CentOS 5.5环境下安装配置Varnish
#!/bin/bash
# BY kerryhu
# MAIL:[email protected]
# BLOG:http://kerry.blog.51cto.com
# Please manual operation yum of before Operation.....
#============================ 更新系统时间 ============================
yum install -y ntp
ntpdate time.nist.gov
echo "00 01 * * * ntpdate time.nist.gov" >> /etc/crontab
#============================ Varnish安装 =============================
如果是RedHat/CentOS系统,在安装varnish的时候首先要安装以下软件包
automake
autoconf
libtool
ncurses-devel
libxslt
groff
pcre-devel
pkgconfig
groupadd www
useradd www -g www -s /sbin/nologin
mkdir -p /data/varnish/{cache,logs}
chmod +w /data/varnish/{cache,logs}
chown -R www:www /data/varnish/{cache,logs}
cd /opt
yum install -y automake autoconf libtool ncurses-devel libxslt groff pcre-devel pkgconfig
wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/varnish/files/varnish/2.1.3/varnish-2.1.3.tar.gz/download
tar -zxvf varnish-2.1.3.tar.gz
cd varnish-2.1.3
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/varnish
make;make install
#============================ varnish配置 ===========================
vi /usr/local/varnish/etc/varnish/kerry.vcl
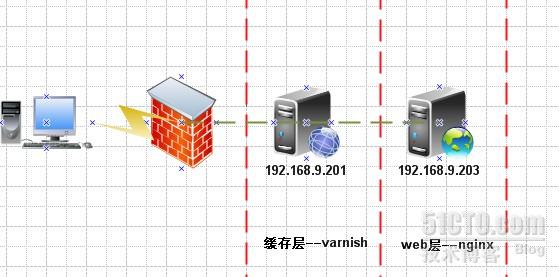
backend kerry { #定义后端服务器名
.host = "192.168.9.203"; #定义后端服务器IP
.port = "80"; #定义后端服务器端口
}
backend king {
.host = "192.168.9.204";
.port = "80";
}
#定义访问控制列表,充许那些IP清除varnish 缓存
acl local {
"localhost";
"127.0.0.1";
}
#判断host请求针对那个后端服务器
sub vcl_recv {
if (req.http.host ~ "^(www.)?kerry.com$") { #泛域名的写法"^(.*.)?kerry.com$"
set req.backend = kerry;
}
elsif (req.http.host ~ "^(www.)?king.com$") {
set req.backend = king;
}
else {
error 404 "Unknown HostName!"; #如果都不匹配,返回404错误
}
#不充许非访问控制列表的IP进行varnish缓存清除
if(req.request == "PURGE") {
if (!client.ip ~ local) {
error 405 "Not Allowed.";
return (lookup);
}
}
#清除url中有jpg|png|gif等文件的cookie
if (req.request == "GET" && req.url ~ "\.(jpg|png|gif|swf|jpeg|ico)$") {
unset req.http.cookie;
}
#取消服务器上images目录下所有文件的cookie
if (req.url ~ "^/images") {
unset req.http.cookie;
}
#判断req.http.X-Forwarded-For,如果前端有多重反向代理,这样可以获取客户端IP地址。
if (req.http.x-forwarded-for) {
set req.http.X-Forwarded-For =
req.http.X-Forwarded-For ", " client.ip;
}
else {
set req.http.X-Forwarded-For = client.ip;
}
if (req.request != "GET" &&
req.request != "HEAD" &&
req.request != "PUT" &&
req.request != "POST" &&
req.request != "TRACE" &&
req.request != "OPTIONS" &&
req.request != "DELETE") {
return (pipe);
}
#针对请求和url地址判断,是否在varnish缓存里查找
if (req.request != "GET" && req.request != "HEAD") {
return (pass);
} ## 对非GET|HEAD请求的直接转发给后端服务器
if (req.http.Authorization || req.http.Cookie) {
return (pass);
}
if (req.request == "GET" && req.url ~ "\.(php)($|\?)") {
return (pass);
} #对GET请求,且url里以.php和.php?结尾的,直接转发给后端服务器
return (lookup);
} #除了以上的访问以外,都在varnish缓存里查找
sub vcl_pipe {
return (pipe);
}
sub vcl_pass {
return (pass);
}
sub vcl_hash {
set req.hash += req.url;
if (req.http.host) {
set req.hash += req.http.host;
} else {
set req.hash += server.ip;
}
return (hash);
}
sub vcl_hit {
if (!obj.cacheable) {
return (pass);
}
if (req.request == "PURGE") {
set obj.ttl = 0s;
error 200 "Purged.";
}
return (deliver);
}
sub vcl_miss {
return (fetch);
}
sub vcl_fetch {
if (!beresp.cacheable) {
return (pass);
}
if (beresp.http.Set-Cookie) {
return (pass);
}
#WEB服务器指明不缓存的内容,varnish服务器不缓存
if (beresp.http.Pragma ~ "no-cache" ||
beresp.http.Cache-Control ~ "no-cache" ||
beresp.http.Cache-Control ~ "private") {
return (pass);
}
#对.txt .js .shtml结尾的URL缓存时间设置1小时,对其他的URL缓存时间设置为10天
if (req.request == "GET" && req.url ~ "\.(txt|js|css|shtml|html|htm)$") {
set beresp.ttl = 3600s;
}
else {
set beresp.ttl = 10d;
}
return (deliver);
}
#添加在页面head头信息中查看缓存命中情况
sub vcl_deliver {
set resp.http.x-hits = obj.hits ;
if (obj.hits > 0) {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT cqtel-bbs";
}
else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "MISS cqtel-bbs";
}
}
sub vcl_error {
set obj.http.Content-Type = "text/html; charset=utf-8";
synthetic {"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<title>"} obj.status " " obj.response {"</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Error "} obj.status " " obj.response {"</h1>
<p>"} obj.response {"</p>
<h3>Guru Meditation:</h3>
<p>XID: "} req.xid {"</p>
<hr>
<address>
<a href="http://www.bbs.com/">bbs cache server</a>
</address>
</body>
</html>
"};
return (deliver);
}
注意:在2.1后的版本里,原"obj.*"的变量全部变为"beresp.*"了,需要留意一下
启动varnish
/usr/local/varnish/sbin/varnishd -u www -g www -f /usr/local/varnish/etc/varnish/kerry.vcl -a 192.168.9.201:80 -s file,/data/varnish/cache/varnish_cache.data,1G -w 1024,51200,10 -t 3600 -T 192.168.9.201:3000
echo "/usr/local/varnish/sbin/varnishd -u www -g www -f /usr/local/varnish/etc/varnish/kerry.vcl -a 192.168.9.201:80 -s file,/data/varnish/cache/varnish_cache.data,1G -w 1024,51200,10 -t 3600 -T 192.168.9.201:3000" >> /etc/rc.local
参数:
-u 以什么用运行
-g 以什么组运行
-f varnish配置文件
-a 绑定IP和端口
-s varnish缓存文件位置与大小
-w 最小,最大线程和超时时间
-T varnish管理端口,主要用来清除缓存
-p client_http11=on 支持http1.1协议
-P(大P) /usr/local/varnish/var/varnish.pid 指定其进程码文件的位置,实现管理
停止varnish
pkill varnishd #结束varnishd进程
启动日志,方便分析网站访问情况
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishncsa -w /data/varnish/logs/varnish.log &
echo "/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishncsa -w /data/varnish/logs/varnish.log &" >> /etc/rc.local
参数: -w 指定varnish访问日志要写入的目录与文件
varnish日志切割
vi /root/cut_varnish_log.sh
#!/bin/sh
logs_path=/data/varnish/logs
vlog=${logs_path}/varnish.log
date=$(date -d "yesterday" +"%Y-%m-%d")
pkill -9 varnishncsa
mkdir -p ${logs_path}/$(date -d "yesterday" +"%Y")/$(date -d "yesterday" +"%m")/
mv /data/varnish/logs/varnish.log ${logs_path}/$(date -d "yesterday" +"%Y")/$(date -d "yesterday" +"%m")/varnish-${date}.log
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishncsa -w /data/varnish/logs/varnish.log &
使用计划任务,每天晚上凌晨00点运行日志切割脚本
echo "0 0 * * * /root/cut_varnish_log.sh" >> /etc/crontab
cat /etc/rc.local
ulimit -SHn 51200
/usr/local/varnish/sbin/varnishd -u www -g www -f /usr/local/varnish/etc/varnish/kerry.vcl -a 192.168.9.201:80 -s file,/data/varnish/cache/varnish_cache.data,1G -w 1024,51200,10 -t 3600 -T 192.168.9.201:3000
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishncsa -w /data/varnish/logs/varnish.log &
#============================ Varnish 缓存清除 ======================
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishadm -T 192.168.9.201:3000 purge "req.http.host ~ www.kerry.com$ && req.url ~ /static/image/tp.php"
说明:
192.168.9.201:3000 为被清除缓存服务器地址
www.kerry.com 为被清除的域名
/static/image/tp.php 为被清除的url地址列表
清除所有缓存
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishadm -T 192.168.9.201:3000 url.purge *$
清除image目录下所有缓存
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishadm -T 192.168.9.201:3000 url.purge /image/
查看Varnish服务器连接数与命中率
/usr/local/varnish/bin/varnishstat –n /data/varnish/cache/varnish_cache.data

#============================ 内核优化 ==============================
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1
#net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 30
#net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 300
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 8192
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 5000
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 65536
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 32768
net.core.somaxconn = 32768
net.core.wmem_default = 8388608
net.core.rmem_default = 8388608
net.core.rmem_max = 16777216
net.core.wmem_max = 16777216
net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 2
net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 2
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1
#net.ipv4.tcp_tw_len = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_mem = 94500000 915000000 927000000
net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 3276800
/sbin/sysctl -p
#===================== Varnish添加到服务自启动 ======================
配置启动文件
vi /etc/init.d/varnish
#! /bin/sh
#
# varnish Control the varnish HTTP accelerator
#
# chkconfig: - 90 10
# description: Varnish is a high-perfomance HTTP accelerator
# processname: varnishd
# config: /etc/sysconfig/varnish
# pidfile: /var/run/varnish/varnishd.pid
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: varnish
# Required-Start: $network $local_fs $remote_fs
# Required-Stop: $network $local_fs $remote_fs
# Should-Start: $syslog
# Short-Description: start and stop varnishd
# Description: Varnish is a high-perfomance HTTP accelerator
### END INIT INFO
# Source function library.
. /etc/init.d/functions
retval=0
pidfile=/var/run/varnish.pid
exec="/usr/local/varnish/sbin/varnishd"
prog="varnishd"
config="/usr/local/varnish/etc/varnish/varnish"
lockfile="/var/lock/subsys/varnish"
# Include varnish defaults
[ -e /usr/local/varnish/etc/varnish/varnish ] && . /usr/local/varnish/etc/varnish/varnish
start() {
if [ ! -x $exec ]
then
echo $exec not found
exit 5
fi
if [ ! -f $config ]
then
echo $config not found
exit 6
fi
echo -n "Starting varnish HTTP accelerator: "
# Open files (usually 1024, which is way too small for varnish)
ulimit -n ${NFILES:-131072}
# Varnish wants to lock shared memory log in memory.
ulimit -l ${MEMLOCK:-82000}
# $DAEMON_OPTS is set in /etc/sysconfig/varnish. At least, one
# has to set up a backend, or /tmp will be used, which is a bad idea.
if [ "$DAEMON_OPTS" = "" ]; then
echo "\$DAEMON_OPTS empty."
echo -n "Please put configuration options in $config"
return 6
else
# Varnish always gives output on STDOUT
daemon $exec -P $pidfile "$DAEMON_OPTS" > /dev/null 2>&1
retval=$?
if [ $retval -eq 0 ]
then
touch $lockfile
echo_success
echo
else
echo_failure
fi
return $retval
fi
}
stop() {
echo -n "Stopping varnish HTTP accelerator: "
killproc $prog
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile
return $retval
}
restart() {
stop
start
}
reload() {
restart
}
force_reload() {
restart
}
rh_status() {
status $prog
}
rh_status_q() {
rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1
}
# See how we were called.
case "$1" in
start)
rh_status_q && exit 0
$1
;;
stop)
rh_status_q || exit 0
$1
;;
restart)
$1
;;
reload)
rh_status_q || exit 7
$1
;;
force-reload)
force_reload
;;
status)
rh_status
;;
condrestart|try-restart)
rh_status_q || exit 0
restart
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload}"
exit 2
esac
exit $?
varnish的配置调用文件,是用来告诉程序从哪里读取配置文件,启动参数有哪些等
vi /usr/local/varnish/etc/varnish
# Configuration file for varnish
#
# /etc/init.d/varnish expects the variable $DAEMON_OPTS to be set from this
# shell script fragment.
#
# Maximum number of open files (for ulimit -n)
NFILES=131072
# Locked shared memory (for ulimit -l)
# Default log size is 82MB + header
MEMLOCK=1000000
## Alternative 2, Configuration with VCL
DAEMON_OPTS="-a 192.168.9.201:80 \
-f /usr/local/varnish/etc/varnish/kerry.vcl \
-T 192.168.9.201:3000 \
-u www -g www \
-n /data/varnish/cache \
-s file,/data/varnish/cache/varnish_cache.data,1G"
添加到系统服务,开机自启动
chmod +x /etc/init.d/varnish
/sbin/chkconfig --add varnish
/sbin/chkconfig --level 2345 varnish on
开启varnish
/etc/init.d/varnish start
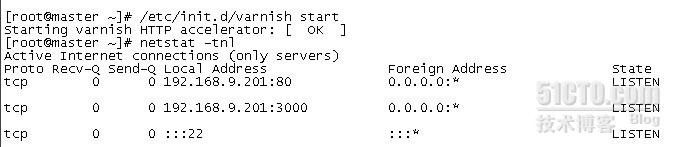
关闭varnish
/etc/init.d/varnish stop