Java集合类--ArrayList
http://www.cnblogs.com/huangfox/archive/2010/10/09/1846758.html
Java集合类
一、 概述
集合类是java中常用的工具,使用频率最多的是Collection和Map两个接口的实现类,Collection存放多个单对象,而Map存放多个Key-value形式的键值对。
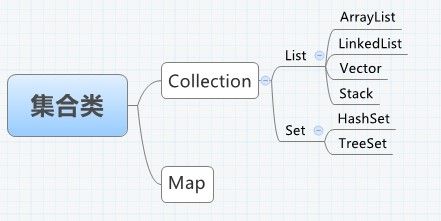
Collection又分成两大接口:List和Set,其最大的区别就是List容许存放重复的对象,而Set不行。常见的实现类参见下图:
图——Collection常见的实现类
在集合类的应用当中,我们需要注意以下几点:
- Collection的创建;
- Collection添加对象;
- Collection删除对象;
- 获取Collection当中单个对象;
- 遍历Collection中的对象;
- 判断对象是否存在于Collection中;
- Collection中对象的排序;
二、 ArrayList
2.1 创建ArrayList()
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
super()为一个空方法,因此在创建ArrayList的最重要的语句是:
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
他实例化了一个Object数组,并且将该数组赋给了当前实例的elementData属性,此数组的大小由initialCapacity指定。因此可知ArrayList是由对象数组存放数据的。
2.2 添加对象:add(E)
添加一个对象即将该对象插入到elementData数组当中,但是当数据满时,需要对其进行扩容。
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacity(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (minCapacity > oldCapacity) {
Object oldData[] = elementData;
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3)/2 + 1;
if (newCapacity < minCapacity)
newCapacity= minCapacity;
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is awin:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
}
当add(E)时,首先将当前ArrayList中的对象数量加1,赋值给变量minCapacity,然后将其与Object数组的大小进行比较,如果minCapacity大,先将Object数组赋值给一个新的数组对象(oldData),然后生成一个新的数组容量值。新数组容量值为当前容量的1.5倍再加1。最后调用Arrays.copyOf来生成新的数组对象。
如果想修改ArrayList的扩容策略,可继承ArrayList,并覆盖ensureCapacity方法。
2.3 添加对象:add(int,E)
将对象添加的到指定位置,那么就必须将该位置以后的所有数据向后移动一个位置。在这个过程中需要考虑数组容量的问题。
public void add(int index, E element) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(
"Index: "+index+",Size: "+size);
ensureCapacity(size+1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData,index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
首先将指定位置后的数据移动一个位置:
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
然后见预添加的对象插入到指定位置:
elementData[index] = element;
※知识点扩充※
arraycopy
publicstatic void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos,int length)
从指定源数组中复制一个数组,复制从指定的位置开始,到目标数组的指定位置结束。从 src 引用的源数组到 dest 引用的目标数组,数组组件的一个子序列被复制下来。被复制的组件的编号等于 length 参数。源数组中位置在 srcPos 到 srcPos+length-1 之间的组件被分别复制到目标数组中的 destPos 到 destPos+length-1 位置。
如果参数 src 和 dest 引用相同的数组对象,则复制的执行过程就好像首先将 srcPos 到 srcPos+length-1 位置的组件复制到一个带有 length 组件的临时数组,然后再将此临时数组的内容复制到目标数组的 destPos 到 destPos+length-1 位置一样。
2.4 删除对象:remove(E)
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
重点关注:
fastRemove(index);
private void fastRemove(int index) {
modCount++;
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData,index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Let gc do its work
}
获得预删除对象的位置(index),传入fastRemove,将index后所有数据向前移动一个单位,并且将最后一个数据设置为null,然gc对其进行回收。
Remove(E)比较耗时的步骤是:遍历数组与目标数据进行比较。
2.5 删除数据:remove(int)
public E remove(int index) {
RangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
EoldValue = (E) elementData[index];
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // Letgc do its work
return oldValue;
}
虽然remove(int)多了一步
RangeCheck(index);范围检测
但是不用对数据进行比较,因此remove(int)的效率比remove(E)的效率要高。
2.6 遍历对象:iterator()
关于iterator实例:
public Iterator<E> iterator(){
return new Itr();
}
每次调用iterator方法返回一个Itr实例,该实例包含属性
Cursor,
Cursor起到光标的作用,在hasNext中与当前数据的长度进行比较,如果相等则说明遍历完成,返回false。
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size();
}
Iterator实例还包含属性
expectedModCount
expecteModeCount描述了在创建iterator时ArrayList实例的状态,即获取那时modCount的值。
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
try {
Enext = get(cursor);
lastRet = cursor++;
return next;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw newNoSuchElementException();
}
}
对ArrayList实例中对象数组的大小产生影响的动作将会影响实例的modCount属性,在next方法中,需要iterator持有的expecteModeCount与当前的modCount进行比较,若不相同则说明在iterator遍历的过程中ArrayList实例发生了变化(对象数组长度发生变化)。该功能由checkForComodfication方法执行:
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw newConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
因此在使用iterator对ArrayList实例进行遍历的过程中,不能使用add、remove等方法。
2.7 判断存在或获取位置
Contains(E)、indexOf、lastIndexOf无非都是对对象数组的遍历和数据之间的比较,不做过多说明。
2.8 注意点
- ArrayList是无容量限制的。
- ArrayList在删除数据时并不会减小数组的容量,如果想要减少数组容量可以使用trimToSize方法。
- 在查找数据时,遍历数组,对非null的数据使用的是equal进行比较。
- ArrayList是非线程安全的。