spring security3.x学习(8)_web的投票器和spEL配置
本文为转载学习
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/dsundsun/article/details/11821233
上次我们说到了"访问决策投票管理"这个概念,那如何使用呢?看一下如下代码:
<http auto-config="true" access-decision-manager-ref="unanimousBased" > <bean class="org.springframework.security.access.vote.UnanimousBased" id="unanimousBased"> <property name="decisionVoters"> <list> <ref bean="roleVoter"/> <ref bean="authenticatedVoter"/> </list> </property> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.security.access.vote.RoleVoter" id="roleVoter"/> <bean class="org.springframework.security.access.vote.AuthenticatedVoter" id="authenticatedVoter"/>
这里使用了一个unanimousBased这样的一个"访问决策投票管理",配置了相关的投票器(roleVoter/authenticatedVoter)
那好。我们仔细关注一下角色投票器(RoleVoter),上边使用了一种配置的方式,其实还有一种更为方便和简单的投票器方法。那就是使用Spring表达式语言配置访问控制:
要实现这一功能的直接方式是在<http>配置元素上添加use-expressions属性。
如:
<http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true">
这时候我们声明的使用就可以使用spEL表达式了。此时你配置的时候就可以像如下配置:
<http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true">
<intercept-url pattern="/*" access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')"/>
</http>
这个就非常方便了,就不用以前在access属性中写死角色信息咯。如果想好好使用这个的话,最好抽出时间多去看一些spEL的文档和说明。
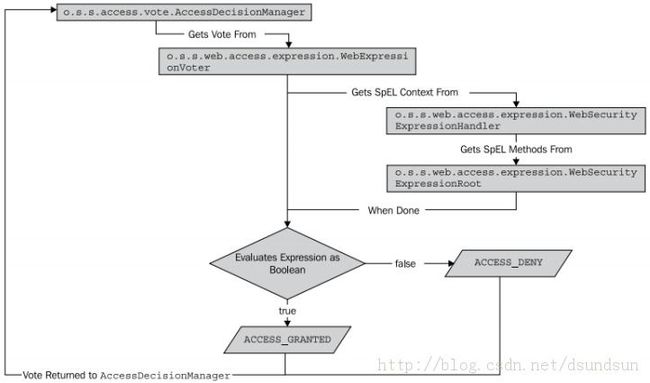
那好,我们现在又遇到了一个问题,我们没有配置投票器,那默认是哪种呢? 使用了spEL的话,系统会默认使用o.s.s.web.access.expression.WebExpressionVoter这样一个投票器,他是通过o.s.s.web.access.expression.WebSecurityExpressionHandler去实现处理的。
WebSecurityExpressionHandler同时负责评估表达式的执行结果以及提供在表达式中应用的安全相关的方法。这个接口的默认实现对外暴露了o.s.s.web.access.expression.WebSecurityExpressionRoot 类中定义的方法。
它的流程图和关系:
通过这个图,我们也能看出来,当真正获取spEL方法时,其实是使用WebSecurityExpressionRoot,我们通过它的父类可以看到一些方法,这样,我贴出来了反编译后的源码,我们可以看一下:
/* */ package org.springframework.security.access.expression;
/* */
/* */ import java.io.Serializable;
/* */ import java.util.Collection;
/* */ import java.util.HashSet;
/* */ import java.util.Set;
/* */ import org.springframework.security.access.PermissionEvaluator;
/* */ import org.springframework.security.access.hierarchicalroles.RoleHierarchy;
/* */ import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationTrustResolver;
/* */ import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
/* */ import org.springframework.security.core.authority.AuthorityUtils;
/* */
/* */ public abstract class SecurityExpressionRoot
/* */ implements SecurityExpressionOperations
/* */ {
/* */ protected final Authentication authentication;
/* */ private AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver;
/* */ private RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy;
/* */ private Set<String> roles;
/* 30 */ public final boolean permitAll = 1;
/* */
/* 33 */ public final boolean denyAll = 0;
/* */ private PermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator;
/* 35 */ public final String read = "read";
/* 36 */ public final String write = "write";
/* 37 */ public final String create = "create";
/* 38 */ public final String delete = "delete";
/* 39 */ public final String admin = "administration";
/* */
/* */ public SecurityExpressionRoot(Authentication a) {
/* 42 */ if (a == null) {
/* 43 */ throw new IllegalArgumentException("Authentication object cannot be null");
/* */ }
/* 45 */ this.authentication = a;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final boolean hasAuthority(String authority) {
/* 49 */ return hasRole(authority);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final boolean hasAnyAuthority(String[] authorities) {
/* 53 */ return hasAnyRole(authorities);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final boolean hasRole(String role) {
/* 57 */ return getAuthoritySet().contains(role);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final boolean hasAnyRole(String[] roles) {
/* 61 */ Set roleSet = getAuthoritySet();
/* */
/* 63 */ for (String role : roles) {
/* 64 */ if (roleSet.contains(role)) {
/* 65 */ return true;
/* */ }
/* */ }
/* */
/* 69 */ return false;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final Authentication getAuthentication() {
/* 73 */ return this.authentication;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final boolean permitAll() {
/* 77 */ return true;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final boolean denyAll() {
/* 81 */ return false;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final boolean isAnonymous() {
/* 85 */ return this.trustResolver.isAnonymous(this.authentication);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final boolean isAuthenticated() {
/* 89 */ return (!(isAnonymous()));
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final boolean isRememberMe() {
/* 93 */ return this.trustResolver.isRememberMe(this.authentication);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public final boolean isFullyAuthenticated() {
/* 97 */ return ((!(this.trustResolver.isAnonymous(this.authentication))) && (!(this.trustResolver.isRememberMe(this.authentication))));
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public Object getPrincipal() {
/* 101 */ return this.authentication.getPrincipal();
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public void setTrustResolver(AuthenticationTrustResolver trustResolver) {
/* 105 */ this.trustResolver = trustResolver;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public void setRoleHierarchy(RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy) {
/* 109 */ this.roleHierarchy = roleHierarchy;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ private Set<String> getAuthoritySet() {
/* 113 */ if (this.roles == null) {
/* 114 */ this.roles = new HashSet();
/* 115 */ Collection userAuthorities = this.authentication.getAuthorities();
/* */
/* 117 */ if (this.roleHierarchy != null) {
/* 118 */ userAuthorities = this.roleHierarchy.getReachableGrantedAuthorities(userAuthorities);
/* */ }
/* */
/* 121 */ this.roles = AuthorityUtils.authorityListToSet(userAuthorities);
/* */ }
/* */
/* 124 */ return this.roles;
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public boolean hasPermission(Object target, Object permission)
/* */ {
/* 129 */ return this.permissionEvaluator.hasPermission(this.authentication, target, permission);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public boolean hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType, Object permission) {
/* 133 */ return this.permissionEvaluator.hasPermission(this.authentication, (Serializable)targetId, targetType, permission);
/* */ }
/* */
/* */ public void setPermissionEvaluator(PermissionEvaluator permissionEvaluator) {
/* 137 */ this.permissionEvaluator = permissionEvaluator;
/* */ }
/* */ }
有这样一个概念:伪属性(pseudo-property)
【伪属性(pseudo-property)是指没有传入参数并符合JavaBeans的getters命名格式的方法。
这允许SpEL表达式能够省略方法的圆括号以及is 或get的前缀。如isAnonymous()方法可以
通过anonymous伪属性来访问。】
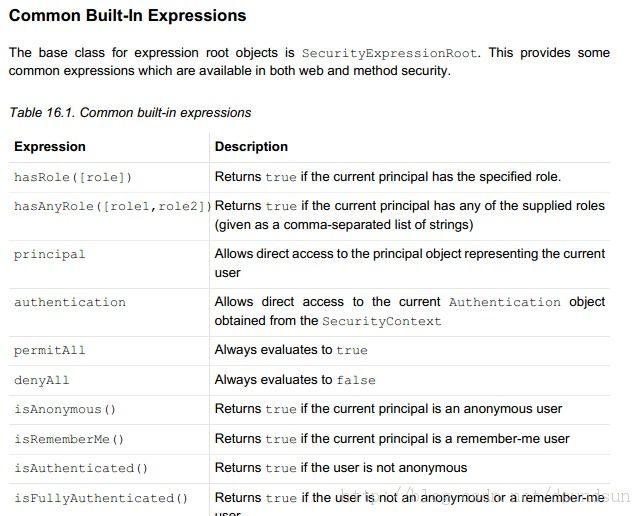
那好,我们继续研究一下他的表达式都是如何支持的呢?。我查了一下spring security帮助文档,它说,表达式有一些是通用的,有一些是web专用的,我们看一下啊。
上边这些可以用于web也可以用于方法。在看一下web上可以使用的:
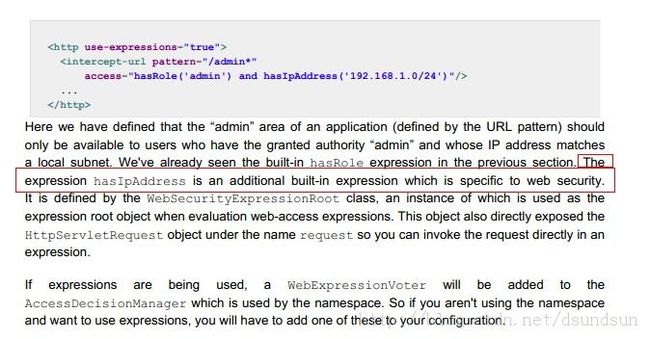
看到我画上红框的部分,那是我们应该特别注意的。
你可能会认为hasRole会返回一个Boolean值,实际上正是如此。基于SpEL的访问控制声明必须是返回Boolean类型的表达式。返回值为true意味着投票器的结果是允许访问,false 的结果意味着投票器拒绝访问
到今天为止,我们就学习了认证和授权了。 还有一些简单标签的配置。