CCNA学习笔记之NAT
目标:
1、了解NAT的作用和工作原理
2、了解各种NAT术语
3、掌握NAT的各种配置(静态NAT、动态NAT、PAT和端口映射)
一、NAT基础:
1、什么是NAT:
Network Address Translation,即网络地址转换,是一种将私有(保留)地址转化为合法IP地址的转换技术。
NAT技术的提出背景:
合法的IP地址资源日益短缺
一个局域网内部有很多台主机,但不是每台主机都有合法的IP地址,为了使所有内部主机都可以连接因特网,需要使用地址转换
地址转换技术可以有效地隐藏内部局域网中的主机,具有一定的网络安全保护作用
地址转换可以在局域网内部提供给外部FTP、WWW、Telnet服务
2、NAT的原理
改变IP包头,使目的地址、源地址或两个地址在包头中被不同地址替换
3、NAT的3种实现方式
静态转换
动态转换
端口多路复用(PAT)
4、NAT的术语――NAT的四种地址类型:
内部局部地址(IL:Inside Local):在内部网络中分配给主机的私有IP地址
Tips:回顾私有IP地址――还记得私有地址有哪些吗?(如下表所示,这些IP地址是不能在公网上使用的哈!)
IP地址分类
地址范围
保留的网络数
A类 10.0.0.0~10.255.255.255 保留了一个A类网络 B类 172.16.0.0~172.31.255.255 保留了32个B类网络 C类 192.168.0.0~192.168.255.255 保留了256个C类网络
内部全局地址(IG:Inside Global):一个合法(即能够在公网使用的)IP地址,由ISP提供,对外代表一个或多个内部局部IP地址
外部全局地址(OG:Outside Global):一系列合法的能够在公网使用IP地址
外部局部地址(OL:Outside Local):由主机拥有者在外部网上分配给主机的IP地址,该地址可以从全局路由地址或网络空间进行分配

自己用的拖鞋代表内部局部地址,给别人用的拖鞋代表外部局部地址;
用的皮鞋代表内部全局地址,别人穿的皮鞋代表外部全局地址;
5、NAT的应用场景:
6、NAT的优缺点:
NAT的优点
NAT的缺点
二、NAT的配置:
实验拓扑:

1、静态NAT的配置:
(1)配置需求:
网络中的计算机和路由器已经配置好了IP地址和路由表
在路由器CPE上配置静态NAT映射
内网计算机PC0的私网地址10.0.0.2使用公网地址131.107.0.2地址
(2)配置过程:
首先在内网的主机PC0上测试能否ping通各个网段:
Packet Tracer PC Command Line 1.0 PC>ipconfig /all FastEthernet0 Connection:(default port) Physical Address................: 00E0.A383.1D51 Link-local IPv6 Address.........: :: IP Address......................: 10.0.0.2 //PC0的IP地址 Subnet Mask.....................: 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway.................: 10.0.0.1 DNS Servers.....................: 0.0.0.0 DHCP Servers....................: 0.0.0.0 PC>ping 10.0.0.1 #能够ping通网关哈 Pinging 10.0.0.1 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 10.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Reply from 10.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255 Reply from 10.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Reply from 10.0.0.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255 Ping statistics for 10.0.0.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 1ms, Average = 0ms PC>ping 131.107.0.1 //因为路由器CPE的接口serial0/0与131.107.0.0网段直连,所以能够ping通哈 Pinging 131.107.0.1 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 131.107.0.1: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=255 Reply from 131.107.0.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255 Reply from 131.107.0.1: bytes=32 time=0ms TTL=255 Reply from 131.107.0.1: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=255 Ping statistics for 131.107.0.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 2ms, Average = 0ms PC>ping 202.99.160.2 //ping不通202.99.160.0网段哈,知道为什么吗?数据包有去无回哈(详见下面的数据包分析)! Pinging 202.99.160.2 with 32 bytes of data: Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Ping statistics for 202.99.160.2: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss)
数据包分析:
(1)从PC0发送到目标主机202.99.160.2的ICMP数据包能够被目标主机接收到,如下图所示:
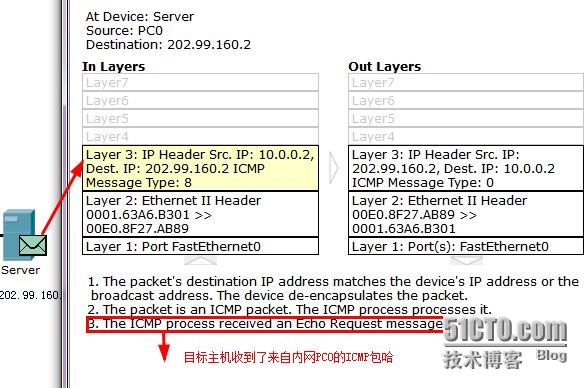
(2)ICMP数据包在回来的时候被路由器ISP丢弃了,如下图所示:
网络畅通的条件是数据包“有去有回”,从上面的分析可以看出,公司内部的IP地址不进行相应的网络地址转换是不能与Internet上的主机通讯的哈!
在路由器CPE上进行如下配置:
CPE#show ip interface brief //查看路由器CPE的接口配置情况 Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol FastEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset up down FastEthernet0/1 10.0.0.1 YES manual up up //fa0/1是内网的网关 Serial0/0 131.107.0.1 YES manual up up //se0/0连接公网 CPE(config)ip nat inside source static 10.0.0.2 131.107.0.2 //内网IP-->外网IP的静态NAT CPE(config)int fastEthernet 0/1 CPE(config-if)#ip nat inside //指定fa0/1是内部接口 CPE(config-if)#interface se0/0 CPE(config-if)#ip nat outside //指定se0/0是外部接口
(3)验证配置:
PC>ping 202.99.160.2 Pinging 202.99.160.2 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 202.99.160.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126 Reply from 202.99.160.2: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=126 Reply from 202.99.160.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126 Reply from 202.99.160.2: bytes=32 time=1ms TTL=126 Ping statistics for 202.99.160.2: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 1ms, Maximum = 2ms, Average = 1ms CPE#show ip nat statistics //统计NAT信息 Total translations: 1 (1 static, 0 dynamic, 0 extended) Outside Interfaces: Serial0/0 //外部接口 Inside Interfaces: FastEthernet0/1 //内部接口 Hits: 4 Misses: 8 Expired translations: 4 Dynamic mappings: CPE#show ip nat translations //查看地址转换表 /*pro字段表示协议,---表示所有协议都使用这个NAT地址并且该条目永久生效;在该条目的基础上会生成基于4层的应用,默认生存时间是60秒*/ Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global icmp 131.107.0.2:17 10.0.0.2:17 202.99.160.2:17 202.99.160.2:17 icmp 131.107.0.2:18 10.0.0.2:18 202.99.160.2:18 202.99.160.2:18 icmp 131.107.0.2:19 10.0.0.2:19 202.99.160.2:19 202.99.160.2:19 icmp 131.107.0.2:20 10.0.0.2:20 202.99.160.2:20 202.99.160.2:20 --- 131.107.0.2 10.0.0.2 --- ---
再来看看数据包的转发情况:
(1)ICMP数据包从路由器CPE的se0/0接口发送出去时的情况,如下图所示:

(2)ICMP数据包从目标主机返回到路由器CPE是的情况,如下图所示:

在路由器CPE上开启debug也可以看到地址转换的过程:
CPE#debug ip nat //开启debug跟踪NAT IP NAT debugging is on CPE# NAT: s=10.0.0.2->131.107.0.2, d=202.99.160.2 [21] //数据包出去时的NAT NAT*: s=202.99.160.2, d=131.107.0.2->10.0.0.2 [12] //数据包回来时的NAT NAT: s=10.0.0.2->131.107.0.2, d=202.99.160.2 [22] NAT*: s=202.99.160.2, d=131.107.0.2->10.0.0.2 [13] NAT: s=10.0.0.2->131.107.0.2, d=202.99.160.2 [23] NAT*: s=202.99.160.2, d=131.107.0.2->10.0.0.2 [14] NAT: s=10.0.0.2->131.107.0.2, d=202.99.160.2 [24] NAT*: s=202.99.160.2, d=131.107.0.2->10.0.0.2 [15]
小结:
(1)静态NAT配置成功后,内网的主机能够访问外网的主机,而外网的主机也能够访问内网的主机,是一种双向的过程,这样没有起到隐藏内网网络的作用。
(2)静态NAT的配置步骤:
第一步: 设置外部端口
第二步 :设置内部端口
第三步:在内部局部和内部全局地址之间建立静态地址转换
第四步:在内部和外部端口上启用NAT
2、动态NAT的配置:
(1)配置需求:
在路由器CPE上配置动态NAT
(2)配置过程:
第一步:在路由器CPE上设置内部和外部接口的IP地址
CPE#show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol FastEthernet0/0 unassigned YES unset up down FastEthernet0/1 10.0.0.1 YES manual up up //内部接口 Serial0/0 131.107.0.1 YES manual up up //外部接口
第二步:定义内部网络中允许访问外部的访问控制列表
CPE(config)#access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 //定义一个标准的ACL用于指定内网中允许访问外网的网段
第三步:定义合法IP地址池
CPE(config)#ip nat pool todd 131.107.0.1 131.107.0.6 netmask 255.255.255.0 //指定合法的IP地址池用于内网-->外网的映射,地址池名称为todd
第四步:指定网络地址映射
CPE(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 pool todd
第五步:在内部和外部端口上启用NAT
Router(config)#Interface serial 0/0 Router(config-if)#Ip nat outside Router(config)#Interface fastEthernet 0/1 Router(config-if)#Ip nat inside
(3)验证配置:
在PC0上ping外网主机PC5
PC>ping202.99.160.3 //ping外网主机PC5 Pinging 202.99.160.3 with 32 bytes of data: Request timed out. Reply from 202.99.160.3: bytes=32time=7ms TTL=126 Reply from 202.99.160.3: bytes=32time=2ms TTL=126 Reply from 202.99.160.3: bytes=32time=5ms TTL=126 Ping statisticsfor202.99.160.3: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 3, Lost = 1 (25% loss), Approximate round triptimesinmilli-seconds: Minimum = 2ms, Maximum = 7ms, Average = 4ms
在路由器CPE上查看地址转换情况:
CPE#show ip nat statistics //查看NAT统计信息 Total translations: 20 (0 static, 20 dynamic, 20 extended) //20个动态NAT Outside Interfaces: Serial0/0#外部接口 Inside Interfaces: FastEthernet0/1 //内部接口 Hits: 23 Misses: 24 Expired translations: 4 Dynamic mappings: //动态映射关系 -- Inside Source access-list 1 pool todd refCount 20 pool todd: netmask 255.255.255.0 start 131.107.0.1 end 131.107.0.6 typegeneric, total addresses 6 , allocated 5 (83%), misses 0 CPE#show ip nat translations //查看地址转换表 Pro Inside global Insidelocal Outsidelocal Outside global icmp 131.107.0.5:10 10.0.0.2:10 202.99.160.3:10 202.99.160.3:10 //随机分配端口号标识ICMP进程,NAT转化的默认时间为60S icmp 131.107.0.5:11 10.0.0.2:11 202.99.160.3:11 202.99.160.3:11 icmp 131.107.0.5:12 10.0.0.2:12 202.99.160.3:12 202.99.160.3:12 icmp 131.107.0.5:9 10.0.0.2:9 202.99.160.3:9 202.99.160.3:9 icmp 131.107.0.6:5 10.0.0.3:5 202.99.160.3:5 202.99.160.3:5 icmp 131.107.0.6:6 10.0.0.3:6 202.99.160.3:6 202.99.160.3:6 icmp 131.107.0.6:7 10.0.0.3:7 202.99.160.3:7 202.99.160.3:7 icmp 131.107.0.6:8 10.0.0.3:8 202.99.160.3:8 202.99.160.3:8 icmp 131.107.0.1:5 10.0.0.4:5 202.99.160.3:5 202.99.160.3:5 icmp 131.107.0.1:6 10.0.0.4:6 202.99.160.3:6 202.99.160.3:6 icmp 131.107.0.1:7 10.0.0.4:7 202.99.160.3:7 202.99.160.3:7 icmp 131.107.0.1:8 10.0.0.4:8 202.99.160.3:8 202.99.160.3:8 icmp 131.107.0.2:5 10.0.0.5:5 202.99.160.3:5 202.99.160.3:5 icmp 131.107.0.2:6 10.0.0.5:6 202.99.160.3:6 202.99.160.3:6 icmp 131.107.0.2:7 10.0.0.5:7 202.99.160.3:7 202.99.160.3:7 icmp 131.107.0.2:8 10.0.0.5:8 202.99.160.3:8 202.99.160.3:8 icmp 131.107.0.3:5 10.0.0.6:5 202.99.160.3:5 202.99.160.3:5 icmp 131.107.0.3:6 10.0.0.6:6 202.99.160.3:6 202.99.160.3:6 icmp 131.107.0.3:7 10.0.0.6:7 202.99.160.3:7 202.99.160.3:7 icmp 131.107.0.3:8 10.0.0.6:8 202.99.160.3:8 202.99.160.3:8 CPE#debug ip nat //跟踪NAT转换情况 IP NAT debugging is on CPE# NAT: s=10.0.0.2->131.107.0.1, d=202.99.160.3 [21] //PC0的NAT NAT*: s=202.99.160.3, d=131.107.0.1->10.0.0.2 [84] NAT: s=10.0.0.2->131.107.0.1, d=202.99.160.3 [22] NAT*: s=202.99.160.3, d=131.107.0.1->10.0.0.2 [85] NAT: s=10.0.0.2->131.107.0.1, d=202.99.160.3 [23] NAT*: s=202.99.160.3, d=131.107.0.1->10.0.0.2 [86] NAT: s=10.0.0.2->131.107.0.1, d=202.99.160.3 [24] NAT*: s=202.99.160.3, d=131.107.0.1->10.0.0.2 [87] NAT: s=10.0.0.3->131.107.0.2, d=202.99.160.3 [17] //PC1的NAT NAT*: s=202.99.160.3, d=131.107.0.2->10.0.0.3 [88] NAT: s=10.0.0.3->131.107.0.2, d=202.99.160.3 [18] NAT*: s=202.99.160.3, d=131.107.0.2->10.0.0.3 [89] NAT: s=10.0.0.3->131.107.0.2, d=202.99.160.3 [19] NAT*: s=202.99.160.3, d=131.107.0.2->10.0.0.3 [90] NAT: s=10.0.0.3->131.107.0.2, d=202.99.160.3 [20] NAT*: s=202.99.160.3, d=131.107.0.2->10.0.0.3 [91] NAT: expiring 131.107.0.1 (10.0.0.2) icmp 21 (21) //ICMP过期信息 NAT: expiring 131.107.0.1 (10.0.0.2) icmp 22 (22) NAT: expiring 131.107.0.1 (10.0.0.2) icmp 23 (23) NAT: expiring 131.107.0.1 (10.0.0.2) icmp 24 (24) NAT: expiring 131.107.0.2 (10.0.0.3) icmp 17 (17) NAT: expiring 131.107.0.2 (10.0.0.3) icmp 18 (18) NAT: expiring 131.107.0.2 (10.0.0.3) icmp 19 (19) NAT: expiring 131.107.0.2 (10.0.0.3) icmp 20 (20)
小结:
动态NAT可以动态实现指定网段的NAT,采用先来先用的策略,如果地址池的IP地址做映射用完了,那么剩余的内网的主机将不能再访问外网。
3、PAT的配置:
实验拓扑:

说明:
由于Cisco Packet Tracer软件有多命令不支持,所以PAT和端口映射的实验改用GNS3来做哈!
PC1和PC2是用两台Cisco C3600的路由器来进行模拟
(1)配置需求:
在路由器R1上启用PAT,使得公司内网的主机能够访问Internet
在路由器上配置端口映射,使得Internet上的主机能够访问公司内网的HTTP服务
(2)配置过程:
第一步:首先配置好所有网络设备的IP地址,IP地址的规划已经在拓扑图中标识出;
第二步:为路由器配置好路由协议,使得除公司内网外的网络设备可以互相通信;
第三步:为PC1和PC2配置PAT,使其可以同时利用路由器R1的外网地址12.0.0.1与外网通信;
PC1#ping 192.168.80.10 //先验证是否可以连通外网 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.80.10, timeout is 2 seconds: ..... //无法连通外网哈 Success rate is 0 percent (0/5) /*以下是具体的PAT配置*/ R1(config)#access-list 10 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 //定义ACL,若内网有多个网段需要NAT,则需要在ACL中都添加上 R1(config)#ip nat pool todd 12.0.0.1 12.0.0.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 //前后地址都一样,因为只有一个公网地址 R1(config)#ip nat inside source list 10 pool todd overload //overload参数的意思是启用PAT R1(config)#interface serial 1/0 R1(config-if)#ip nat outside //指定NAT的外网接口 R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#interface fastEthernet 0/0 R1(config-if)#ip nat inside //指定NAT的内网接口
第四步:验证配置
PC1#ping 192.168.80.10 //内网PC1上ping外网主机 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.80.10, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! //能够ping通哈 Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 124/179/300 ms PC2#ping 192.168.80.10 //内网PC2上ping外网主机 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.80.10, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! //能够ping通哈 Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 96/162/264 ms R1#show ip nat statistics //查看NAT的统计信息 Total active translations: 1 (0static, 1 dynamic; 1 extended) Outside interfaces: Serial1/0 Inside interfaces: FastEthernet0/0 Hits: 36 Misses: 4 Expired translations: 3 Dynamic mappings: //动态映射 -- Inside Source [Id: 1] access-list 10 pool todd refcount 1 pool todd: netmask 255.255.255.0 start 12.0.0.1 end 12.0.0.1 type generic, total addresses 1, allocated 1 (100%), misses 0 R1#show ip nat translations verbose //在路由器R1上查看地址转换的详细信息 Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global icmp 12.0.0.1:4 192.168.1.1:4 192.168.80.10:4 192.168.80.10:4 create 00:00:40, use00:00:39, left00:00:20, Map-Id(In):1,//NAT转换的默认过期时间为60秒 flags: static, extended, extendable, use_count: 0 R1#debug ip nat //跟踪NAT情况 IP NAT debugging is on R1# //PC1上ICMP包的跟踪情况 *Apr 814:39:29.619:NAT: s=192.168.1.1->12.0.0.1, d=192.168.80.10 [30] *Apr 814:39:29.759:NAT*: s=192.168.80.10, d=12.0.0.1->192.168.1.1 [61040] *Apr 814:39:29.787: NAT*: s=192.168.1.1->12.0.0.1, d=192.168.80.10 [31] *Apr 814:39:29.883: NAT*: s=192.168.80.10, d=12.0.0.1->192.168.1.1 [61084] *Apr 814:39:29.899: NAT*: s=192.168.1.1->12.0.0.1, d=192.168.80.10 [32] *Apr 814:39:30.087: NAT*: s=192.168.80.10, d=12.0.0.1->192.168.1.1 [61126] *Apr 814:39:30.135: NAT*: s=192.168.1.1->12.0.0.1, d=192.168.80.10 [33] *Apr 814:39:30.227: NAT*: s=192.168.80.10, d=12.0.0.1->192.168.1.1 [61137] *Apr 814:39:30.259: NAT*: s=192.168.1.1->12.0.0.1, d=192.168.80.10 [34] R1# *Apr 814:39:30.383: NAT*: s=192.168.80.10, d=12.0.0.1->192.168.1.1 [61148] R1# //PC2上ICMP包的跟踪情况 *Apr 815:41:26.355: NAT: s=192.168.1.2->12.0.0.1, d=192.168.80.10 [15] *Apr 815:41:26.483: NAT*: s=192.168.80.10, d=12.0.0.1->192.168.1.2 [4378] *Apr 815:41:26.563: NAT*: s=192.168.1.2->12.0.0.1, d=192.168.80.10 [16] *Apr 815:41:26.607: NAT*: s=192.168.80.10, d=12.0.0.1->192.168.1.2 [4459] *Apr 815:41:26.687: NAT*: s=192.168.1.2->12.0.0.1, d=192.168.80.10 [17] *Apr 815:41:26.779: NAT*: s=192.168.80.10, d=12.0.0.1->192.168.1.2 [4470] *Apr 815:41:26.795: NAT*: s=192.168.1.2->12.0.0.1, d=192.168.80.10 [18] *Apr 815:41:26.891: NAT*: s=192.168.80.10, d=12.0.0.1->192.168.1.2 [4483] *Apr 815:41:26.951: NAT*: s=192.168.1.2->12.0.0.1, d=192.168.80.10 [19] R1# *Apr 814:39:33.835: NAT*: s=192.168.80.10, d=12.0.0.1->192.168.1.2 [62505] R1# *Apr 814:39:47.287: NAT: expiring 12.0.0.1 (192.168.1.1) icmp 5 (5)R1# *Apr 814:40:07.975: NAT: expiring 12.0.0.1 (192.168.1.2) icmp 0 (0)R1# *Apr 814:40:30.383: NAT: expiring 12.0.0.1 (192.168.1.1) icmp 6 (6)R1# *Apr 814:40:33.835: NAT: expiring 12.0.0.1 (192.168.1.2) icmp 1 (1)
配置端口映射:
第一步:在PC1上启用HTTP服务,使其成为WEB服务器
第二步:在PC2上启用TELNET服务
第三步:在路由器R1上配置端口映射
PC1(config)#ip http server //在PC1上启用HTTP服务 PC2(config)#line vty 0 10 //PC2上启用TELNET服务 PC2(config-line)#password telnet PC2(config-line)#login PC2(config-line)#exit PC2(config)#enable password cisco R1(config)#ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.1.1 80 12.0.0.1 8080 //配置端口映射,外网的HTTP端口为8080 R1(config)#ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.1.2 23 12.0.0.1 23 //配置端口映射,外网可以TELNET到内网的PC2 R1(config)#interface f0/0 R1(config-if)#ip nat inside //内部接口 R1(config-if)#exit R1(config)#interface s1/0 R1(config-if)#ip nat outside //外部接口
第四步:在外网主机192.168.80.10上通过客户端的相应工具连接内网的服务器:
在物理机上打开IE浏览器,输入地址“http://12.0.0.1:8080”,如下图所示:

在物理机上telnet内网的PC2:

小结:
PAT是NAT技术中应用最多的一种技术,不仅可以在路由器上实现,也可以在操作系统和宽带路由器中实现;
通过端口映射技术,可以很好的隐藏内网中的服务?
三、本次博文涉及到的命令总结:
1、静态NAT:
第一种:(一个私有地址对应一个公有地址)
ip nat inside source static 192.168.1.2 202.1.1.3
ip nat inside source static 192.168.1.3 202.1.1.4
int f0/0
ip nat inside
int f1/0
ip nat outside
第二种:(多个私有地址不同服务对应一个公有地址的不同服务,可以节省IP也可以隐藏内部服务)
ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.1.2 23 202.1.1.3 23 extendable
ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.1.3 80 202.1.1.3 80 extendable
ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.1.3 80 202.1.1.3 8080 extendable
int f0/0
ip nat inside
int f1/0
ip nat outside
show ip nat translation //查看NAT转化表
clear ip nat translation * //清除NAT转化关系(静态的不能被清除)
show ip nat translation verbose //查看NAT转化的默认时间
ip nat translation timeout 60 //将动态nat转化时间改为60s
debug ip nat //动态查看NAT的转化关系
2、动态NAT:
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 //定义ACL圈定私有地址
ip nat pool tuoyu 202.1.1.3 202.1.1.10 netmask 255.255.255.0//定义地址池,圈定公有地址
ip nat inside source list 1 pool tuoyu //动态NAT的对应关系
int f0/0
ip nat inside //指定F0/0为NAT的内网地址
int f1/0
ip nat outside //指定F1/0为NAT的外网地址
3、PAT:
第一种:(私有地址转化到地址池,地址池里就一个公有ip,通过端口多路复用的方式)
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
ip nat pool cisco 202.1.1.3 202.1.1.3 netmask 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside source list 1 pool cisco overload //overload代表端口多路复用的意思
int f0/0
ip nat inside
int f1/0
ip nat outside
第二种:(私有地址转换成接口IP地址,也是通过端口多路复用的方式)
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
ip nat inside source list 1 int f1/0 overload //overload代表端口多路复用的意思
int f0/0
ip nat inside
int f1/0
ip nat outside
本次博文的内容就这些了哈,欢迎大家拍砖!~~
本文出自 “技术日志” 博客,谢绝转载!


