刨根问底-struts-http请求逻辑执行
上一节分析了FilterDispatcher中的doFilter()方法中的前半部分,主要是分析了通过actionMapper.getMapping获取ActionMapping对象,解析请求路径,寻找出namespace,name等信息。
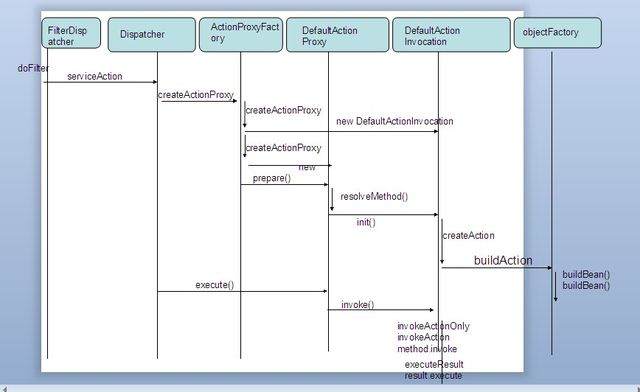
这章详细讲解doFilter()后面的重点dispatcher.serviceAction()。
这里主要的工作是根据ActionMapping对象,创建一个新的action对象,action对象是通过java反射机制差创建的,这里也就是说明了为什么struts2是单实例。然后再创建action方法实例,并且执行该方法。
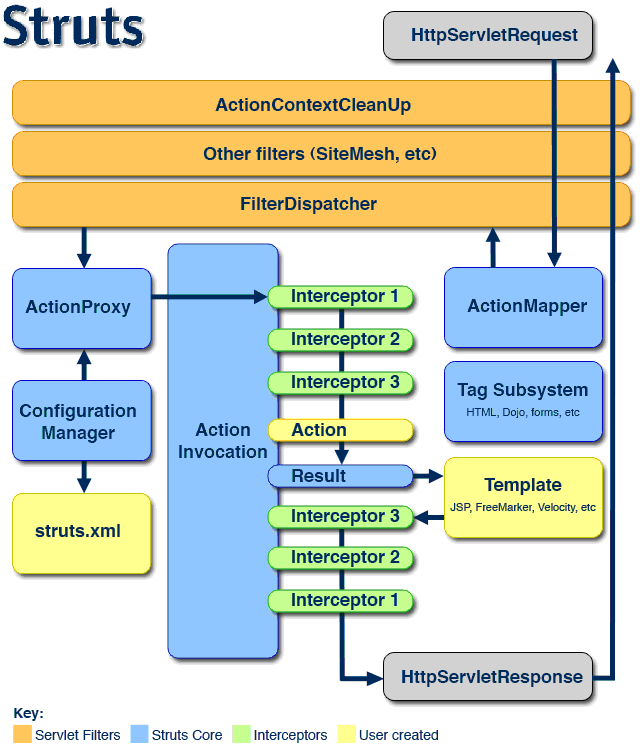
整个流程如图:
1、 继续分析doFilter(),正式执行action
dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);
public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext context,
ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
//创建mvc运行的数据环境
Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping, context);
// If there was a previous value stack, then create a new copy and pass it in to be used by the new Action
ValueStack stack = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
boolean nullStack = stack == null;
//没有找到已存在的valueStack,则从ActionContext中获取当前线程的values
if (nullStack) {
ActionContext ctx = ActionContext.getContext();
if (ctx != null) {
stack = ctx.getValueStack();
}
}
if (stack != null) {
extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, valueStackFactory.createValueStack(stack));
}
String timerKey = "Handling request from Dispatcher";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();
String name = mapping.getName();
String method = mapping.getMethod();
Configuration config = configurationManager.getConfiguration();
//创建一个ActionProxy,这里已经完全进入xwork的世界了
ActionProxy proxy = config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(
namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false);
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
// if the ActionMapping says to go straight to a result, do it!
if (mapping.getResult() != null) {
Result result = mapping.getResult();
result.execute(proxy.getInvocation());
} else {
//执行ActionProxy,真正运行xwork中的mvc实现
proxy.execute();
}
// If there was a previous value stack then set it back onto the request
if (!nullStack) {
request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, stack);
}
} catch (ConfigurationException e) {
// WW-2874 Only log error if in devMode
if(devMode) {
String reqStr = request.getRequestURI();
if (request.getQueryString() != null) {
reqStr = reqStr + "?" + request.getQueryString();
}
LOG.error("Could not find action or result\n" + reqStr, e);
}
else {
if (LOG.isWarnEnabled()) {
LOG.warn("Could not find action or result", e);
}
}
sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e);
} catch (Exception e) {
sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e);
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
}
注释:(1) //createContextMap方法主要把Application、Session、Request的key value值拷贝到Map中
(2) config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class)创建一个Action的代理对象,ActionProxyFactory是创建ActionProxy的工厂
参考实现类:DefaultActionProxy和DefaultActionProxyFactory
(3)createActionProxy()方法创建一个action 的代理对象
2、createActionProxy()创建一个新的action对象,源码:
public ActionProxy createActionProxy(String namespace, String actionName, Map<String, Object> extraContext, boolean executeResult, boolean cleanupContext) {
return createActionProxy(namespace, actionName, null, extraContext, executeResult, cleanupContext);
}
public ActionProxy createActionProxy(String namespace, String actionName, String methodName, Map<String, Object> extraContext, boolean executeResult, boolean cleanupContext) {
ActionInvocation inv = new DefaultActionInvocation(extraContext, true);
container.inject(inv);
return createActionProxy(inv, namespace, actionName, methodName, executeResult, cleanupContext);
}
注释:(1)首先调用了带有5个参数的createActionProxy方法,在这个方法并没有复杂的处理,知识简单的调用了多了一个参数methodName的createActionProxy(),请注意这个methodName参数赋值为null.
(2)创建了DefaultActionInvocation对象,并且把上面封装的参数map传进去
在这首先有必要详细讲解一下DefaultActionInvocation这个类,这个类主要的作用操作ActionProxy,然后再回来:
3、DefaultActionInvocation中init()方法:
public void init(ActionProxy proxy) {
this.proxy = proxy;
//创建上下文环境,这里的contextMap与ActionContext的上下文环境一致
Map<String, Object> contextMap = createContextMap();
// Setting this so that other classes, like object factories, can use the ActionProxy and other
// contextual information to operate
//将ActionInvocation对象设置到actionContext中,这样做得好处可以利用actionContext的数据共享特性,将ActionInvocation在整个执行周期共享。
ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext();
if (actionContext != null) {
actionContext.setActionInvocation(this);
}
createAction(contextMap);//这里是重点,创建action对象
//将action对象置于valueStack中
if (pushAction) {
stack.push(action);
contextMap.put("action", action);
}
invocationContext = new ActionContext(contextMap);
invocationContext.setName(proxy.getActionName());
// get a new List so we don't get problems with the iterator if someone changes the list
List<InterceptorMapping> interceptorList = new ArrayList<InterceptorMapping>(proxy.getConfig().getInterceptors());
interceptors = interceptorList.iterator();//拦截器
}
注释:(1)创建上下文环境
(2)ActionInvocation对象的共享
(3)创建action对象,createAction(contextMap)创建Action,struts2中每一个Request都会创建一个新的Action
(4)将action对象置入valueStack
(5)创建ActionInvocation的上下文环境
(6)将拦截器堆栈置于初始调度状态,并且把proxy中的拦截器,传值给全局变量interceptors(Iterator<InterceptorMapping>)
3.1 看看createAction()方法
protected void createAction(Map<String, Object> contextMap) {
// load action
String timerKey = "actionCreate: " + proxy.getActionName();
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
action = objectFactory.buildAction(proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getNamespace(), proxy.getConfig(), contextMap);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new XWorkException("Unable to intantiate Action!", e, proxy.getConfig());
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new XWorkException("Illegal access to constructor, is it public?", e, proxy.getConfig());
} catch (Exception e) {
String gripe = "";
if (proxy == null) {
gripe = "Whoa! No ActionProxy instance found in current ActionInvocation. This is bad ... very bad";
} else if (proxy.getConfig() == null) {
gripe = "Sheesh. Where'd that ActionProxy get to? I can't find it in the current ActionInvocation!?";
} else if (proxy.getConfig().getClassName() == null) {
gripe = "No Action defined for '" + proxy.getActionName() + "' in namespace '" + proxy.getNamespace() + "'";
} else {
gripe = "Unable to instantiate Action, " + proxy.getConfig().getClassName() + ", defined for '" + proxy.getActionName() + "' in namespace '" + proxy.getNamespace() + "'";
}
gripe += (((" -- " + e.getMessage()) != null) ? e.getMessage() : " [no message in exception]");
throw new XWorkException(gripe, e, proxy.getConfig());
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
if (actionEventListener != null) {
action = actionEventListener.prepare(action, stack);
}
} 注释: action = objectFactory.buildAction(proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getNamespace(), proxy.getConfig(), contextMap)创建action对象
3.2buildAction()方法:
public Object buildAction(String actionName, String namespace, ActionConfig config, Map<String, Object> extraContext) throws Exception {
return buildBean(config.getClassName(), extraContext);
}
public Object buildBean(String className, Map<String, Object> extraContext) throws Exception {
return buildBean(className, extraContext, true);
}
public Object buildBean(String className, Map<String, Object> extraContext, boolean injectInternal) throws Exception {
Class clazz = getClassInstance(className);
Object obj = buildBean(clazz, extraContext);
if (injectInternal) {
injectInternalBeans(obj);
}
return obj;
}
注释:最后通过java反射机制创建对象,这里就是为什么struts2是单实例的原因吧。因为每次请求来都是java反射机制创建一个新的对象。
4、DefaultActionInvocation中的invoke()方法:
/**
* @throws ConfigurationException If no result can be found with the returned code
*/
public String invoke() throws Exception {
String profileKey = "invoke: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey);
if (executed) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Action has already executed");
} //递归执行interceptor if (interceptors.hasNext()) { //通过调用Invocation.invoke()实现递归牡循环 final InterceptorMapping interceptor = (InterceptorMapping) interceptors.next();
String interceptorMsg = "interceptor: " + interceptor.getName();
UtilTimerStack.push(interceptorMsg);
try {
resultCode = interceptor.getInterceptor().intercept(DefaultActionInvocation.this);
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(interceptorMsg);
}
} else {//当所有interceptor都执行完,最后执行Action,invokeActionOnly会调用invokeAction()方法 resultCode = invokeActionOnly();
}
// this is needed because the result will be executed, then control will return to the Interceptor, which will
// return above and flow through again //在Result返回之前调用preResultListeners //通过executed控制,只执行一次 if (!executed) {
if (preResultListeners != null) {
for (Object preResultListener : preResultListeners) {
PreResultListener listener = (PreResultListener) preResultListener;
String _profileKey = "preResultListener: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(_profileKey);
listener.beforeResult(this, resultCode);
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(_profileKey);
}
}
}
// now execute the result, if we're supposed to
if (proxy.getExecuteResult()) { //执行Result executeResult();
}
executed = true;
}
return resultCode;
}
finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey);
}
}
注释:(1)执行每一个拦截器
(2)执行action方法,并且返回结果类型
(3)执行每一个PreResultListener对象的beforeResult()方法
(4)执行结果
这个流程就是典型的struts流程图中的中间的那一部分。
4.1 invokeActionOnly()方法:
public String invokeActionOnly() throws Exception {
return invokeAction(getAction(), proxy.getConfig());
}
protected String invokeAction(Object action, ActionConfig actionConfig) throws Exception {
String methodName = proxy.getMethod();
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Executing action method = " + actionConfig.getMethodName());
}
String timerKey = "invokeAction: " + proxy.getActionName();
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
boolean methodCalled = false;
Object methodResult = null;
Method method = null;
try {//java反射机制得到要执行的方法 method = getAction().getClass().getMethod(methodName, new Class[0]);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
// hmm -- OK, try doXxx instead
try { //如果没有对应的方法,则使用do+Xxxx来再次获得方法 String altMethodName = "do" + methodName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + methodName.substring(1);
method = getAction().getClass().getMethod(altMethodName, new Class[0]);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e1) {
// well, give the unknown handler a shot
if (unknownHandlerManager.hasUnknownHandlers()) {
try {
methodResult = unknownHandlerManager.handleUnknownMethod(action, methodName);
methodCalled = true;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e2) {
// throw the original one
throw e;
}
} else {
throw e;
}
}
}
if (!methodCalled) {//执行Method methodResult = method.invoke(action, new Object[0]);
}
if (methodResult instanceof Result) {
this.explicitResult = (Result) methodResult;
// Wire the result automatically
container.inject(explicitResult);
return null;
} else {
return (String) methodResult;
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The " + methodName + "() is not defined in action " + getAction().getClass() + "");
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
// We try to return the source exception.
Throwable t = e.getTargetException();
if (actionEventListener != null) {
String result = actionEventListener.handleException(t, getStack());
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
if (t instanceof Exception) {
throw (Exception) t;
} else {
throw e;
}
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
} 注释:(1)getAction()获得就是上面
createAction()创建的action对象,然后通过java反射机制获得要执行的方法
(2)执行该方法
4.2action执行完了,还要根据ResultConfig返回到view,也就是在invoke方法中调用executeResult方法
private void executeResult() throws Exception {
result = createResult();
String timerKey = "executeResult: " + getResultCode();
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
if (result != null) {
result.execute(this);
} else if (resultCode != null && !Action.NONE.equals(resultCode)) {
throw new ConfigurationException("No result defined for action " + getAction().getClass().getName()
+ " and result " + getResultCode(), proxy.getConfig());
} else {
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("No result returned for action " + getAction().getClass().getName() + " at " + proxy.getConfig().getLocation());
}
}
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
}
} 注释:(1)通过createResult()创建Result
(2)执行该结果
4.2.1 createResult()
public Result createResult() throws Exception { //如果Action中直接返回的Result类型,在invokeAction()保存在explicitResult if (explicitResult != null) {
Result ret = explicitResult;
explicitResult = null;
return ret;
}
ActionConfig config = proxy.getConfig();
Map<String, ResultConfig> results = config.getResults();
ResultConfig resultConfig = null;
synchronized (config) {
try { //返回的是String则从config中得到当前Action的Results列表 resultConfig = results.get(resultCode);
} catch (NullPointerException e) {
// swallow
}
if (resultConfig == null) {
// If no result is found for the given resultCode, try to get a wildcard '*' match.//如果找不到对应name的ResultConfig,则使用name为*的Result //说明可以用*通配所有的Result resultConfig = results.get("*");
}
}
if (resultConfig != null) {
try { //创建Result return objectFactory.buildResult(resultConfig, invocationContext.getContextMap());
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("There was an exception while instantiating the result of type " + resultConfig.getClassName(), e);
throw new XWorkException(e, resultConfig);
}
} else if (resultCode != null && !Action.NONE.equals(resultCode) && unknownHandlerManager.hasUnknownHandlers()) {
return unknownHandlerManager.handleUnknownResult(invocationContext, proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getConfig(), resultCode);
}
return null;
}
注释:(1)
如果Action中直接返回的Result类型,在invokeAction()保存在explicitResult
(2)如果explicitResult为null,就通过resultCode在返回列表中查找相应的返回配置、
(3)通过objectFactory.buildResult创建result对象
5、返回到步骤2createActionProxy()中,创建完成DefaultActionInvocation对象,继续调用createActionProxy(inv, namespace, actionName, methodName, executeResult, cleanupContext)
public ActionProxy createActionProxy(ActionInvocation inv, String namespace, String actionName, String methodName, boolean executeResult, boolean cleanupContext) {
DefaultActionProxy proxy = new DefaultActionProxy(inv, namespace, actionName, methodName, executeResult, cleanupContext);
container.inject(proxy);
proxy.prepare();
return proxy;
} 注释:(1)创建DefaultActionProxy对象
(2)执行proxy.prepare()
6、DefaultActionProxy的构造函数:
protected DefaultActionProxy(ActionInvocation inv, String namespace, String actionName, String methodName, boolean executeResult, boolean cleanupContext) {
this.invocation = inv;
this.cleanupContext = cleanupContext;
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Creating an DefaultActionProxy for namespace " + namespace + " and action name " + actionName);
}
this.actionName = actionName;
this.namespace = namespace;
this.executeResult = executeResult;
this.method = methodName;
} 7、
DefaultActionProxy的prepare() 代码:
protected void prepare() {
String profileKey = "create DefaultActionProxy: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey);
config = configuration.getRuntimeConfiguration().getActionConfig(namespace, actionName);
if (config == null && unknownHandler != null) {
config = unknownHandler.handleUnknownAction(namespace, actionName);
}
if (config == null) {
String message;
if ((namespace != null) && (namespace.trim().length() > 0)) {
message = LocalizedTextUtil.findDefaultText(XWorkMessages.MISSING_PACKAGE_ACTION_EXCEPTION, Locale.getDefault(), new String[]{
namespace, actionName
});
} else {
message = LocalizedTextUtil.findDefaultText(XWorkMessages.MISSING_ACTION_EXCEPTION, Locale.getDefault(), new String[]{
actionName
});
}
throw new ConfigurationException(message);
}
resolveMethod();
if (!config.isAllowedMethod(method)) {
throw new ConfigurationException("Invalid method: "+method+" for action "+actionName);
}
invocation.init(this);
} finally {
UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey);
}
} 注释:(1)config = configuration.getRuntimeConfiguration().getActionConfig(namespace, actionName),通过namespace和actionName查找struts.xml配置中相对应的
config
(2) resolveMethod()解析方法名称
(3) invocation.init(this)
8、resolveMethod()
private void resolveMethod() {
// if the method is set to null, use the one from the configuration
// if the one from the configuration is also null, use "execute"
if (!TextUtils.stringSet(this.method)) {
this.method = config.getMethodName();
if (!TextUtils.stringSet(this.method)) {
this.method = "execute";
}
}
} 注释;这里判断this.method是否为空,这里是null,因为上面创建
DefaultActionProxy对象时候这个参数为null。所以需要从config.getMethodName()获得方法名称,如果方法名称还为空,这里就会默认 "execute"。哈哈,这就是为什么我们不配置action的方法名称,默认的执行execute方法。
8、到这里就创建好ActionProxy对象,返回到步骤1serviceAction方法中,分析ActionProxy proxy = config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(
namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false)。
创建完成ActionProxy对象,就会执行 proxy.execute()
public String execute() throws Exception {
ActionContext nestedContext = ActionContext.getContext();
ActionContext.setContext(invocation.getInvocationContext());
String retCode = null;
String profileKey = "execute: ";
try {
UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey);
retCode = invocation.invoke();
} finally {
if (cleanupContext) {
ActionContext.setContext(nestedContext);
}
UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey);
}
return retCode;
}
注释:这里调用invocation.invoke()。