基于AR模型谱估计算法(Yule-Walker方法与Burg方法)的C++实现
头文件:
/* * Copyright (c) 2008-2011 Zhang Ming (M. Zhang), [email protected] * * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it * under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the * Free Software Foundation, either version 2 or any later version. * * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: * * 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, * this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * * 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the * documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. * * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for * more details. A copy of the GNU General Public License is available at: * http://www.fsf.org/licensing/licenses */ /***************************************************************************** * levinson.h * * If the coefficient matrix of a linear equations is Toeplitz, then it can * be solved in a high computational efficiency way through Levinson-Durbin * algorithm. The subroutiones in this file will be used for solving Wiener * -Hopf equeations in Wiener filtring and Yule- Walker equations in * parametric spectrum estimation, respectively. * * Zhang Ming, 2010-11, Xi'an Jiaotong University. *****************************************************************************/ #ifndef LEVINSON_H #define LEVINSON_H #include <vector.h> namespace splab { template<typename Type> Vector<Type> levinson( const Vector<Type>&, const Vector<Type>& ); template<typename Type> Vector<Type> levinson( const Vector<Type>&, Type& ); #include <levinson-impl.h> } // namespace splab #endif // LEVINSON_H
/* * Copyright (c) 2008-2011 Zhang Ming (M. Zhang), [email protected] * * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it * under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the * Free Software Foundation, either version 2 or any later version. * * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: * * 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, * this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * * 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the * documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. * * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for * more details. A copy of the GNU General Public License is available at: * http://www.fsf.org/licensing/licenses */ /***************************************************************************** * parametricpse.h * * Parametric Power Spectrum Estimation Mothods. * * Techniques for spectrum estimation can generally be divided into parametric * (such as classical spectrum estimation) and non-parametric methods. The * parametric approaches assume that the underlying stationary stochastic * process has a certain structure which can be described using a small number * of parameters (for example, auto-regressive model). In these approaches, * the task is to estimate the parameters of the model that describes the * stochastic process. * * The widely used model is AR model, so this file provides three subroutines * to estimate the parameter of AR model, they are Yule-Walker method, Burg's * recursive mothod and forward-and-backward linear prediction least square * method. * * Zhang Ming, 2010-11, Xi'an Jiaotong University. *****************************************************************************/ #ifndef PARAMETRICPSE_H #define PARAMETRICPSE_H #include <vector.h> #include <fft.h> #include <correlation.h> #include <levinson.h> #include <linequs1.h> namespace splab { template<typename Type> Vector<Type> yulewalkerPSE( const Vector<Type>&, int, Type& ); template<typename Type> Vector<Type> burgPSE( const Vector<Type>&, int, Type& ); template<typename Type> Vector<Type> fblplsPSE( const Vector<Type>&, int, Type& ); template<typename Type> Vector<Type> armaPSD( const Vector<Type>&, const Vector<Type>&, const Type&, int ); #include <parametricpse-impl.h> } // namespace splab #endif // PARAMETRICPSE_H
实现文件:
/* * Copyright (c) 2008-2011 Zhang Ming (M. Zhang), [email protected] * * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it * under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the * Free Software Foundation, either version 2 or any later version. * * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: * * 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, * this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * * 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the * documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. * * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for * more details. A copy of the GNU General Public License is available at: * http://www.fsf.org/licensing/licenses */ /***************************************************************************** * levinson-impl.h * * Implementationfor Levinson-Durbin alogrithm. * * Zhang Ming, 2010-11, Xi'an Jiaotong University. *****************************************************************************/ /** * Levinson algorithm for solving Toeplitz equations. * t : t(0), t(1), ..., t(n-1) of Toeplitz coefficient matrix * b : constant vector */ template <typename Type> Vector<Type> levinson( const Vector<Type> &t, const Vector<Type> &b ) { assert( t.size() == b.size() ); int n = t.size(); Type alpha, beta, q, c, omega; Vector<Type> y(n), yy(n), x(n); alpha = t[0]; if( abs(alpha) < EPS ) { cerr << "The matrix is ill-conditioned!" << endl; return x; } y[0] = 1; x[0] = b[0] / alpha; for( int k=1; k<n; ++k ) { q = 0; beta = 0; for( int j=0; j<k; ++j ) { q += x[j] * t[k-j]; beta += y[j] * t[j+1]; } c = -beta / alpha; yy[0] = c * y[k-1]; y[k] = y[k-1]; for( int i=1; i<k; ++i ) yy[i] = y[i-1] + c*y[k-i-1]; yy[k] = y[k-1]; alpha += c*beta; if( abs(alpha) < EPS ) { cerr << "The matrix is ill-conditioned!" << endl; return x; } omega = (b[k]-q) / alpha; for( int i=0; i<k; ++i ) { x[i] += omega*yy[i]; y[i] = yy[i]; } x[k] = omega*y[k]; } return x; } /** * Levinson-Durbin algorithm for solving Youle-Walker equations. * rn : r(0), r(1), ..., r(p) * sigma2 : the variance of exciting white noise */ template <typename Type> Vector<Type> levinson( const Vector<Type> &rn, Type &sigma2 ) { int p = rn.size()-1; Type tmp; Vector<Type> ak(p+1), akPrev(p+1); ak[0] = Type(1.0); sigma2 = rn[0]; ak[1] = -rn[1]/sigma2; sigma2 *= 1 - ak[1]*ak[1]; for( int k=2; k<=p; ++k ) { tmp = 0; for( int i=0; i<k; ++i ) tmp += ak[i]*rn[k-i]; ak[k] = -tmp/sigma2; for( int i=1; i<k; ++i ) akPrev[i] = ak[i] + ak[k]*ak[k-i]; for( int i=1; i<k; ++i ) ak[i] = akPrev[i]; sigma2 *= 1 - ak[k]*ak[k]; } return ak; }
/* * Copyright (c) 2008-2011 Zhang Ming (M. Zhang), [email protected] * * This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it * under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the * Free Software Foundation, either version 2 or any later version. * * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: * * 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, * this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * * 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the * documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. * * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for * more details. A copy of the GNU General Public License is available at: * http://www.fsf.org/licensing/licenses */ /***************************************************************************** * parametricpse-impl.h * * Implementation for parametric power spectrum estimatoin methods. * * Zhang Ming, 2010-11, Xi'an Jiaotong University. *****************************************************************************/ /** * The Yule-Walker method for AR power spectral estimation. * xn : input signal * p : the AR model order * sigma2 : the variance of exciting white noise * return : coefficients of AR model --- a(0), a(1), ..., a(p) */ template <typename Type> Vector<Type> yulewalkerPSE( const Vector<Type> &xn, int p, Type &sigma2 ) { int N = xn.size(); assert( p <= N ); Vector<Type> rn(p+1); for( int i=0; i<=p; ++i ) for( int k=0; k<N-i; ++k ) rn[i] += xn[k+i]*xn[k]; rn /= Type(N); return levinson( rn, sigma2 ); } /** * The Burg method for AR power spectral estimation. * xn : input signal * p : the AR model order * sigma2 : the variance of exciting white noise * return : coefficients of AR model --- a(0), a(1), ..., a(p) */ template <typename Type> Vector<Type> burgPSE( const Vector<Type> &xn, int p, Type &sigma2 ) { int N = xn.size(); Type numerator, denominator; Vector<Type> ak(p+1), akPrev(p+1), ef(N), eb(N); ak[0] = Type(1.0); sigma2 = sum(xn*xn) / Type(N); for( int i=1; i<N; ++i ) { ef[i] = xn[i]; eb[i-1] = xn[i-1]; } for( int k=1; k<=p; ++k ) { numerator = 0; denominator = 0; for( int i=k; i<N; ++i ) { numerator += ef[i]*eb[i-1]; denominator += ef[i]*ef[i] + eb[i-1]*eb[i-1]; } ak[k] = -2*numerator/denominator; for( int i=1; i<k; ++i ) akPrev[i] = ak[i] + ak[k]*ak[k-i]; for( int i=1; i<k; ++i ) ak[i] = akPrev[i]; sigma2 *= 1 - ak[k]*ak[k]; for( int i=N-1; i>k; --i ) { ef[i] = ef[i] + ak[k]*eb[i-1]; eb[i-1] = eb[i-2] + ak[k]*ef[i-1]; } } return ak; } /** * Forward and backward linear prediction least square method for * AR power spectral estimation. * xn : input signal * p : the AR model order * sigma2 : the variance of exciting white noise * return : coefficients of AR model --- a(0), a(1), ..., a(p) */ template <typename Type> Vector<Type> fblplsPSE( const Vector<Type> &xn, int p, Type &sigma2 ) { int N = xn.size(), M = 2*(N-p); Vector<Type> u(p+1); u[0] = Type(1.0); Matrix<Type> X(M,p+1); // for( int i=0; i<=p; ++i ) // { // for( int j=0; j<N-p; ++j ) // X[j][i] = xn[i+j]; // for( int j=p; j<N; ++j ) // X[j][i] = xn[j-i]; // } for( int i=0; i<N-p; ++i ) for( int j=0; j<=p; ++j ) X[i][j] = xn[i+j]; for( int i=p; i<N; ++i ) for( int j=0; j<=p; ++j ) X[i][j] = xn[i-j]; Matrix<Type> Rp = trMult(X,X) / Type(M); Vector<Type> ak = luSolver( Rp, u ); sigma2 = 1/ak[0]; ak *= sigma2; return ak; } /** * The Bartlett method of power spectral estimation. * ak : AR coefficients * bk : MA coefficients * sigma2 : the variance of exciting white noise * L : the points number of PSD * return : spectral density at L frequencies: * w = 0, 2*pi/L, ..., 2*pi(L-1)/L */ template <typename Type> Vector<Type> armaPSD( const Vector<Type> &ak, const Vector<Type> &bk, const Type &sigma2, int L ) { int p = ak.size()-1, q = bk.size()-1; Vector<Type> Xk(L); Type zRe, zIm, aRe, aIm, bRe, bIm, Xre, Xim, re, im; Type omega, den, numRe, numIm; for( int k=0; k<L; ++k ) { omega = Type(TWOPI*k/L); zRe = cos(-omega); zIm = sin(-omega); // numerator bRe = 0; bIm = 0; for( int i=q; i>0; --i ) { re = bRe; im = bIm; bRe = (re+bk[i])*zRe - im*zIm; bIm = (re+bk[i])*zIm + im*zRe; } bRe += bk[0]; // denominator aRe = 0; aIm = 0; for( int i=p; i>0; --i ) { re = aRe; im = aIm; aRe = (re+ak[i])*zRe - im*zIm; aIm = (re+ak[i])*zIm + im*zRe; } aRe += ak[0]; // Power Spectrum Density numRe = aRe*bRe + aIm*bIm; numIm = aRe*bIm - aIm*bRe; den = aRe*aRe + aIm*aIm; Xre = numRe/(den); Xim = numIm/(den); Xk[k] = sigma2 * (Xre*Xre + Xim*Xim); } return Xk; }
测试代码:
/*****************************************************************************
* parametricpse_test.cpp
*
* parametric power spectrum estimation testing.
*
* Zhang Ming, 2010-11, Xi'an Jiaotong University.
*****************************************************************************/
#define BOUNDS_CHECK
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstring>
#include <random.h>
#include <vectormath.h>
#include <parametricpse.h>
#include "engine.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace splab;
typedef double Type;
const int N = 50;
const int L = 200;
const int yuleOrder = 4;
const int burgOrder = 4;
const int lplsOrder = 4;
int main()
{
/******************************* [ signal ] ******************************/
cout << setiosflags(ios::fixed) << setprecision(4);
int mfn = L/2+1;
Type amp1 = Type(1.0),
amp2 = Type(1.0);
Type f1 = Type(0.2),
f2 = Type(0.4);
Type sigma2, SNR;
Vector<Type> tn = linspace(Type(0), Type(N-1), N );
Vector<Type> sn = amp1*sin(TWOPI*f1*tn) + amp2*sin(TWOPI*f2*tn);
Vector<Type> wn = randn( 37, Type(0.0), Type(0.1), N );
Vector<Type> xn = sn + wn;
SNR = 20*log10(norm(sn)/norm(wn));
cout << "The SNR = " << SNR << endl << endl;
/********************************* [ PSD ] *******************************/
// Vector<Type> ak = yulewalkerPSE( xn, yuleOrder, sigma2 );
// cout << "The estimated AR coefficients by Youle-Walker method are: "
// << ak << endl;
// Vector<Type> ak = burgPSE( xn, burgOrder, sigma2 );
// cout << "The estimated AR coefficients by Burg method are: "
// << ak << endl;
Vector<Type> ak = fblplsPSE( xn, lplsOrder, sigma2 );
cout << "The estimated AR coefficients by Youle-Walker method are: "
<< ak << endl;
cout << "The estimated variance is: " << sigma2 << endl << endl;
Vector<Type> bk(1,Type(1.0));
Vector<Type> Px = armaPSD( ak, bk, sigma2, L );
/******************************** [ PLOT ] *******************************/
Engine *ep = engOpen( NULL );
if( !ep )
{
cerr << "Cannot open Matlab Engine!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
mxArray *mxn = mxCreateDoubleMatrix( N, 1, mxREAL );
mxArray *mPx = mxCreateDoubleMatrix( mfn, 1, mxREAL );
memcpy( mxGetPr(mxn), xn, N*sizeof(Type) );
memcpy( mxGetPr(mPx), Px, mfn*sizeof(Type) );
engPutVariable( ep, "xn", mxn );
engPutVariable( ep, "Px", mPx );
const char *mCmd = " figure('name','FBLPLS Method of Spectrum Estimation'); \
N = length(xn); mfn = length(Px); \
subplot(2,1,1); \
plot((0:N-1), xn); \
axis([0,N,min(xn),max(xn)]); \
title('(a) Signal', 'FontSize',12); \
xlabel('Samples', 'FontSize',12); \
ylabel('Amplitude', 'FontSize',12); \
subplot(2,1,2); \
h = stem((0:mfn-1)/(mfn-1)/2, Px); \
axis([0,0.5,min(Px),max(Px)]); \
set(h,'MarkerFaceColor','blue'); \
set(gca, 'XTick', 0:0.1:0.5); \
grid on; \
title('(b) Spectrum', 'FontSize',12); \
xlabel('Normalized Frequency ( f / fs )', 'FontSize',12); \
ylabel('Amplitude', 'FontSize',12); ";
engEvalString( ep, mCmd );
mxDestroyArray( mxn );
mxDestroyArray( mPx );
system( "pause" );
engClose(ep);
return 0;
}
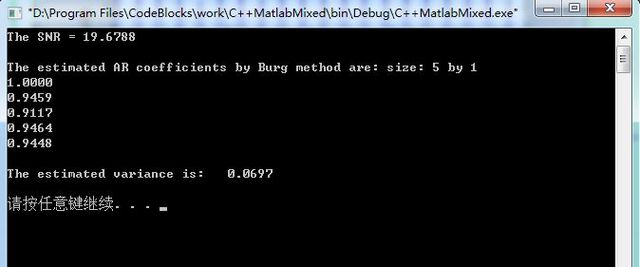
运行结果: