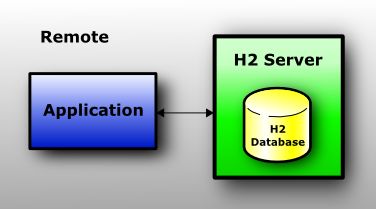
嵌入式 内存 数据库H2 Mixed Mode布署
Connection Modes
The following connection modes are supported:
- Embedded mode (local connections using JDBC)
- Remote mode (remote connections using JDBC or ODBC over TCP/IP)
- Mixed mode (local and remote connections at the same time)
Embedded Mode
In embedded mode, an application opens a database from within the same JVM using JDBC. This is the fastest and easiest connection mode. The disadvantage is that a database may only be open in one virtual machine (and class loader) at any time. As in all modes, both persistent and in-memory databases are supported. There is no limit on the number of database open concurrently, or on the number of open connections.
Remote Mode
When using the remote mode (sometimes called server mode or client/server mode), an application opens a database remotely using the JDBC or ODBC API. A server needs to be started within the same or another virtual machine (or on another computer). Many applications can connect to the same database at the same time. The remote mode is slower than the embedded mode, because all data is transferred over TCP/IP. As in all modes, both persistent and in-memory databases are supported. There is no limit on the number of database open concurrently, or on the number of open connections.
Mixed Mode
The mixed mode is a combination of the embedded and the remote mode. The main application connects to a database in embedded mode, but also starts a server so that other applications (running in different virtual machines) can concurrently access the same data. The embedded connections are as fast as if the database is used in just the embedded mode, while the remote connections are a bit slower.
Mixed Mode Deploy
Method 1: Start server in J2EE application
Java Code (MixedMode.java):
package org.h2.samples;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.h2.tools.Server;
/**
* This sample program opens the same database once in embedded mode,
* and once in the server mode. The embedded mode is faster, but only
* the server mode supports remote connections.
*/
public class MixedMode {
/**
* This method is called when executing this sample application from the
* command line.
*
* @param args the command line parameters
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// start the server, allows to access the database remotely
Server server = Server.createTcpServer(new String[] { "-tcpPort", "9101" });
server.start();
System.out.println("You can access the database remotely now, using the URL:");
System.out.println("jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost:9081/~/test (user: sa, password: sa)");
// now use the database in your application in embedded mode
Class.forName("org.h2.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:h2:file:E:/Products/Opensource/h2/lee_test/test", "sa", "");
//Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:h2:file:E:/Products/Opensource/h2/lee_test/test;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE", "sa", "");
// some simple 'business usage'
Statement stat = conn.createStatement();
stat.execute("DROP TABLE TIMER IF EXISTS");
stat.execute("CREATE TABLE TIMER(ID INT PRIMARY KEY, TIME VARCHAR)");
System.out.println("Execute this a few times: SELECT TIME FROM TIMER");
System.out.println("To stop this application (and the server), run: DROP TABLE TIMER");
try {
while (true) {
// runs forever, except if you drop the table remotely
stat.execute("MERGE INTO TIMER VALUES(1, NOW())");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.toString());
}
conn.close();
// stop the server
server.stop();
}
}
主程序Run后,是以Embeded模式连接,此时利用H2 Tools中的Broswer UI,进行连接(模拟另一Client),可以有以下几种连接方式:
1. jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost:9101/file:E:/Products/Opensource/h2/lee_test/test
2. jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost:9101/file:E:/Products/Opensource/h2/lee_test/test;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE
如果将程序中的黄底部分的语句换成绿底部分的语句,可以有以下几种连接方式:
1. jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost:9101/file:E:/Products/Opensource/h2/lee_test/test
2. jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost:9101/file:E:/Products/Opensource/h2/lee_test/test;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE
3. jdbc:h2:file:E:/Products/Opensource/h2/lee_test/test;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE (这种方式自动转换为Server模式,谁先连上谁是Embed模式)
Method 2: Start server via command line:
Command line:
@java -cp "h2.jar;%H2DRIVERS%;%CLASSPATH%" org.h2.tools.Server -tcp -tcpPort 9101
@if errorlevel 1 pause
Java Code (MixedMode.java):
package org.h2.samples;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import org.h2.tools.Server;
/**
* This sample program opens the same database once in embedded mode,
* and once in the server mode. The embedded mode is faster, but only
* the server mode supports remote connections.
*/
public class MixedMode {
/**
* This method is called when executing this sample application from the
* command line.
*
* @param args the command line parameters
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// start the server, allows to access the database remotely
Server server = Server.createTcpServer(new String[] { "-tcpPort", "9101" });
server.start();
System.out.println("You can access the database remotely now, using the URL:");
System.out.println("jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost:9081/~/test (user: sa, password: sa)");
// now use the database in your application in embedded mode
Class.forName("org.h2.Driver");
//Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:h2:file:E:/Products/Opensource/h2/lee_test/test", "sa", ""); //以Command Line方式启Server,不能使用这种方式了
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:h2:file:E:/Products/Opensource/h2/lee_test/test;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE", "sa", "");
// some simple 'business usage'
Statement stat = conn.createStatement();
stat.execute("DROP TABLE TIMER IF EXISTS");
stat.execute("CREATE TABLE TIMER(ID INT PRIMARY KEY, TIME VARCHAR)");
System.out.println("Execute this a few times: SELECT TIME FROM TIMER");
System.out.println("To stop this application (and the server), run: DROP TABLE TIMER");
try {
while (true) {
// runs forever, except if you drop the table remotely
stat.execute("MERGE INTO TIMER VALUES(1, NOW())");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.toString());
}
conn.close();
// stop the server
server.stop();
}
}
主程序Run后,是以Embeded模式连接,此时利用H2 Tools中的Broswer UI,进行连接(模拟另一Client),可以有以下几种连接方式:
1. jdbc:h2:file:E:/Products/Opensource/h2/lee_test/test;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE (这种方式自动转换为Server模式,谁先连上谁是Embed模式)