OO JavaScript
如何创建JavaScript Object呢?有如下几种方法:
一、Constructor Pattern
function Person(name, age, job) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.job = job;
this.sayName = function() {
return this.name;
}
};
var p1 = new Person('Nicolas', 29, 'Software Engineer');
var p2 = new Person('Greg', 27, 'Doctor');
//function Person(name, age, job) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.job = job; this.sayName = function () {return this.name;}; }
println(1, Person.toString());
println(2, Person.length);//3
println(3, Person.constructor);//function Function() { [native code] }
println(4, Person.prototype.constructor == Person);//1 true;
println(5, Person.prototype.name);//undefined;
println(6, Person.prototype.age);//undefined;
println(6, Person.prototype.job);//undefined;
println(7, Person.prototype.sayName);//undefined;
println(8, Person.prototype == p1.__proto__);//2 true;
println(9, p2.__proto__ == p1.__proto__);//2 true;
println(10, p2.sayName);//function(){return this.name);
println(11, p2.sayName());//Greg
println(10, p1.sayName);//function(){return this.name);
println(11, p1.sayName());//Nicolas
println(11, p2.sayName == p1.sayName);//false
function println(i, value) {
document.write(i + ' ' + value + '<hr/>');
}
注意:
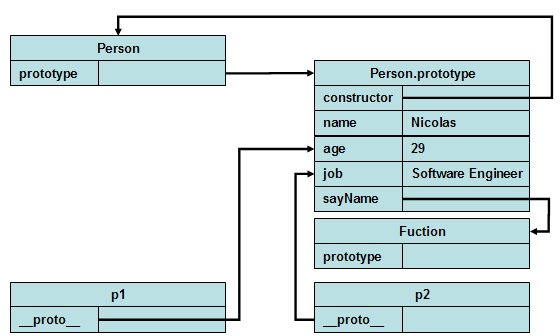
1. 当JavaScript解析从第一行~第九行的代码的时候,发现时一段function声明代码的时候,会做如下几个工作
A1:在heap里面生成一个Function对象代表这段function代码
A2:给这个Function对象,这个对象会自动获得一个prototype的属性。这个属性指向该对象的prototype object。默认说来,所有的prototype object都会自动获得一个constructor的属性,该属性存放指向Function对象的pointer
A3:设定这个Function的名字(因为这里不是一个匿名function)
A4:在global object对象建立Person的属性,这个属性的值为指向Function对象的指针。
2. 第11行:var p1 = new Person('Nicolas', 29, 'Software Engineer'),这里function作为new的方式呼叫,javascript是如何处理的呢?
A1:首先在heap去new Object,然后以这个Object作为这段code的execute context,加入到scope chain的头部。此时this-->这个object,然后进入code
A2:this.name = name,this.age = age,this.job=job,这三段代码,对刚才生成的那个Object添加属性,并赋值
A3:this.sayName = function(){...},这段会首先在heap里面生成一个function的对象,然后将该对象的pointer赋给刚才生成对象的sayName属性上
A4:对这个object.__proto__赋值,指向function Person(name,age,job){...},然后将这个object的pointer赋值给stack里面的p1;(注意这个__proto__属性,可以在firefox,safari,chrome等浏览器可以访问,但在ie等浏览器则不能访问,这是因为实现EMCScript 262的规范不同造成的)
3.第30行的输出结果是false,为什么呢?
从上面的分析,我们可以知道在new Person的时候,执行this.sayName=function(){...},会首先去heap里面new Function Object,然后赋值给sayName,所以在p1和p2都会执行这个过程。这样就会new 2个逻辑上相等的Function Object,但是由于他们的内存位置不同,所以在p1.sayName == p2.sayName的结果为false。这也是Contructor Pattern方式最大的问题,需要产生的Function Object太多了。
其内存结构为:
请参看代码:
function Person() {
};
//Person是一个Function的对象
Person.prototype.name = 'Nicolas';
Person.prototype.age = 29
Person.prototype.sayName = function() {
return this.name;
};
var p1 = new Person();
var p2 = new Person();
println(1, Person.toString());
println(2, Person.length);
println(3, Person.constructor);
println(4, Person.prototype.constructor == Person);//1 true;
println(5, Person.prototype.name);//Nicolas;
println(6, Person.prototype.name == p2.name);//Nicolas;
println(7, Person.prototype.sayName == p2.sayName);//Nicolas;
println(8, Person.prototype == p1.__proto__);//2 true;
println(9, p2.__proto__ == p1.__proto__);//2 true;
println(10, p2.__proto__.sayName == p1.__proto__.sayName);
println(11, p2.sayName() == 'Nicolas');
println(12, p1.sayName == p1.sayName);
println(13, p2.sayName() == p1.sayName());
function println(i, value) {
document.write(i + ' ' + value + '<hr/>');
}
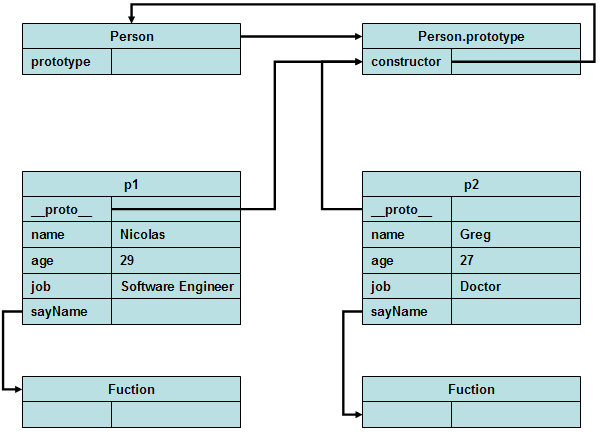
注意:
这里是将property和method都加到Person.prototype所指向的prototype的对象上,因为p1和p2都指向这个prototype对象的指针,所以访问的时候,他们共享同一片内存区域。对于方法而言是共享了,但是property却混淆在了一块儿。参看如下的内存图: