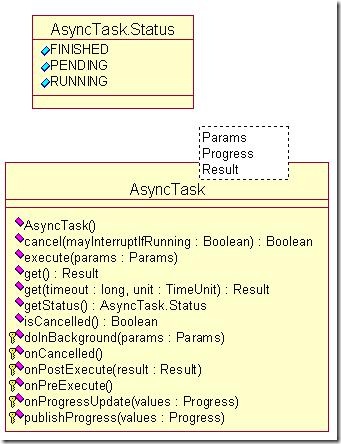
- android系统selinux中添加新属性property
辉色投像
1.定位/android/system/sepolicy/private/property_contexts声明属性开头:persist.charge声明属性类型:u:object_r:system_prop:s0图12.定位到android/system/sepolicy/public/domain.te删除neverallow{domain-init}default_prop:property
- 《人世间》
南询yi
今日分享十点推文,《人世间》有感苏格拉底说:“天地只有三尺,而人在五尺开外,所以人人都要懂得低头。”深以为然。懂得低头,不是认输。而是于人世间找寻温存的成熟,于困境中寻觅柳暗花明的智慧,于争执中展示屈伸自如的格局。正如仰头不是骄傲,是要看见自己的天空;低头也不是认输,而是要看清自己的路。成大事者,不仅要抬头挺胸,还得低头看路。懂得低头,进退有度,不是认输,而是竭尽全力过好这一生。宫崎骏说过:“所有
- pyecharts——绘制柱形图折线图
2224070247
信息可视化pythonjava数据可视化
一、pyecharts概述自2013年6月百度EFE(ExcellentFrontEnd)数据可视化团队研发的ECharts1.0发布到GitHub网站以来,ECharts一直备受业界权威的关注并获得广泛好评,成为目前成熟且流行的数据可视化图表工具,被应用到诸多数据可视化的开发领域。Python作为数据分析领域最受欢迎的语言,也加入ECharts的使用行列,并研发出方便Python开发者使用的数据
- 2022-08-28
蔚蓝一片晴
初三暑假培训收获点滴从8月25至8月27日三天两晚的培训结束了,回到家中,该静下心来整理一下触动心灵的收获,成为成长的积淀。1.在优秀团队中快速成长与提升,做一名反思成长型教师一名专业型教师的教学指导包括了教学原理知识、案例知识、策略知识。面对教学中的遇到的有趣的情形、问题会去研究其理,寻找更好的教法学法对策。从新手到成熟型教师,再走向专业型教师,需要的是觉醒与反思,多进行案例研究,从案例中观察、
- 2.2.6 通知类控件 Toast、Menu
常思行
本文例程下载:WillFlow_Toast、WillFlowMenu一、什么是Toast?Toast也被叫做吐司,是Android系统提供的一种非常好的提醒方式,在程序中可以使用它将一些短小的信息通知给用户,它有如下两个特点:Toast是没有焦点的Toast显示的时间有限过一定的时间就会自动消失所以一般来讲Toast的使用并不会影响我们的正常操作,并且它通常不会占用太大的屏幕空间,有着良好的用户体
- 现代汉语粗糙版 文学史与经典
学习搬运工
第十六章文学史与经典文学史的兴起在西方,虽然从亚里士多德开始,在人类的著述中已经可以找到文学史概念与写作方式的萌芽,但是,人们一般认为17世纪后期到18世纪是现代文学史写作真正开始的时期。长达百年波及整个欧洲的“古今之争”孕育出文学研究的历史意识,现代意义上的文学史观念在这场影响深远的论争中初见端倪。从18世纪晚期到19世纪初,由于席勒、弗·施莱格尔和赫尔德等人的介入,文学史研究逐渐变得复杂和成熟
- mac 备份android 手机通讯录导入iphone,iphone如何导出通讯录(轻松教你iPhone备份通讯录的方法)...
weixin_39762838
mac备份android手机通讯录导入iphone
在日新月异的手机更替中,换手机已经成为一个非常稀松平常的事情,但将旧手机上面的通讯录导入到新手机还是让不少小伙伴为难,本篇将给大家详细讲解这方面的知识:“苹果手机通讯录怎么导入到新手机”及“安卓手机通讯录导入到新手机”的方法。一、苹果手机通讯录导入到新手机常用方法(SIM卡导入)在苹果手机主频幕上找到“设置”,单击进入设置菜单,下拉菜单列表,点击“邮件、通讯录、日历”,然后找到“导入SIM卡通讯录
- android 更改窗口的层次,浮窗开发之窗口层级
Ms.Bu
android更改窗口的层次
最近在项目中遇到了这样的需求:需要在特定的其他应用之上悬浮自己的UI交互(拖动、输入等复杂的UI交互),和九游的浮窗类似,不过我们的比九游的体验更好,我们越过了很多授权的限制。浮窗效果很多人都知道如何去实现一个简单的浮窗,但是却很少有人去深入的研究背后的流程机制,由于项目中浮窗交互比较复杂,遇到了些坑查看了很多资料,故总结浮窗涉及到的知识点:窗口层级关系(浮窗是如何“浮”的)?浮窗有哪些限制,如何
- 黄景瑜工作人员怒怼营销号!肖战事件就是他的前车之鉴
板凳吃瓜小分队
无论社会怎样浮躁,我们自己也不可以浮躁。战胜浮躁的关键是明白自己真正的需要,保持一颗平常心,不要盲目攀比,不要羡慕别人,更不要唯利是图。一辈子很短,我们不能总是望着别人的精彩,羡慕着别人的人生,而忘记了经营自己生活,要知道,通过努力,你也能成为让人仰望的明星。如今,随着娱乐产业越来越成熟,每年的新星也是扎堆冒出。在我看来,与前几年不同的是,如今的新生代质量明显好过从前。“更专业了,更有礼貌了”也是
- Android应用性能优化
轻口味
Android
Android手机由于其本身的后台机制和硬件特点,性能上一直被诟病,所以软件开发者对软件本身的性能优化就显得尤为重要;本文将对Android开发过程中性能优化的各个方面做一个回顾与总结。Cache优化ListView缓存:ListView中有一个回收器,Item滑出界面的时候View会回收到这里,需要显示新的Item的时候,就尽量重用回收器里面的View;每次在getView函数中inflate新
- Android实现监听事件的方法
Amy木婉清
1.通过内部类实现2.通过匿名内部类实现3.通过事件源所在类实现4.通过外部类实现5.布局文件中onclick属性(针对点击事件)1.通过内部类实现代码:privateButtonmBtnEvent;//oncreate中mBtnEvent.setOnClickListener(newOnClick());//内部类实现监听classOnClickimplementsView.OnClickLis
- 高级UI<第二十四篇>:Android中用到的矩阵常识
NoBugException
(1)定义在数学中,矩阵(Matrix)是一个按照长方阵列排列的复数或实数集合。由m×n个数aij排成的m行n列的数表称为m行n列的矩阵,简称m×n矩阵。记作:图片.png这m×n个数称为矩阵A的元素,简称为元,数aij位于矩阵A的第i行第j列,称为矩阵A的(i,j)元,以数aij为(i,j)元的矩阵可记为(aij)或(aij)m×n,m×n矩阵A也记作Amn。元素是实数的矩阵称为实矩阵,元素是复
- RK3229_Android9.0_Box 4G模块EC200A调试
suifen_
网络
0、kernel修改这部分完全可以参考Linux的移植:RK3588EC200A-CN【4G模块】调试_rkec200a-cn-CSDN博客1、修改device/rockchip/rk322xdiff--gita/device.mkb/device.mkindexec6bfaa..e7c32d1100755---a/device.mk+++b/device.mk@@-105,6+105,8@@en
- 极度休闲的一天
淡泊孤峰
国庆国庆,普天同庆。在家躺着看大家游山玩水,长辈走亲戚,我的微信一天没几条消息,标准结局,习惯了。哈利波特系列电影真不错,童年总幻想着像主角哈利一样,像《龙族》少年楚子航浪迹江湖,风云天下。而现在却败给华为ICT大赛题还有永无止境的代码视频,唉,真可笑!
- 2021.9.26 王老师直播笔记
wan恋空
案例一孩子想要iPad,爸爸妈妈不同意,孩子在家闹平时老公暴躁会摔手机,孩子会不尊重骂自己总结问题老公儿子很任性1.注意力放到老公和自己的身上一个成熟比较横的男人,需要一个成熟比较理智的女人。2.做好自己的角色*儿子你必须尊重我,接受原则做事。少说教,多谈感受3.找一群志同道合的朋友聊聊,改变圈子案例二女儿六岁觉得老师讲课有问题指出来。做事要有策略六岁可以指出来,六岁以后就不可以了女儿小时候在姥姥
- kt文件和java文件_Java与Kotlin之间怎样进行互操作
铭空间
kt文件和java文件
Java与Kotlin之间怎样进行互操作发布时间:2021-02-0210:50:43来源:亿速云阅读:98作者:小新这篇文章主要介绍了Java与Kotlin之间怎样进行互操作,具有一定借鉴价值,感兴趣的朋友可以参考下,希望大家阅读完这篇文章之后大有收获,下面让小编带着大家一起了解一下。前言目前kotlin是谷歌首推的开发Android的语言,但由于历史原因,我们绝大部分项目依旧还是以Java为主
- Android shell 常用 debug 命令
晨春计
Audiodebugandroidlinux
目录1、查看版本2、am命令3、pm命令4、dumpsys命令5、sed命令6、log定位查看APK进程号7、log定位使用场景1、查看版本1.1、Android串口终端执行getpropro.build.version.release#获取Android版本uname-a#查看linux内核版本信息uname-r#单独查看内核版本1.2、linux服务器执行lsb_release-a#查看Lin
- 未来软件市场是怎么样的?做开发的生存空间如何?
cesske
软件需求
目录前言一、未来软件市场的发展趋势二、软件开发人员的生存空间前言未来软件市场是怎么样的?做开发的生存空间如何?一、未来软件市场的发展趋势技术趋势:人工智能与机器学习:随着技术的不断成熟,人工智能将在更多领域得到应用,如智能客服、自动驾驶、智能制造等,这将极大地推动软件市场的增长。云计算与大数据:云计算服务将继续普及,大数据技术的应用也将更加广泛。企业将更加依赖云计算和大数据来优化运营、提升效率,并
- 2018年12月23日 星期日 晴
刘一鸣妈妈
早晨舒舒服服睡个懒觉,睁开眼已经快八点了。简单洗漱之后,准备吃早饭。嫂子给煎的牛排,七成熟,孩子吃的津津有味。我只能吃十二分熟的,可以外焦,不要里嫩。早饭后到世纪金源给然然选照片,几番挣扎后忍痛割爱删掉近百张,最后只保留三十张做相册。下午然然继续拍一套影楼赠送的台历照片,商家看到我带着孩子,也赠送了一套作为体验。拍照的过程特别欢乐,孩子很享受穿着帅气的衣服摆出帅帅的动作。然然拍过一套照片后明显找到
- Rust是否会取代C/C++?Rust与C/C++的较量
AI与编程之窗
源码编译与开发rustc语言c++内存安全并发编程代码安全性能优化
目录引言第一部分:Rust语言的优势内存安全性并发性性能社区和生态系统的成长第二部分:C/C++语言的优势和地位历史积淀和成熟度广泛的库和工具支持性能优化和硬件控制丰富的行业应用社区和行业支持第三部分:挑战和阻碍学习曲线现有代码库的迁移成本生态系统和工具链的完善度社区和人才培养行业应用和推广法规和标准化第四部分:未来趋势和可能性行业趋势教育和人才培养兼容和共存行业标准化企业支持和应用开源社区和生态
- 2024年最全Flutter如何和Native通信-Android视角,Electron开发Android界面
2401_84544531
程序员android面试学习
总结【Android详细知识点思维脑图(技能树)】其实Android开发的知识点就那么多,面试问来问去还是那么点东西。所以面试没有其他的诀窍,只看你对这些知识点准备的充分程度。so,出去面试时先看看自己复习到了哪个阶段就好。虽然Android没有前几年火热了,已经过去了会四大组件就能找到高薪职位的时代了。这只能说明Android中级以下的岗位饱和了,现在高级工程师还是比较缺少的,很多高级职位给的薪
- 踩咸菜
小豆本子
听到这个名字,你是不是觉得很奇怪,咸菜怎么是用来踩的呢?你小时候洗完澡站在浴巾上,两只脚用力踩浴巾,还让我给你唱《采蘑菇的小男孩》你还记得么?对了,这回说的就是那个用脚丫子用力“踩”的踩咸菜。我小的时候家家户户都要踩咸菜。时间大概就是这几天(今天11月23号,农历十月十六)开始准备咸菜的菜。这种菜的学名叫雪里蕻,也叫雪菜。我小时候在农场长大,你外公和你外婆会种很大一片的雪里蕻。到了雪里蕻长大成熟的
- 2020-03-24
艺鹰空间设计
从欧美的复古奢华,到现代极简的北欧风,一个太沉闷,一个略单调,设计师梁博,在自己的作品中融入一点点的复古元素,即能保留现代风格的清爽和功能上的便利,又可以收获复古的奢华和优雅,简直是太完美的搭配!古典风格住宅,设计师重新设计,厨房和起居室结合在一起,走廊和厨房起居室之间的墙从地板到天花板变成了一个透明隔断,给空间带来了更多的空气和光线。主卧室的设计颇有高级酒店的味道,左侧设置了休闲椅,右侧则有办公
- 莆田鞋十大良心微商推荐,莆田鞋推荐微商排名一览表
腕表鞋屋
莆田鞋是广受欢迎的一种休闲鞋,因其舒适耐穿而备受消费者喜爱。在如今的微商市场中,有许多卖家代理莆田鞋,但是有些卖家并不那么负责,售卖的鞋子品质堪忧。因此,今天我们就来盘点一下莆田鞋的十大良心微商,为大家推荐一些靠谱的卖家。微信:726865(下单赠送精美礼品)1.小尼鞋铺小尼鞋铺是一家专注于莆田鞋销售的微商店铺,主打高品质的鞋子,深受用户好评。2.快乐小屋快乐小屋作为一个专业的莆田鞋代理店,拥有丰
- 协作机器人关节模组总结
雪花飞龙
协作机器人本体结构
协作机器人关节模块总结关节模组介绍关节模组一般部件:通讯协议泰科机器人关节模组RJS系列RJS-II系列RJU系列SHD系列RGM机器人关节模组关节模组介绍协作机器人的技术已经相对成熟,如何快速生产协作机器人?如何降低机器人成本?等问题是现在研究的一个重点。协作机器人的关节功能相对独立,可以做成一个独立模块,只需要提供电源和控制信号就好。关节模组一般部件:1.减速器:谐波减速器是最常用的减速器,此
- 手机小游戏开发
红匣子实力推荐
随着智能手机的普及,手机小游戏已经成为人们日常生活中不可或缺的一部分。从简单的消除游戏到复杂的策略游戏,手机小游戏为玩家提供了丰富的娱乐体验。本文将为您介绍手机小游戏开发的基本概念、工具和技术。开发-联系电话:13642679953(微信同号)1.游戏类型手机小游戏可以分为多种类型,如益智游戏、休闲游戏、动作游戏、策略游戏等。开发者可以根据自己的兴趣和技能选择合适的游戏类型进行开发。2.开发工具手
- 分享一个基于python的电子书数据采集与可视化分析 hadoop电子书数据分析与推荐系统 spark大数据毕设项目(源码、调试、LW、开题、PPT)
计算机源码社
Python项目大数据大数据pythonhadoop计算机毕业设计选题计算机毕业设计源码数据分析spark毕设
作者:计算机源码社个人简介:本人八年开发经验,擅长Java、Python、PHP、.NET、Node.js、Android、微信小程序、爬虫、大数据、机器学习等,大家有这一块的问题可以一起交流!学习资料、程序开发、技术解答、文档报告如需要源码,可以扫取文章下方二维码联系咨询Java项目微信小程序项目Android项目Python项目PHP项目ASP.NET项目Node.js项目选题推荐项目实战|p
- 软件测试缺陷的管理流程(上):构成要素与流程说明
程序员笑笑
软件测试自动化测试软件测试功能测试程序人生职场和发展
实施测试活动过程中,针对缺陷开展有效跟踪管理是测试工程师质量保证活动的重点。因此,在一个成熟的测试团队或组织内,缺陷管理流程的完善与否直接决定了测试活动的质量。缺陷管理流程通常由角色定义、流程定义、工具应用、缺陷分析模型等几个关键因素构成:角色定义:表述了在缺陷管理流程中所涉及的若干角色及其职责内容,从而清晰明确定义每个流程节点中角色所需完成的事务。流程定义:规定了在项目或产品实施测试活动时所需遵
- 我们在读书会尝试OKR,结果成了PDCA
湖边的阿曦
“读书要玩味,好玩又有味。”前面有了不成熟的理解——《OKR的优势是什么?它的实践原则有哪些?》,现在又有了不成熟的实践——在读书会尝试OKR。我们的现状我们读书会是个小组织,每个月一次线下活动,每次参加人数在10位左右。也是个自组织,没有管理员,没有固定组织者,只有每次活动时的临时主持者。我们也没有任何规定,一切基于个人的自我驱动及相互尊重。活动的内容,可能是一本书,也可能是一个主题。在活动前,
- Dubbo架构概览:服务注册与发现、远程调用、监控与管理
木南曌
dubbo架构
Dubbo是一个成熟的、高性能的、基于Java的微服务开发框架,它主要用于解决分布式系统中的服务治理问题,包括服务的注册与发现、远程过程调用(RPC)、服务监控与管理等多个关键环节。以下是Dubbo架构概览的详细介绍:服务注册与发现Dubbo的服务注册与发现机制是其核心功能之一,它依赖于注册中心来管理服务的生命周期和定位服务提供者。1.服务提供者(Provider)服务提供者是实际提供服务的节点,
- Enum 枚举
120153216
enum枚举
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Kavlez/p/4268601.html Enumeration
于Java 1.5增加的enum type...enum type是由一组固定的常量组成的类型,比如四个季节、扑克花色。在出现enum type之前,通常用一组int常量表示枚举类型。比如这样:
public static final int APPLE_FUJI = 0
- Java8简明教程
bijian1013
javajdk1.8
Java 8已于2014年3月18日正式发布了,新版本带来了诸多改进,包括Lambda表达式、Streams、日期时间API等等。本文就带你领略Java 8的全新特性。
一.允许在接口中有默认方法实现
Java 8 允许我们使用default关键字,为接口声明添
- Oracle表维护 快速备份删除数据
cuisuqiang
oracle索引快速备份删除
我知道oracle表分区,不过那是数据库设计阶段的事情,目前是远水解不了近渴。
当前的数据库表,要求保留一个月数据,且表存在大量录入更新,不存在程序删除。
为了解决频繁查询和更新的瓶颈,我在oracle内根据需要创建了索引。但是随着数据量的增加,一个半月数据就要超千万,此时就算有索引,对高并发的查询和更新来说,让然有所拖累。
为了解决这个问题,我一般一个月会进行一次数据库维护,主要工作就是备
- java多态内存分析
麦田的设计者
java内存分析多态原理接口和抽象类
“ 时针如果可以回头,熟悉那张脸,重温嬉戏这乐园,墙壁的松脱涂鸦已经褪色才明白存在的价值归于记忆。街角小店尚存在吗?这大时代会不会牵挂,过去现在花开怎么会等待。
但有种意外不管痛不痛都有伤害,光阴远远离开,那笑声徘徊与脑海。但这一秒可笑不再可爱,当天心
- Xshell实现Windows上传文件到Linux主机
被触发
windows
经常有这样的需求,我们在Windows下载的软件包,如何上传到远程Linux主机上?还有如何从Linux主机下载软件包到Windows下;之前我的做法现在看来好笨好繁琐,不过也达到了目的,笨人有本方法嘛;
我是怎么操作的:
1、打开一台本地Linux虚拟机,使用mount 挂载Windows的共享文件夹到Linux上,然后拷贝数据到Linux虚拟机里面;(经常第一步都不顺利,无法挂载Windo
- 类的加载ClassLoader
肆无忌惮_
ClassLoader
类加载器ClassLoader是用来将java的类加载到虚拟机中,类加载器负责读取class字节文件到内存中,并将它转为Class的对象(类对象),通过此实例的 newInstance()方法就可以创建出该类的一个对象。
其中重要的方法为findClass(String name)。
如何写一个自己的类加载器呢?
首先写一个便于测试的类Student
- html5写的玫瑰花
知了ing
html5
<html>
<head>
<title>I Love You!</title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
</head>
<body>
<canvas id="c"></canvas>
- google的ConcurrentLinkedHashmap源代码解析
矮蛋蛋
LRU
原文地址:
http://janeky.iteye.com/blog/1534352
简述
ConcurrentLinkedHashMap 是google团队提供的一个容器。它有什么用呢?其实它本身是对
ConcurrentHashMap的封装,可以用来实现一个基于LRU策略的缓存。详细介绍可以参见
http://code.google.com/p/concurrentlinke
- webservice获取访问服务的ip地址
alleni123
webservice
1. 首先注入javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext,
@Resource
private WebServiceContext context;
2. 在方法中获取交换请求的对象。
javax.xml.ws.handler.MessageContext mc=context.getMessageContext();
com.sun.net.http
- 菜鸟的java基础提升之道——————>是否值得拥有
百合不是茶
1,c++,java是面向对象编程的语言,将万事万物都看成是对象;java做一件事情关注的是人物,java是c++继承过来的,java没有直接更改地址的权限但是可以通过引用来传值操作地址,java也没有c++中繁琐的操作,java以其优越的可移植型,平台的安全型,高效性赢得了广泛的认同,全世界越来越多的人去学习java,我也是其中的一员
java组成:
- 通过修改Linux服务自动启动指定应用程序
bijian1013
linux
Linux中修改系统服务的命令是chkconfig (check config),命令的详细解释如下: chkconfig
功能说明:检查,设置系统的各种服务。
语 法:chkconfig [ -- add][ -- del][ -- list][系统服务] 或 chkconfig [ -- level <</SPAN>
- spring拦截器的一个简单实例
bijian1013
javaspring拦截器Interceptor
Purview接口
package aop;
public interface Purview {
void checkLogin();
}
Purview接口的实现类PurviesImpl.java
package aop;
public class PurviewImpl implements Purview {
public void check
- [Velocity二]自定义Velocity指令
bit1129
velocity
什么是Velocity指令
在Velocity中,#set,#if, #foreach, #elseif, #parse等,以#开头的称之为指令,Velocity内置的这些指令可以用来做赋值,条件判断,循环控制等脚本语言必备的逻辑控制等语句,Velocity的指令是可扩展的,即用户可以根据实际的需要自定义Velocity指令
自定义指令(Directive)的一般步骤
&nbs
- 【Hive十】Programming Hive学习笔记
bit1129
programming
第二章 Getting Started
1.Hive最大的局限性是什么?一是不支持行级别的增删改(insert, delete, update)二是查询性能非常差(基于Hadoop MapReduce),不适合延迟小的交互式任务三是不支持事务2. Hive MetaStore是干什么的?Hive persists table schemas and other system metadata.
- nginx有选择性进行限制
ronin47
nginx 动静 限制
http {
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=addr:10m;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=5r/s;...
server {...
location ~.*\.(gif|png|css|js|icon)$ {
- java-4.-在二元树中找出和为某一值的所有路径 .
bylijinnan
java
/*
* 0.use a TwoWayLinkedList to store the path.when the node can't be path,you should/can delete it.
* 1.curSum==exceptedSum:if the lastNode is TreeNode,printPath();delete the node otherwise
- Netty学习笔记
bylijinnan
javanetty
本文是阅读以下两篇文章时:
http://seeallhearall.blogspot.com/2012/05/netty-tutorial-part-1-introduction-to.html
http://seeallhearall.blogspot.com/2012/06/netty-tutorial-part-15-on-channel.html
我的一些笔记
===
- js获取项目路径
cngolon
js
//js获取项目根路径,如: http://localhost:8083/uimcardprj
function getRootPath(){
//获取当前网址,如: http://localhost:8083/uimcardprj/share/meun.jsp
var curWwwPath=window.document.locati
- oracle 的性能优化
cuishikuan
oracleSQL Server
在网上搜索了一些Oracle性能优化的文章,为了更加深层次的巩固[边写边记],也为了可以随时查看,所以发表这篇文章。
1.ORACLE采用自下而上的顺序解析WHERE子句,根据这个原理,表之间的连接必须写在其他WHERE条件之前,那些可以过滤掉最大数量记录的条件必须写在WHERE子句的末尾。(这点本人曾经做过实例验证过,的确如此哦!
- Shell变量和数组使用详解
daizj
linuxshell变量数组
Shell 变量
定义变量时,变量名不加美元符号($,PHP语言中变量需要),如:
your_name="w3cschool.cc"
注意,变量名和等号之间不能有空格,这可能和你熟悉的所有编程语言都不一样。同时,变量名的命名须遵循如下规则:
首个字符必须为字母(a-z,A-Z)。
中间不能有空格,可以使用下划线(_)。
不能使用标点符号。
不能使用ba
- 编程中的一些概念,KISS、DRY、MVC、OOP、REST
dcj3sjt126com
REST
KISS、DRY、MVC、OOP、REST (1)KISS是指Keep It Simple,Stupid(摘自wikipedia),指设计时要坚持简约原则,避免不必要的复杂化。 (2)DRY是指Don't Repeat Yourself(摘自wikipedia),特指在程序设计以及计算中避免重复代码,因为这样会降低灵活性、简洁性,并且可能导致代码之间的矛盾。 (3)OOP 即Object-Orie
- [Android]设置Activity为全屏显示的两种方法
dcj3sjt126com
Activity
1. 方法1:AndroidManifest.xml 里,Activity的 android:theme 指定为" @android:style/Theme.NoTitleBar.Fullscreen" 示例: <application
- solrcloud 部署方式比较
eksliang
solrCloud
solrcloud 的部署其实有两种方式可选,那么我们在实践开发中应该怎样选择呢? 第一种:当启动solr服务器时,内嵌的启动一个Zookeeper服务器,然后将这些内嵌的Zookeeper服务器组成一个集群。 第二种:将Zookeeper服务器独立的配置一个集群,然后将solr交给Zookeeper进行管理
谈谈第一种:每启动一个solr服务器就内嵌的启动一个Zoo
- Java synchronized关键字详解
gqdy365
synchronized
转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/mengdd/archive/2013/02/16/2913806.html
多线程的同步机制对资源进行加锁,使得在同一个时间,只有一个线程可以进行操作,同步用以解决多个线程同时访问时可能出现的问题。
同步机制可以使用synchronized关键字实现。
当synchronized关键字修饰一个方法的时候,该方法叫做同步方法。
当s
- js实现登录时记住用户名
hw1287789687
记住我记住密码cookie记住用户名记住账号
在页面中如何获取cookie值呢?
如果是JSP的话,可以通过servlet的对象request 获取cookie,可以
参考:http://hw1287789687.iteye.com/blog/2050040
如果要求登录页面是html呢?html页面中如何获取cookie呢?
直接上代码了
页面:loginInput.html
代码:
<!DOCTYPE html PUB
- 开发者必备的 Chrome 扩展
justjavac
chrome
Firebug:不用多介绍了吧https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/bmagokdooijbeehmkpknfglimnifench
ChromeSnifferPlus:Chrome 探测器,可以探测正在使用的开源软件或者 js 类库https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/chrome-sniffer-pl
- 算法机试题
李亚飞
java算法机试题
在面试机试时,遇到一个算法题,当时没能写出来,最后是同学帮忙解决的。
这道题大致意思是:输入一个数,比如4,。这时会输出:
&n
- 正确配置Linux系统ulimit值
字符串
ulimit
在Linux下面部 署应用的时候,有时候会遇上Socket/File: Can’t open so many files的问题;这个值也会影响服务器的最大并发数,其实Linux是有文件句柄限制的,而且Linux默认不是很高,一般都是1024,生产服务器用 其实很容易就达到这个数量。下面说的是,如何通过正解配置来改正这个系统默认值。因为这个问题是我配置Nginx+php5时遇到了,所以我将这篇归纳进
- hibernate调用返回游标的存储过程
Supanccy2013
javaDAOoracleHibernatejdbc
注:原创作品,转载请注明出处。
上篇博文介绍的是hibernate调用返回单值的存储过程,本片博文说的是hibernate调用返回游标的存储过程。
此此扁博文的存储过程的功能相当于是jdbc调用select 的作用。
1,创建oracle中的包,并在该包中创建的游标类型。
---创建oracle的程
- Spring 4.2新特性-更简单的Application Event
wiselyman
application
1.1 Application Event
Spring 4.1的写法请参考10点睛Spring4.1-Application Event
请对比10点睛Spring4.1-Application Event
使用一个@EventListener取代了实现ApplicationListener接口,使耦合度降低;
1.2 示例
包依赖
<p