架师”,架构是从广意上来讲的,它的知识需要覆盖到硬件、软件、协议甚至业务背景。
但是一个架构师在项目中时它又必须是一个“框架师”,就和造房子一样,框架搭的好,房子造出来才能坚固。
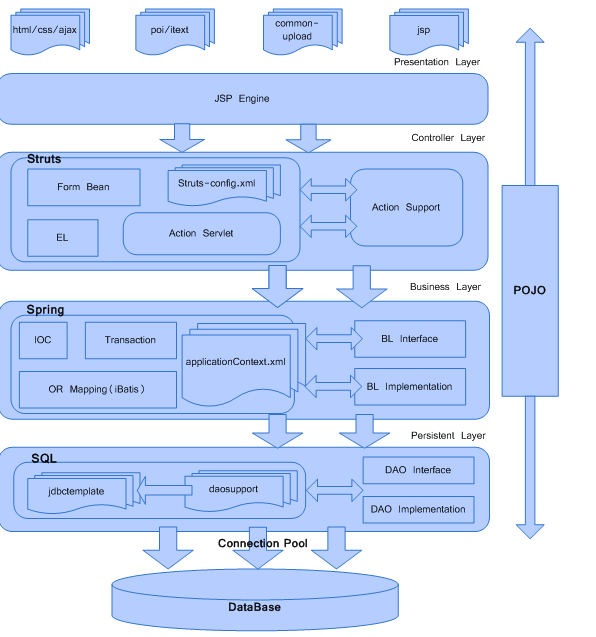
我们就先来看我们第一幢房子的脚手加架-Spring在我们项目中的使用吧,先来看架构图,一般我喜欢用Visio来画架构图,画完后直接在Visio的workspace里ctrl+a全选后回到 word后按ctrl+v,这样你的word文本中就有了一幅visio的图了,而你在word文档中双击这个visio图它会自动在当前的文档中打开visio的workspace以便于你来编辑你的visio图,这样你就不用来回在word与 visio间进行切换了,也不用每次把visio转成jpg后再到word中插入图片了,这是一个标准操作模式,希望能够为大家今后的操作带来方便。当然,平时看到好的文档,好的架构图把它收藏起来、分门别类相信你的文档会越写越漂亮.
Look,这就是我们的框架。
ØSpring
在此我们使用3.1,它负责IOC,AOP等工作,用于代理业务层(Service层)的事务。
ØStruts
在此我们使用1.3,它负责控制层以及相关的JSP页面(采用Struts标签)。
控制层通过业务层再访问数据库层。
ØSpring Jdbc Template
负责ORMapping,由于我们使用的数据还需要进行一些复杂的汇总与计算,因此在未来系统开发中还需要开发一系列的StoreProcedure(存储过程),用jdbc template不仅可以方便灵活的使用SQL查询语句,同时也为访问各种数据库的存储过程带来了方便。
该框架优点:
Ø分层清晰,替换灵活,易于扩展
上述框架采用View Layer,Controller Layer,Service Layer,DAOLayer进行分层。层与层之间全部基于接口。
1) 逻辑的任何变动不影响到代码的运行
2) 自动代理数据库的事务操作,尤于采用了Spring的DataSourceTransactionManager,该类是
一个完全基于AOP的事务自动代理,由于使用的是AOP中的围绕机制,因此该类会自动利用AOP功能
在数据库操作时进行事务的开启、提交、关闭并且在遇见Exception时会自动回滚。该类使用通配符
的方式,对于业务层进行事务管理。由于Controller层不直接操作DAO,而是通过Service层来操作
事务的,因此事务的切片定位在Service层。另外,由于一个Service方法有可能涉及到多个DAO操
作,所以将事务定位在Service层有助于保持数据的一致性。
3) 层中相关技术的替换不影响到其它层面,层与层之间的全部基于接口,因此各个层内自身的逻辑
或者是采用的相关技术的变化不影响到其它层。举例来说:现在的DAO层是Spring JdbcTemplate,
如果将来换成Hibernate或者是EJB的JPA来做DAO层的话,对于整个DAO层只需要按照原有接口重
写相关的impl类,而view层, controller层与Service层的变动为“零代码”改动。
Ø简化配置,提高生产力
本框架使用的是Spring3.0+Struts2.x作为系统框架的核心。传统的框架伴随着一堆xml文件的配置,比如说用于描述Struts中Action的配置,层与层之间的依赖关系,甚至特定的class需要用到的外部变量都需要进行基于xml格式的配置文件的修改。
Xml配置文件的改动,如果出现一处错误往往会影响整个系统的运行,或者甚至导致系统运行崩溃。而本框架使用了JDK1.6中的“全注解”技术,除了需要改动一个cbbs.properties文件,各层之间的调用全部使用的Annotation,比如说我们需要在一个Struts的Action中调用一个Service, 只需要在相关的Action的Class里进行如下的注释即可:
| @Resource EmailActivationService activateService; |
而传统的需要作下面这样的配置:
| <bean id=”activation” class=”xxx.xxx.xxx.xx”> <ref bean=”activateService”/> </bean> <bean id=”activateService” class=”xxx.xxx.xxx.EmailActivationServiceImpl”/> |
设想,假如有100个类,上百个Service,再加上数百个DAO,我们的xml的配置将是多么的庞大啊,这就是典型的“xml泛滥”,这同时也将导致程员工工作效率,生产效率的低下。
而现在采用了Annotation方式来搭建框架,这在极大程度上使得程序员与框架之间是“透明”的,让程序员将更多时间花在“业务”的实现上。这一切都用的是Spring的“注解”特性,即
| “<context:component-scan base-package="xxx.xxx.xxx" />”。 |
Ø该框架不需要使用容器的jdbcjndi,而自带了一个 c3p0的jdbcconnection pool,它将会随着容器的启动而启动,结束而销亡.
Ø实现了基本的资源保护
我们在该框架中使用了以下几种技术的混合来实现外部资源文件的安全保护
1) 基于Spring的Properties的注入
2) 在properties文件与spring的配置xml文件里实现了placeholder,即替换符,记住它的英文的表达叫“place holder”。
3) 使用了第三方开源免费包jasypt与spring结合自动对properties文件中的关键内容如:password进行加密与解密
3.2 框架搭建
首先使用eclipse建立一个”dynamice web project”,我们管它叫”alpha”吧,我们的第一个孩子。

然后与src同级的地方建立一个resource目录,并把它加入classpath
别忘了把Defaultoutput folder:从bin改成alpha/WebContent/WEB-INF/classes
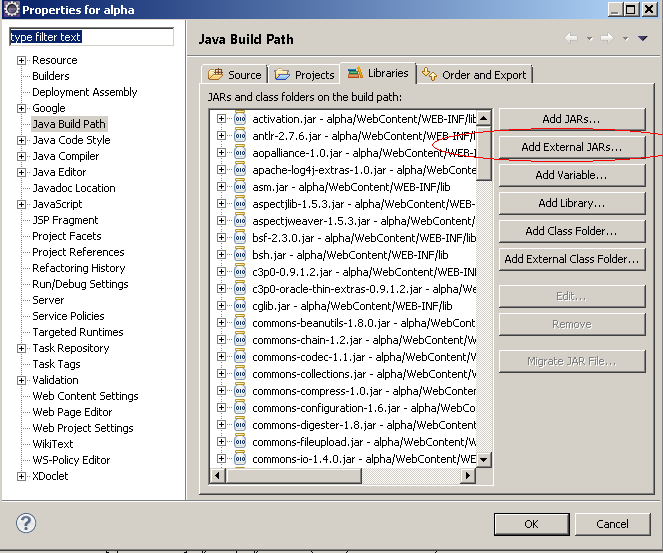
再建立一个目录叫ext-lib的目录,把tomcat的lib目录内的jsp-api.jar与servlet-api.jar两个文件拷入该文件夹内.因为我们在涉及到一些servlet与jsp的编写时,需要使用这两个jar进行编译,但我们又不能把这两个jar文件与我们的工程一起发布到tomcat的webapp目录下,因为tomcat已经含有这两个jar文件了,所以这两个jar文件需要以下面的方式引入我们的工程而不随着我们的工程一起发布:
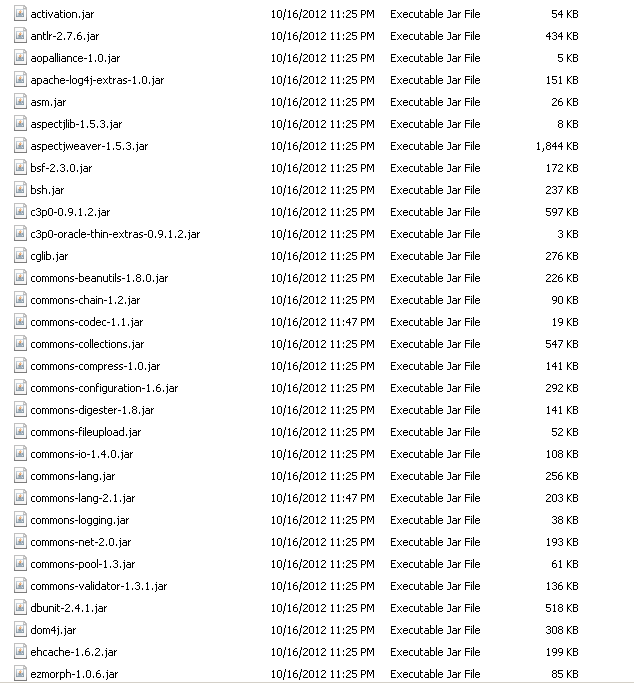
这是工程目录结构整理完后的样子,请照着该结构在resource目录下自行建立其它几个目录(不要去管文件,先把目录建完)。
然后我们把
1) struts
2) spring
3) c3p0-0.9.1.2.jar等
一些需要的jar文件一个个都copy到我们工程的WEB-INF/lib目录下并刷新工程。这些jar在你下载的spring、struts、hibernate包中都有带,可以自行去查找.
修改我们的web.xml文件,尤其注意下面红色与加粗的部分,一粗就爽了是吧,嘿!
web.xml
| <?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-appxmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID"version="2.5"> <display-name>alpha</display-name> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/classes/spring/**/*.xml</param-value> </context-param> <filter> <filter-name>characterEncoding</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>forceEncoding</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>characterEncoding</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <servlet> <servlet-name>action</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.apache.struts.action.ActionServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>config</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/struts-config.xml, /WEB-INF/struts-config/login.xml, /WEB-INF/struts-config/index.xml </param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>debug</param-name> <param-value>3</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>detail</param-name> <param-value>3</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup> </servlet> <!-- Action Servlet Mapping --> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>action</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <jsp-config> <taglib> <taglib-uri>/WEB-INF/struts-bean.tld</taglib-uri> <taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-bean.tld</taglib-location> </taglib> <taglib> <taglib-uri>/WEB-INF/struts-html.tld</taglib-uri> <taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-html.tld</taglib-location> </taglib> <taglib> <taglib-uri>/WEB-INF/struts-logic.tld</taglib-uri> <taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-logic.tld</taglib-location> </taglib> </jsp-config> </web-app> |
在该web.xml文件内我们
首先:
声明了把我们的工程目录下的“/WEB-INF/classes/spring/**/*.xml”让spring去加载,因为我们这些.xml文件都在我们的resource目录下,而我们的resource目录和src目录一样是会在编译时自动跑到WEB-INF/classes目录下的,是不是?
其次:
我们声明了一个filter叫“characterEncoding”,该filter的作用可以支持你的工程中无论是从jsp到.do还是从.do到jsp时对于中文字符的输入不用你再去手动的转newString(“xxx”,”UTF-8”)这样的转码操作了。
最后:
我们声明了我们的struts的action mapping文件所在的位置,我们在此处声明了3个struts-config文件,主config文件为:/WEB-INF/struts-config.xml,其它两个为我们的“模拟级config文件”。
/WEB-INF/struts-config.xml
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts-config PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 1.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-config_1_3.dtd"> <struts-config> <form-beans /> <global-forwards> <forward name="error" path="/jsp/error/syserror.jsp" /> </global-forwards> <!-- ========== Action Mapping Definitions ============================== --> <action-mappings /> <!-- ========== Controller Configuration ================================ --> <controller> <set-property property="processorClass" value="org.springframework.web.struts.DelegatingRequestProcessor" /> </controller> <!-- ========== Message Resources Definitions =========================== --> <message-resources parameter="org.apache.struts.webapp.example2.ApplicationResources" /> <plug-in className="fr.improve.struts.taglib.layout.workflow.LayoutPlugin" /> </struts-config> |
该文件中:
| <controller> <set-property property="processorClass" value="org.springframework.web.struts.DelegatingRequestProcessor" /> </controller> |
的作用就是把我们的struts中的action委托给了spring去管理,因为我们的一切都是通过action/.do入手的,因此一旦我们的action被spring托管起来后,那么action下调用的service, service调用的dao都被我们的spring进行托管了,于是一切就都可以“注入”了.
下面,我们来看我们的applicationContext.xml文件,这个非常核心的一个文件。
applicationContext.xml文件
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:annotation-config/> <context:component-scan base-package="org.sky.ssh1.alpha" /> <bean id="environmentVariablesConfiguration" class="org.jasypt.encryption.pbe.config.EnvironmentStringPBEConfig" p:algorithm="PBEWITHMD5ANDDES" p:passwordEnvName="APP_ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD" /> <bean id="configurationEncryptor" class="org.jasypt.encryption.pbe.StandardPBEStringEncryptor" p:config-ref="environmentVariablesConfiguration" /> <bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.jasypt.spring.properties.EncryptablePropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <constructor-arg ref="configurationEncryptor" /> <property name="locations"> <list> <value> classpath:jdbc.properties </value> </list> </property> </bean> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties" /> <bean id="commonsConfigurationFactoryBean" class="org.sky.ssh1.alpha.util.CommonsConfigurationFactoryBean" p:encryptor-ref="configurationEncryptor" p:systemPropertiesModeName="SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE"> <constructor-arg> <bean class="org.apache.commons.configuration.PropertiesConfiguration"> <constructor-arg value="jdbc.properties" /> </bean> </constructor-arg> </bean> <bean id="propertiesConfiguration" factory-bean="&commonsConfigurationFactoryBean" factory-method="getConfiguration" /> <!-- you can ignore following lines --> <bean id="methodLoggerAdvisor" class="org.sky.ssh1.alpha.util.LoggerAdvice"> </bean> <bean id="springUtil" class="org.sky.ssh1.alpha.util.SpringUtil"> </bean> <aop:config> <aop:aspect id="originalBeanAspect" ref="methodLoggerAdvisor"> <aop:pointcut id="loggerPointCut" expression="execution(* org.sky.ssh1.service.impl.*.*(..))" /> <aop:around method="aroundAdvice" pointcut-ref="loggerPointCut" /> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans> |
主要还是红色加粗的部分,解释如下:
1)<context:annotation-config/>
可以在你的struts的action文件中启用@Controller这样的注解将struts的action委托给spring进行管理
2)<context:component-scanbase-package="org.sky.ssh1.alpha" />
在该“package”下所有的类都委托给了spring进行管理
3)
Øbean id="environmentVariablesConfiguration"
Øbean id="configurationEncryptor"
ØBean id="propertyConfigurer"
Øcontext:property-placeholderlocation="classpath:jdbc.properties"
Øbeanid="commonsConfigurationFactoryBean"、beanid="propertiesConfiguration"
这些个bean的申明可以让你如以下场景般的去使用,请看:
我有一个jdbc.properties文件,内容如下:
| jdbc.driverClassName=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver jdbc.databaseURL=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ymkorcl jdbc.username=alpha jdbc.password=ENC(W1BJSjx6+1O1z3ArmojmaQG+r80ty3zX) |
注意这个jdbc.password,这个value是被加密了的。
然后我有一个datasource.xml文件,内容如下:
| <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.databaseURL}" /> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> <property name="initialPoolSize" value="10" /> <property name="minPoolSize" value="10" /> <property name="maxPoolSize" value="15" /> <property name="acquireIncrement" value="1" /> <property name="maxIdleTime" value="5" /> </bean> |
看到了没有?这就叫“property-placeholder“,因为。。。因为如果哪天我的数据库换成了mysql后,是不是我只要在我的jdbc.properties文件里换换内容就可以了而不需要再去动这个datasource.xml文件啊?
那么说到加密这个问题很简单,这个加密我们用的是“StandardPBEStringEncryptor”里的
PBEWITHMD5ANDDES p:passwordEnvName="APP_ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD",所谓PBE就是password base的意思,因此我们这个加密首先用的是DES,然后为了解密这个DES还需要一个password,而这个password我们设在哪边?
| <bean id="configurationEncryptor" class="org.jasypt.encryption.pbe.StandardPBEStringEncryptor" p:config-ref="environmentVariablesConfiguration" / |
啊。。。environmentVariablesConfiguration, 所以我们来看:
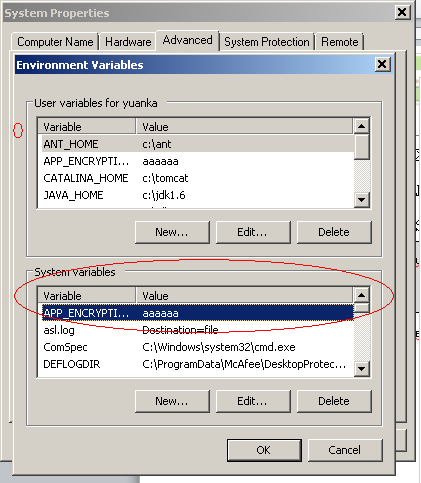
看到了没有,如果你是linux系统则需要在/etc/profile文件中加入:
export APP_ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD=”aaaaaa”
所以我们为了解这个DES密码时需要一个口令,这个口令在我们的系统环境变量,值为六个a。
我们看到在commonsConfigurationFactoryBean里我们自定义了一个class为:
org.sky.ssh1.alpha.util.CommonsConfigurationFactoryBean的类,我们来看这个类吧.
org.sky.ssh1.alpha.util.CommonsConfigurationFactoryBean内容:
| package org.sky.ssh1.alpha.util; import static org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.DEFAULT_PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX; import static org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.DEFAULT_PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX; import static org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_FALLBACK; import static org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; import org.apache.commons.configuration.CompositeConfiguration; import org.apache.commons.configuration.Configuration; import org.apache.commons.configuration.ConfigurationConverter; import org.apache.commons.configuration.PropertiesConfiguration; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.jasypt.encryption.StringEncryptor; import org.jasypt.properties.PropertyValueEncryptionUtils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer; import org.springframework.core.Constants; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * Creates a commons configuration factory bean, by using the best of both * worlds Jakarta Commons Configuration and SpringSource PropertyPlaceHolder * * @author lifetragedy * @since Apr 28, 2009 * */ public class CommonsConfigurationFactoryBean extends org.springmodules.commons.configuration.CommonsConfigurationFactoryBean { protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); private CompositeConfiguration configuration; private static final Constants constants = new Constants( PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.class); private String placeholderPrefix = DEFAULT_PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX; private String placeholderSuffix = DEFAULT_PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX; private int systemPropertiesMode = SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_FALLBACK; private boolean searchSystemEnvironment = true; private boolean ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders = false; private StringEncryptor encryptor; @SuppressWarnings("unused") private String nullValue = null; public CommonsConfigurationFactoryBean() { super(); } public CommonsConfigurationFactoryBean(Configuration configuration) { super(configuration); } @Override public Object getObject() throws Exception { return (configuration != null) ? ConfigurationConverter .getProperties(configuration) : null; } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { super.afterPropertiesSet(); processConfiguration((Properties) super.getObject()); } @Override public CompositeConfiguration getConfiguration() { return configuration; } protected void processConfiguration(final Properties properties) { Configuration propertiesConfiguration = new PropertiesConfiguration(); if (properties != null) { for (Iterator iter = properties.entrySet().iterator(); iter .hasNext();) { Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next(); String key = (String) entry.getKey(); String value = parseStringValue((String) entry.getValue(), properties, new HashSet()); if (value != null && value.trim().length() > 0) // logger.info("the key======"+key+" value======"+value); propertiesConfiguration.setProperty(key, value); } } configuration = new CompositeConfiguration(propertiesConfiguration); } // Source taken SpringSource class PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer for the // placeholder logic /** * Set the prefix that a placeholder string starts with. The default is * "${". * * @see #DEFAULT_PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX */ public void setPlaceholderPrefix(String placeholderPrefix) { this.placeholderPrefix = placeholderPrefix; } /** * Set the suffix that a placeholder string ends with. The default is "}". * * @see #DEFAULT_PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX */ public void setPlaceholderSuffix(String placeholderSuffix) { this.placeholderSuffix = placeholderSuffix; } /** * Set the system property mode by the name of the corresponding constant, * e.g. "SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE". * * @param constantName * name of the constant * @throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException * if an invalid constant was specified * @see #setSystemPropertiesMode */ public void setSystemPropertiesModeName(String constantName) throws IllegalArgumentException { this.systemPropertiesMode = constants.asNumber(constantName).intValue(); } /** * Set how to check system properties: as fallback, as override, or never. * For example, will resolve ${user.dir} to the "user.dir" system property. * <p> * The default is "fallback": If not being able to resolve a placeholder * with the specified properties, a system property will be tried. * "override" will check for a system property first, before trying the * specified properties. "never" will not check system properties at all. * * @see #SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_NEVER * @see #SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_FALLBACK * @see #SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE * @see #setSystemPropertiesModeName */ public void setSystemPropertiesMode(int systemPropertiesMode) { this.systemPropertiesMode = systemPropertiesMode; } /** * Set whether to search for a matching system environment variable if no * matching system property has been found. Only applied when * "systemPropertyMode" is active (i.e. "fallback" or "override"), right * after checking JVM system properties. * <p> * Default is "true". Switch this setting off to never resolve placeholders * against system environment variables. Note that it is generally * recommended to pass external values in as JVM system properties: This can * easily be achieved in a startup script, even for existing environment * variables. * <p> * <b>NOTE:</b> Access to environment variables does not work on the Sun VM * 1.4, where the corresponding {@link System#getenv} support was disabled - * before it eventually got re-enabled for the Sun VM 1.5. Please upgrade to * 1.5 (or higher) if you intend to rely on the environment variable * support. * * @see #setSystemPropertiesMode * @see java.lang.System#getProperty(String) * @see java.lang.System#getenv(String) */ public void setSearchSystemEnvironment(boolean searchSystemEnvironment) { this.searchSystemEnvironment = searchSystemEnvironment; } /** * Set whether to ignore unresolvable placeholders. Default is "false": An * exception will be thrown if a placeholder cannot be resolved. */ public void setIgnoreUnresolvablePlaceholders( boolean ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) { this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders = ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders; } /** * Set a value that should be treated as <code>null</code> when resolved as * a placeholder value: e.g. "" (empty String) or "null". * <p> * Note that this will only apply to full property values, not to parts of * concatenated values. * <p> * By default, no such null value is defined. This means that there is no * way to express <code>null</code> as a property value unless you explictly * map a corresponding value here. */ public void setNullValue(String nullValue) { this.nullValue = nullValue; } /** * Set the Text based Encryptor which will be used to decrypt the passwords * as per JASYPT * * @param encryptor */ public void setEncryptor(StringEncryptor encryptor) { this.encryptor = encryptor; } /** * Parse the given String value recursively, to be able to resolve nested * placeholders (when resolved property values in turn contain placeholders * again). * * @param strVal * the String value to parse * @param props * the Properties to resolve placeholders against * @param visitedPlaceholders * the placeholders that have already been visited during the * current resolution attempt (used to detect circular references * between placeholders). Only non-null if we're parsing a nested * placeholder. * @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException * if invalid values are encountered * @see #resolvePlaceholder(String, java.util.Properties, int) */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected String parseStringValue(String strVal, Properties props, Set visitedPlaceholders) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer(strVal); int startIndex = strVal.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix); while (startIndex != -1) { int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(buf, startIndex); if (endIndex != -1) { String placeholder = buf.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex); if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(placeholder)) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Circular placeholder reference '" + placeholder + "' in property definitions"); } // Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the // placeholder key. placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, props, visitedPlaceholders); // Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key... String propVal = resolvePlaceholder(placeholder, props, this.systemPropertiesMode); if (propVal != null) { // Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in // the // previously resolved placeholder value. propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, props, visitedPlaceholders); buf.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'"); } startIndex = buf.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length()); } else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) { // Proceed with unprocessed value. startIndex = buf.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length()); } else { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Could not resolve placeholder '" + placeholder + "'"); } visitedPlaceholders.remove(placeholder); } else { startIndex = -1; } } return convertPropertyValue(buf.toString()); } private int findPlaceholderEndIndex(CharSequence buf, int startIndex) { int index = startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(); int withinNestedPlaceholder = 0; while (index < buf.length()) { if (StringUtils.substringMatch(buf, index, this.placeholderSuffix)) { if (withinNestedPlaceholder > 0) { withinNestedPlaceholder--; index = index + this.placeholderSuffix.length(); } else { return index; } } else if (StringUtils.substringMatch(buf, index, this.placeholderPrefix)) { withinNestedPlaceholder++; index = index + this.placeholderPrefix.length(); } else { index++; } } return -1; } /** * Resolve the given placeholder using the given properties, performing a * system properties check according to the given mode. * <p> * Default implementation delegates to <code>resolvePlaceholder * (placeholder, props)</code> before/after the system properties check. * <p> * Subclasses can override this for custom resolution strategies, including * customized points for the system properties check. * * @param placeholder * the placeholder to resolve * @param props * the merged properties of this configurer * @param systemPropertiesMode * the system properties mode, according to the constants in this * class * @return the resolved value, of null if none * @see #setSystemPropertiesMode * @see System#getProperty * @see #resolvePlaceholder(String, java.util.Properties) */ protected String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholder, Properties props, int systemPropertiesMode) { String propVal = null; if (systemPropertiesMode == SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE) { propVal = resolveSystemProperty(placeholder); } if (propVal == null) { propVal = resolvePlaceholder(placeholder, props); } if (propVal == null && systemPropertiesMode == SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_FALLBACK) { propVal = resolveSystemProperty(placeholder); } return propVal; } /** * Resolve the given placeholder using the given properties. The default * implementation simply checks for a corresponding property key. * <p> * Subclasses can override this for customized placeholder-to-key mappings * or custom resolution strategies, possibly just using the given properties * as fallback. * <p> * Note that system properties will still be checked before respectively * after this method is invoked, according to the system properties mode. * * @param placeholder * the placeholder to resolve * @param props * the merged properties of this configurer * @return the resolved value, of <code>null</code> if none * @see #setSystemPropertiesMode */ protected String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholder, Properties props) { return convertPropertyValue(props.getProperty(placeholder)); } /** * Resolve the given key as JVM system property, and optionally also as * system environment variable if no matching system property has been * found. * * @param key * the placeholder to resolve as system property key * @return the system property value, or <code>null</code> if not found * @see #setSearchSystemEnvironment * @see java.lang.System#getProperty(String) * @see java.lang.System#getenv(String) */ protected String resolveSystemProperty(String key) { try { String value = System.getProperty(key); if (value == null && this.searchSystemEnvironment) { value = System.getenv(key); } return value; } catch (Throwable ex) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Could not access system property '" + key + "': " + ex); } return null; } } protected String convertPropertyValue(String originalValue) { if (!PropertyValueEncryptionUtils.isEncryptedValue(originalValue)) { return originalValue; } if (this.encryptor != null) { return PropertyValueEncryptionUtils.decrypt(originalValue, this.encryptor); } return PropertyValueEncryptionUtils.decrypt(originalValue, this.encryptor); } } |
了解完了applicationContext.xml文件内容后我们继续看下去:
jdbc.properties文件
| jdbc.driverClassName=oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver jdbc.databaseURL=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ymkorcl jdbc.username=alpha jdbc.password=ENC(W1BJSjx6+1O1z3ArmojmaQG+r80ty3zX) |
如何把这个jdbc.password后的值进行加密呢?我们来看:
Jasypt加密解密步骤一
首先你要下载最新版的jasypt,目前是1.9,除了把这三个jar文件
Jasypt加密解密步骤二
打开一个command窗口输入如下的命令,假设我们的jdbc.password后的值为:password_1,要把这个password_1用PBEWITHMD5ANDDES加密,我们输入如下的命令:
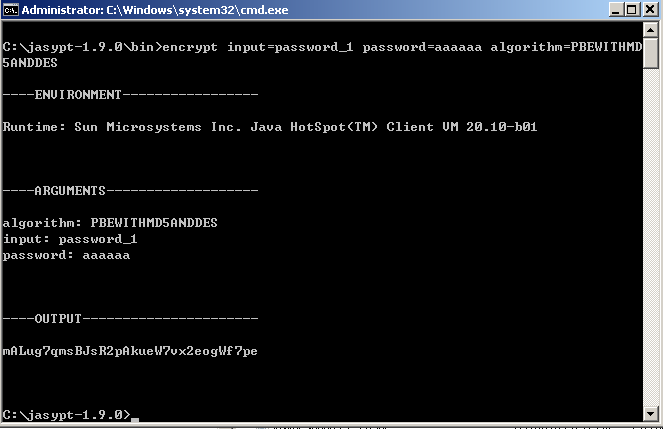
把OUTPUT这段复制下来后放入我们的properties 文件内,并用ENC()包括起来,这样我们的spring就会在我们的J2EE容器启动时碰到指定的properties文件中如果含有ENC()括起来的东西,去自动执行相当于如下的解密命令了:
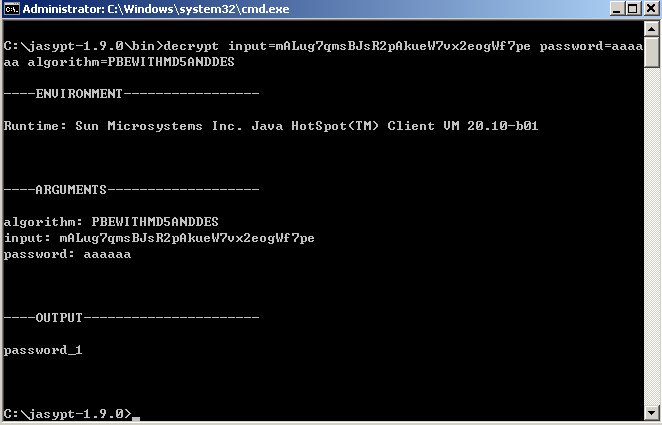
而这边的password就是你在环境变量中设定的:APP_ENCRYPTION_PASSWORD的值。
datasource.xml文件
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" p:dataSource-ref="dataSource" /> <!-- configure data base connection pool by using C3P0 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" /> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.databaseURL}" /> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}" /> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" /> <property name="initialPoolSize" value="10" /> <property name="minPoolSize" value="10" /> <property name="maxPoolSize" value="15" /> <property name="acquireIncrement" value="1" /> <property name="maxIdleTime" value="5" /> </bean> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /> </bean> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="submit*" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" /> <tx:method name="add*" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" /> <tx:method name="del*" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" /> <tx:method name="upd*" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" /> <tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" /> <tx:method name="query*" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="find*" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="get*" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="view*" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="search*" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="check*" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="is*" read-only="true" /> <tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="java.lang.Exception" /> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="serviceMethod" expression="execution(* org.sky.ssh1.alpha.service.impl.*.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="serviceMethod" /> </aop:config> </beans> |
我们来解读这个datasource.xml文件吧,很简单。
1) 该工程不使用任何容器内设的jdbcconnection pool的jndi也不使用jdbc直连,而是自带一个叫c3p0的开源免费connection pool,因此你需要把
这个jar拷入工程的WEB-INF/lib目录下,并且要把它拷入tomcat的lib目录下。
1) 该工程使用jdbctemplate来调用我们的sql
2) 该工程使用声明式事务管理
所谓声明式事务就是“容器事务管理”,这就是在远古时学习过ejb2.x的人的好处了,因为的远古的 ejb2.0时就已经说了容器事务管理的好处了,就是你的service方法如果抛出指定的exception,那么容器会自动rollback你这个service中所有的操作,如果在到达service结尾处还是没有指定的exception抛出,那么该service内执行的所有数据库相关将自动被commit(笔者记得这种方法的使用,那已经是11年前的事了已经是,当时是P都看不懂什么叫“声明式”)。
还有一种事务叫“编程式事务”,即你自己在代码里手工在try{}块的最后调用tran.commit,在catch{}块中手工调用tran.rollback。当然,难免漏commit,忘rollback,所以声明式事务的好处也体现了出来了。
3) 对于所有的“org.sky.ssh1.alpha.service.impl”这个包下所有的以:
is,check,select,query,get,search开头的public方法,以只读的方式即不启用事务的方式来进行数据库调用
对于所有的“org.sky.ssh1.alpha.service.impl“这个包下的所有的以:
upd,del,add,submit,save开头的public方法全部进行事务调用,如果碰到抛出
java.lang.Exception或者继承自java.lang.Exception的异常自动进行rollback。
看到这儿,我们明白了,网上一直说的:
Ø事务要切在service方法上;
Ø数据库调用必须套在service方法内;
的真正意思了.
3.3 login的例子
我们先用一个简单的login例子来使用我们的框架吧,先来看login例子的流程,很简单。
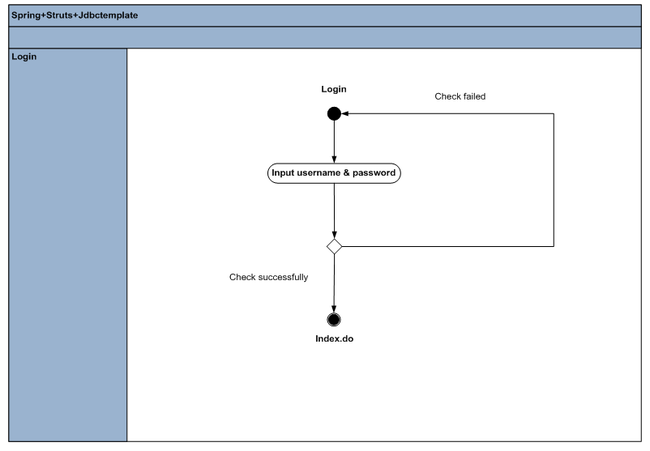
相关的sql也很简单:
| SELECT count(1) from t_login where login_id=? and login_pwd=? |
如何该sql返回0,代表不存在该用户或者是用户名/密码输出了,如果返回为1则代表登录成功.
3.3.1 让我们的sql变得可配置
我们在做工程时经常面临这样的一个问题,就是我们要么把我们的sql写成我们的class文件里和我们的代码混写,好一点的人喜欢声明成constants变量(这个还好一点),但是这两种方法都需要我们重编译我们的工程,我们有没有一种方法直接把我们的sql就写成外部的xml文件里,然后在工程布署后我们可以经常修改(比如说长的SQL语句需要调优,这个如果改在代码里工作量不得了,引起的牵连问题也会很多)。当然现在我们有了spring,我们可以这么做,我们声明一个loginDAO.xml文件,把SQL通过外部注入进loginDAO的相关方法。
3.3.2工程的结构安排
3.3.3 LoginDAO模块
LoginDAO有LoginDAO接口与LoginDAOImpl实现类两个类组成:
loginDAO.xml
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="loginDAO" class="org.sky.ssh1.alpha.dao.impl.LoginDAOImpl"> <property name="sql"> <value> <![CDATA[ SELECT count(1) from t_login where login_id=? and login_pwd=? ]]> </value> </property> </bean> </beans> |
LoginDAO.java
| package org.sky.ssh1.alpha.dao; public interface LoginDAO { public boolean login(String loginId, String loginPwd) throws Exception; } |
LoginDAOImpl.java
| package org.sky.ssh1.alpha.dao.impl; import org.sky.ssh1.alpha.dao.LoginDAO; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import javax.sql.*; @Repository public class LoginDAOImpl implements LoginDAO { @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; private String sql = ""; public void setSql(String sql) { this.sql = sql; } public boolean login(String loginId, String loginPwd) throws Exception { boolean answer = false; int recordCount = 0; recordCount = jdbcTemplate.queryForInt(sql, loginId, loginPwd); if (recordCount == 1) { answer = true; } return answer; } } |
注意类上方的“@Repository“,代表该类作为一个spring bean由spring进行管理(即可将其注入到其它类中去)
3.3.4 LoginService模块
一个Service模块由Service接口与ServiceImpl实现类组成
LoginService.java
| package org.sky.ssh1.alpha.service; public interface LoginService { public boolean login(String loginId, String loginPwd) throws Exception; } |
LoginServiceImpl.java
| package org.sky.ssh1.alpha.service.impl; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.sky.ssh1.alpha.dao.LoginDAO; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class LoginServiceImpl implements org.sky.ssh1.alpha.service.LoginService { private Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(this.getClass()); @Resource private LoginDAO loginDAO; public boolean login(String loginId, String loginPwd) throws Exception { boolean answer = false; try { answer = loginDAO.login(loginId, loginPwd); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("login error:" + e.getMessage(), e); } return answer; } } |
注意两个加粗处的使用,一个是声明该类为一个Service类(要被事务切),一个是如何用注解的方式引用另一个dao类。
然后我们再来看Login的Struts模块
3.3.5 Login相关的Controller
一个controller有两部分组成:
struts-config.xml文件与action相关class。
WEB-INF/struts-config/login.xml
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts-config PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 1.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-config_1_3.dtd"> <struts-config> <form-beans> <form-bean name="loginForm" type="org.sky.ssh1.alpha.login.form.LoginForm" /> </form-beans> <global-forwards /> <action-mappings> <action path="/login" name="loginForm" scope="request" parameter="method" input="/jsp/login/login.jsp"> <forward name="login_init" path="/jsp/login/login.jsp" /> <forward name="login_fail" path="/login.do" /> <forward name="login_success" path="/index.do" /> </action> </action-mappings> </struts-config> |
LoginAction.java
| package org.sky.ssh1.alpha.login.action; import org.apache.struts.actions.DispatchAction; import javax.annotation.Resource; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward; import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping; import org.sky.ssh1.alpha.service.LoginService; import org.sky.ssh1.alpha.student.form.StudentForm; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; @Controller("/login") public class LoginAction extends DispatchAction { protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); @Resource LoginService loginService; public ActionForward submit(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { String loginId = ""; String loginPwd = ""; try { loginId = (String) request.getParameter("loginId"); loginPwd = (String) request.getParameter("loginPwd"); if (loginService.login(loginId, loginPwd)) { return new ActionForward("/index.do", true); } else { request.setAttribute("loginCode", "101"); return new ActionForward("/jsp/login/login.jsp", false); } } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("UserLogin Exception:" + e.getMessage(), e); return mapping.findForward("error"); } } public ActionForward unspecified(ActionMapping mapping, ActionForm form, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { try { StudentForm stdForm = new StudentForm(); request.setAttribute("stdForm", stdForm); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("UserLogin Exception:" + e.getMessage(), e); return mapping.findForward("error"); } return null; } } |
注意:
@Controller("/login")的使用,该注解将这个LoginAction委托给了spring进行管理了,这边的路径名必须和你在struts-config相关配置文件里的action的mapping名完全相等。
@Resource
LoginServiceloginService;
的使用,代表把service相关的功能注入给了LoginAction类。
登录失败效果:
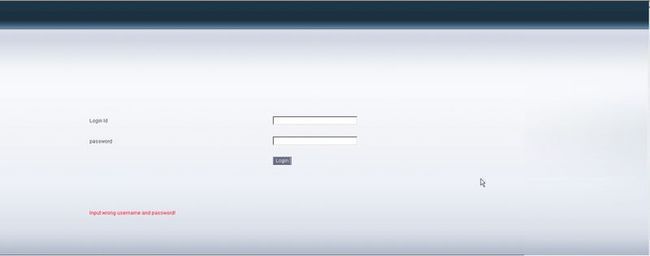
登录成功效果:
3.4 如何处理一个DAO对应多个SQL语句
有时,我们一个DAO方法除了select、get方法还会有del,add,upd等public方法,我们不可能为了每个publich方法再单独去声明一个*DAO.xml文件对吧,这样做的话就会造成xml文件泛滥,那么我们可以在xml文件中使用如下的技巧,如studentDAO类:
studentDAO.xml
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <bean id="studentDAO" class="org.sky.ssh1.alpha.dao.impl.StudentDAOImpl"> <property name="sql"> <map> <entry key="getAllStudent"> <value> <![CDATA[ SELECT student_no, student_name from t_student ]]> </value> </entry> <entry key="delStudent"> <value> <![CDATA[ delete from t_student where student_no=? ]]> </value> </entry> <entry key="addStudent"> <value> <![CDATA[ insert into t_student(student_no, student_name)values(seq_student_no.nextval,?) ]]> </value> </entry> </map> </property> </bean> </beans> |
那么我们在使用时就可以如
StudentDAOImpl.java
| public List<StudentDBO> getAllStudent() throws Exception { List<StudentDBO> stdList = new ArrayList<StudentDBO>(); stdList = jdbcTemplate.query((String) sql.get("getAllStudent"), new Object[] {}, stdItemRowMapper()); return stdList; } public void addStudent(final String stdName) throws Exception { jdbcTemplate.update((String) sql.get("addStudent"), new PreparedStatementSetter() { public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException { ps.setString(1, stdName); } }); } public void delStudent(final String stdNo) throws Exception { jdbcTemplate.update((String) sql.get("delStudent"), new PreparedStatementSetter() { public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException { ps.setString(1, stdNo); } }); } |
看到没有,加粗部分对于“一个dao如何对应多个 sql的使用”技巧。
3.5 验证我们的声明式事务
我们前面说了,只要我们使用表达式内指定的service的public方法抛出一个java.lang.Exception,容器就会为我们自动回滚该事务吗?
即一个service方法内,如果调用了一连串的dao,如果没有任何exception抛出则commit,如果有exception抛出则自动rollback该service的public方法中的所有数据库操作。
我们来看一个例子。
StudentService中的delStudent方法
| package org.sky.ssh1.alpha.service; import java.util.List; import org.sky.ssh1.alpha.dbo.StudentDBO; import org.sky.ssh1.alpha.student.form.StudentForm; public interface StudentService { public List<StudentForm> getAllStudent() throws Exception; public void addStudent(String stdName) throws Exception; public void delStudent(String[] stdNo) throws Exception; } |
StudentServiceImpl实现类片段
| public void delStudent(String[] stdNo) throws Exception { for (String s : stdNo) { studentDAO.delStudent(s); throw new Exception("force system to throw a exception"); } } |
该方法接受一个String数组,循环调用相关的dao方法来删除从页面选择的student。
我们在for循环下方故意抛出一个exception,来看效果.
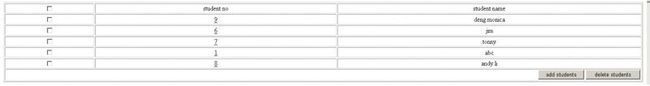
这是原来的数据:
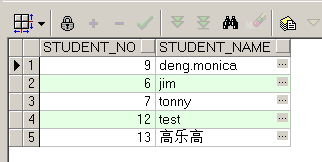
下面是相关的页面显示:
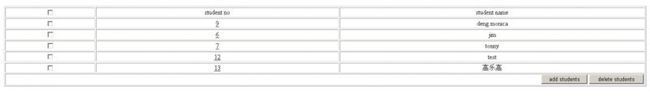
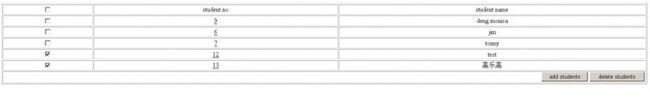
我们选择Student_No=12和Student_No=13(是蛮13的)的两个学生,进行删除。
通过时候关的service方法内的逻辑我们可以得知,Student_No=12的删除dao调用是成功的,而到了删除的dao要调用Student_No=13时会遭遇一个强制抛错,于是页面出错,按照声明式事务的理论,这两个dao在一个service的public方法中被调用,因此一旦这个service方法抛错,这个service中所有的dao操作将会被容器自动回滚,那我们来看:
选择Student_No=12和Student_No=13,点删除按钮
页面出错了:
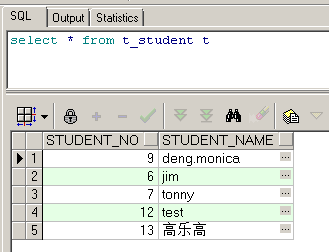
后台抛:

查看数据库发觉记录依然在(13的人真是难删,呵呵),说明我们的事务的声明是成功的.
结束今天的教程.
相关数据库表结构
4.1 t_login表
4.2 t_student表

4.3 seq_student_no序列
| CREATESEQUENCE "ALPHA"."SEQ_STUDENT_NO"MINVALUE1MAXVALUE9999999999999999999INCREMENTBY1STARTWITH21CACHE20NOORDERNOCYCLE ; |