root 对象
CompoundRoot, CompoundRoot扩展了ArrayList,具有容纳对象及后进先出类似“栈”的能力。
public class CompoundRoot extends ArrayList {
public CompoundRoot() {
}
public CompoundRoot(List list) {
super(list);
}
public CompoundRoot cutStack(int index) {
return new CompoundRoot(subList(index, size()));
}
public Object peek() {
return get(0);
}
public Object pop() {
return remove(0);
}
public void push(Object o) {
add(0, o);
}
}
(不明白为啥用0做栈顶呢?ArrayList 每次push 或remove 之后都需要重建数组)
CompoundRoot中元素的添加及提取:
OgnlValueStack提供的peek,pop,push 方法,从root中提取元素或添加元素:
- /**
- * @see com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack#peek()
- */
- public Object peek() {
- return root.peek();
- }
- /**
- * @see com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack#pop()
- */
- public Object pop() {
- return root.pop();
- }
- /**
- * @see com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack#push(java.lang.Object)
- */
- public void push(Object o) {
- root.push(o);
- }
通过表达式对CompoundRoot中元素的访问
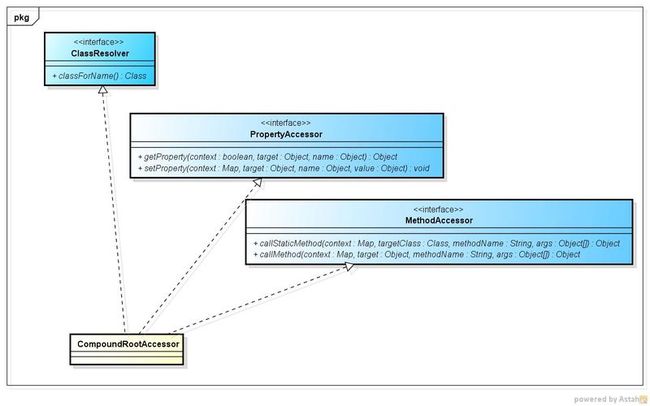
CompoundRootAccessor 实现了对 CompoundRoot 中元素以表达式方式的访问,
CompoundRootAccessor类扩展了ognl的PropertyAccessor,MethodAccessor,ClassResolver
Ognl中的root对象一般是一个javabean或Map,通过表达式中指定的属性名或key,就可以定位到属性对象
CompoundRoot 是一个ArrayList,对于表达式中指定的属性,是ArrayList中哪一个元素的属性呢? 这就需要遍历每一个元素,进行判断。
以表达式方式对CompoundRoot 中元素的属性赋值(setProperty):
对 CompoundRoot 遍历,遍历顺序由栈顶到栈底,遍历的每一个元素,都当做ognl的root对象,判断是否存在指定的属性,如果存在则对该root对象的属性赋值,遍历中下一个元素是Map,则直接使用put 方法存属性和名称,就不继续查找了:
for (Object o : root) {//CompoudRoot是ArrayList,遍历内部所有对象
if (o == null) {
continue;
}
try {
if (OgnlRuntime.hasSetProperty(ognlContext, o, name)) {
OgnlRuntime.setProperty(ognlContext, o, name, value);
//当前元素有name属性,则调用ognl进行赋值
return;
} else if (o instanceof Map) {
Map<Object, Object> map = (Map) o;
try {
map.put(name, value);
return;//如果下一个元素是Map,则直接使用put方法存属性名和值
} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
// This is an unmodifiable Map, so move on to the next element in the stack
}
}
}
以表达式方式对CompoundRoot 中元素的属性值的获值(getProperty):
对 CompoundRoot 遍历,遍历顺序由栈顶到栈底,遍历的每一个元素,都当做ognl的root对象,判断是否存在指定的属性,如果存在则获值属性值:
for (Object o : root) {//遍历
if (o == null) {
continue;
}
try {
if ((OgnlRuntime.hasGetProperty(ognlContext, o, name)) || ((o instanceof Map) && ((Map) o).containsKey(name))) {
return OgnlRuntime.getProperty(ognlContext, o, name);//当前元素有该属性,则获取
}
} catch (OgnlException e) {
if (e.getReason() != null) {
final String msg = "Caught an Ognl exception while getting property " + name;
throw new XWorkException(msg, e);
}
} catch (IntrospectionException e) {
// this is OK if this happens, we'll just keep trying the next
}
}
以表达式方式对CompoundRoot 中元素的方法调用(callMethod):
对 CompoundRoot 遍历,遍历顺序由栈顶到栈底,遍历的每一个元素,都当做ognl的root对象,对其调用指定的方法,如果返回值不为空,则说明正确,并返回方法返回值。
for (Object o : root) {//遍历
if (o == null) {
continue;
}
Class clazz = o.getClass();
Class[] argTypes = getArgTypes(objects);
MethodCall mc = null;
if (argTypes != null) {
mc = new MethodCall(clazz, name, argTypes);
}
if ((argTypes == null) || !invalidMethods.containsKey(mc)) {
try {
Object value = OgnlRuntime.callMethod((OgnlContext) context, o, name, name, objects);
if (value != null) {//返回值不为空,该元素上有此方法并调用成功
return value;
}
} catch (OgnlException e) {
// try the next one
Throwable reason = e.getReason();
if (!context.containsKey(OgnlValueStack.THROW_EXCEPTION_ON_FAILURE) && (mc != null) && (reason != null) && (reason.getClass() == NoSuchMethodException.class)) {
invalidMethods.put(mc, Boolean.TRUE);
} else if (reason != null) {
throw new MethodFailedException(o, name, e.getReason());
}
}
}
}
对 CompoundRoot 指定位置元素的访问:
1.top.属性名 (top 栈顶元素)
2.[index].top CompoundRoot 中的第N个元素[index]会调用 CompoundRoot.cutStack从第indedx位置开始的元素组成新的 CompoundRoot,top是栈顶元素