centos-网卡流量监控-iftop
在Linux/类Unix系统中可以使用top查看系统资源、进程、内存占用等信息。查看网络状态可以使用netstat、nmap等工具。若要查看实时的网络流量,监控TCP/IP连接等,则可以使用iftop。
iftop是什么?
Iftop 主要用来显示本机网络流量情况及各相互通信的流量集合,如单独同那台机器间的流量大小,非常适合于代理服务器和iptables服务器使用。官方网站:http://www.ex-parrot.com/~pdw/iftop/
iftop有什么用?
iftop可以用来监控网卡的实时流量(可以指定网段)、反向解析IP、显示端口信息等,详细的将会在后面的使用参数中说明。
安装iftop
如果采用编译安装可以到iftop官网下载最新的源码包。安装前需要已经安装好基本的编译所需的环境,比如make、gcc、autoconf等。安装iftop还需要安装libpcap和libcurses。
CentOS上安装所需依赖包:
# yum install -y gcc flex byacc libpcap ncurses ncurses-devel libpcap-devel tcpdump
附:Debian上安装所需依赖包:
# apt-get install flex byacc libpcap0.8 libncurses5
下载源码并编译安装
# cd /usr/local/src # wget http://www.ex-parrot.com/pdw/iftop/download/iftop-0.17.tar.gz # tar xvf iftop-0.17.tar.gz # cd iftop-0.17 # ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/iftop # make # make install # chmod 700 /usr/local/sbin/iftop #修改IFTOP权限
使用方法
/usr/local/iftop/sbin/iftop /usr/local/iftop/sbin/iftop -i eth0 -n 就可以看到eth0网卡的流量状况 附:Debian系统 运行:apt-get install iftop"
如果安装iftop时没有自定义路径,那么直接运行iftop就可以查看流量统计了,例如:iftop或者iftop -i eth0 -n
相关参数及说明
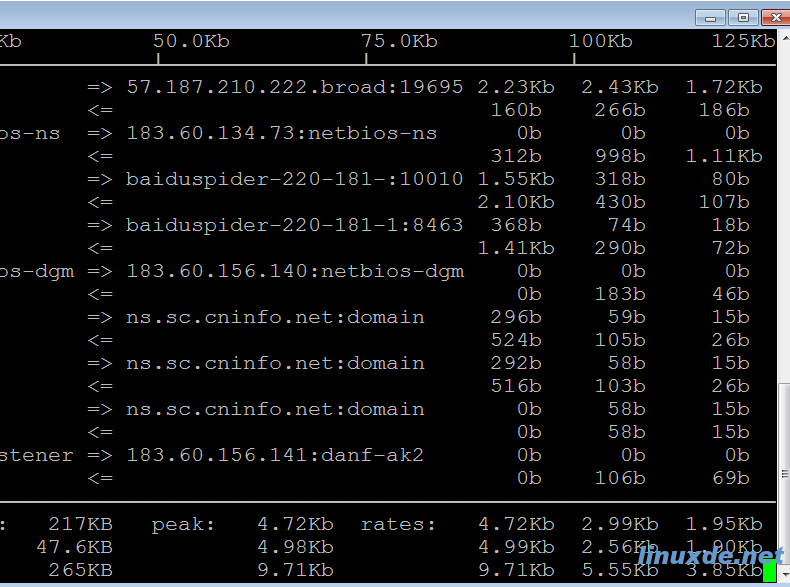
1、iftop界面相关说明
界面上面显示的是类似刻度尺的刻度范围,为显示流量图形的长条作标尺用的。中间的<= =>这两个左右箭头,表示的是流量的方向。
TX:发送流量
RX:接收流量
TOTAL:总流量
Cumm:运行iftop到目前时间的总流量
peak:流量峰值
rates:分别表示过去 2s 10s 40s 的平均流量
2、iftop相关参数
常用的参数
-i设定监测的网卡,如:# iftop -i eth1
-B 以bytes为单位显示流量(默认是bits),如:# iftop -B
-n使host信息默认直接都显示IP,如:# iftop -n
-N使端口信息默认直接都显示端口号,如: # iftop -N
-F显示特定网段的进出流量,如# iftop -F 10.10.1.0/24或# iftop -F 10.10.1.0/255.255.255.0
-h(display this message),帮助,显示参数信息
-p使用这个参数后,中间的列表显示的本地主机信息,出现了本机以外的IP信息;
-b使流量图形条默认就显示;
-f这个暂时还不太会用,过滤计算包用的;
-P使host信息及端口信息默认就都显示;
-m设置界面最上边的刻度的最大值,刻度分五个大段显示,例:# iftop -m 100M
进入iftop画面后的一些操作命令(注意大小写)
按h切换是否显示帮助;
按n切换显示本机的IP或主机名;
按s切换是否显示本机的host信息;
按d切换是否显示远端目标主机的host信息;
按t切换显示格式为2行/1行/只显示发送流量/只显示接收流量;
按N切换显示端口号或端口服务名称;
按S切换是否显示本机的端口信息;
按D切换是否显示远端目标主机的端口信息;
按p切换是否显示端口信息;
按P切换暂停/继续显示;
按b切换是否显示平均流量图形条;
按B切换计算2秒或10秒或40秒内的平均流量;
按T切换是否显示每个连接的总流量;
按l打开屏幕过滤功能,输入要过滤的字符,比如ip,按回车后,屏幕就只显示这个IP相关的流量信息;
按L切换显示画面上边的刻度;刻度不同,流量图形条会有变化;
按j或按k可以向上或向下滚动屏幕显示的连接记录;
按1或2或3可以根据右侧显示的三列流量数据进行排序;
按<根据左边的本机名或IP排序;
按>根据远端目标主机的主机名或IP排序;
按o切换是否固定只显示当前的连接;
按f可以编辑过滤代码,这是翻译过来的说法,我还没用过这个!
按!可以使用Shell命令,这个没用过!没搞明白啥命令在这好用呢!
按q退出监控。
常见问题1
make: yacc: Command not found make: *** [grammar.c] Error 127
解决方法:
apt-get install byacc / yum install byacc
常见问题2
configure: error: Curses! Foiled again! (Can't find a curses library supporting mvchgat.) Consider installing ncurses.
解决方法:
apt-get install libncurses5-dev / yum install ncurses-devel
Shell 脚本如何监控程序占用带宽
1.iftop把结果重定向到文本中,是图形格式的
重定向到文本中的内容,全部是一行,根本无法用脚本取值。最开始我使用python读取这个文件,得到所有特殊符号,找到规律,然后使用sed替换成规范的格式。终于在自己测试机上完成,能展示出正常的格式。当放到线上机器时,特殊符号变了…又变成乱糟糟的了。网上找了很久的资料,终于找到了解决方法:iftop 1.0-pre之后的版本都能输出文本格式,之前用的是iftop 0.7版本。当晚心里有种流泪的感觉,弄了一天,结果有简单现成的方法。。。
2.一个程序不仅仅只使用一个端口
原以为程序仅仅监听一个端口进行通信,后来询问研发得知,当这个程序是服务端的时候,端口是固定的;当这个程序主动访问外面的时候,端口是随机的。所以要想监控的准确,必须找到这个程序打开的所有端口。解决方法是:用netstat所这个程序的所有端口找出来。
3.iftop输出的流量单位不一样,且没有调整一致的命令
单位不一样,里面有Mb,Kb,b单位,需要进行换算。我的解决方法是:把Mb替换成*1000,把Kb替换成空,把b直接不要过滤掉。最后用bc一算直接得结果。
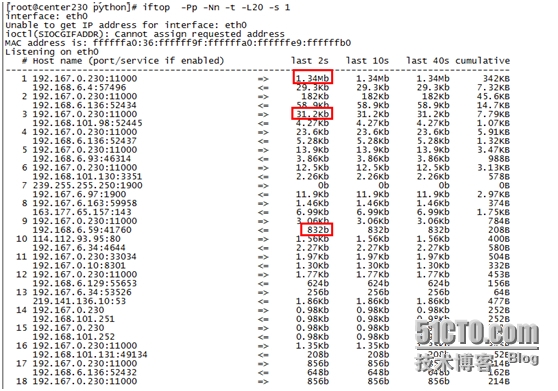
4.程序发送占用带宽好算,接收带宽不好算
根据第2步找到的几个端口,过滤出发送出去的流量一加就可以。但是接收的怎么算?见上边图中第一条流量,有"<="的则为接收流量,"<="这些行都是未知的IP与端口,怎么把它过滤出来得出结果??我的解决方法是:把"=>"行和"<="放两个临时文件中,图中有"=>"的行第一列都有序号,那么全部是"<="行的都和它一一对应,如:发送"=>"中的是序号12,13,15。那么"<="文件中的第12,13,15行就是对应的接收流量。。是不是理解了?
5.shell脚本代码如下
#!/bin/sh #author:yangrong #mail:[email protected] #date:2014-05-14 file_name="test.txt" temp_file1="liuliang.txt" temp_file2="liuliang2.txt" iftop -Pp -Nn -t -L 100 -s 1 >$temp_file1 pragrom_list=(VueDaemon VueCenter VueAgent VueCache VueSERVER VUEConnector Myswitch Slirpvde) #pragrom_list=(VueSERVER VueCenter) >$file_name for i in ${pragrom_list[@]} do port_list=`netstat -plnt|grep $i|awk '{print $4}'|awk -F: '{print $2}'` port_all="" for port in $port_list do port_all="${port}|${port_all}" port_all=`echo $port_all|sed 's/\(.*\)|$/\1/g'` done if [[ $port_all == "" ]];then echo "${i}sendflow=0" >> $file_name echo "${i}receiveflow=0" >> $file_name continue fi send_flow=`cat $temp_file1 |grep -E "${port_all}"|grep -E 'Mb|Kb'|grep '=>'|awk '{print $4}'|\ tr '\n' '+' |sed -e s/Mb/*1000/g |sed s/Kb//g |sed 's/\(.*\)+$/\1\n/g'|bc` #echo "cat liuliang.txt |grep -E "${port_all}"|grep -E 'Mb|Kb'|grep '=>'|awk '{print $4}'|\ #tr '\n' '+' |sed -e s/Mb/*1000/g |sed s/Kb//g |sed 's/\(.*\)+$/\1\n/g'|bc" if [[ ${send_flow} == "" ]];then send_flow=0 fi send_num=`cat $temp_file1 |grep -E "${port_all}"|grep "=>"|awk '{print $1}'` echo "" > $temp_file2 for num in $send_num do cat $temp_file1 |grep '<='|sed -n ${num}p|grep -E 'Mb|Kb' >>$temp_file2 done receive_flow=`cat $temp_file2 |grep -E 'Mb|Kb'|awk '{print $4}'|\ tr '\n' '+' |sed -e s/Mb/*1000/g |sed s/Kb//g |sed 's/\(.*\)+$/\1\n/g'|bc` if [[ $receive_flow == "" ]];then receive_flow=0 fi echo "${i}sendflow=${send_flow}" >>$file_name echo "${i}receiveflow=${receive_flow}" >>$file_name done
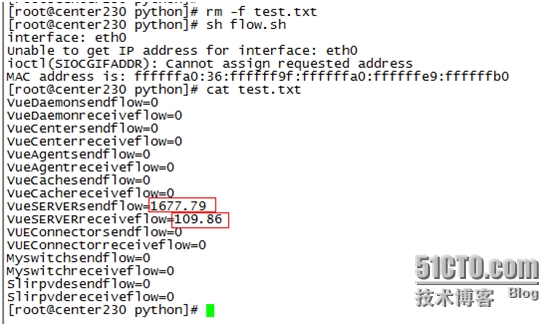
6.shell脚本执行效果
脚本中定义的进程列表为:pragrom_list=(VueDaemonVueCenter VueAgent VueCache VueSERVER VUEConnector Myswitch Slirpvde)
执行脚本的输出单位是Kb。
7.附:iftop命令用法
[root@center230 python]# iftop --help iftop: unknown option -- iftop: display bandwidth usage on aninterface by host Synopsis: iftop -h | [-npblNBP] [-iinterface] [-f filter code] [-F net/mask][-G net6/mask6] -h display thismessage #帮助信息 -n don't do hostname lookups #禁用主机解析,即不会出现IP显示域名 -N don't convertport numbers to services #以数字为示端口号,如21端口不会显示成ftp -p run inpromiscuous mode (show traffic between other hosts on the samenetwork segment) -b don't displaya bar graph of traffic #以b单位显示 -B Displaybandwidth in bytes #以B单位显示 -iinterface listen on namedinterface #指定监听的网口 -ffilter code use filter code toselect packets to count (default: none, but onlyIP packets are counted) -Fnet/mask show traffic flowsin/out of IPv4 network #显示指定Ipv4段流量 -Gnet6/mask6 show traffic flowsin/out of IPv6 network #显示指定Ipv6段流量 -l display andcount link-local IPv6 traffic (default: off) #显示Ipv6的流量 -P show ports aswell as hosts #显示端口信息 -mlimit sets the upper limit forthe bandwidth scale -cconfig file specifies an alternativeconfiguration file -t use textinterface without ncurses #使用文本模式输出 Sorting orders: -o2s Sort by first column(2s traffic average) #按2s平均流量列排序 -o10s Sort by second column(10s traffic average) [default] #按10s平均流量列排序 -o40s Sort by third column(40s traffic average) #按50s平均流量列排序 -osource Sort by source address #按源IP列排序 -odestination Sort by destinationaddress #按目的IP列排序 The following options are only available in combination with -t -snum print one single textoutput afer num seconds, then quit #指定刷新几次。 -Lnum number of lines to print #显示多少行数据。当程序多流量大时,则要显示行数多些才行。 iftop, version 1.0pre4 #版本信息。
文本输出方法:
iftop -Pp -Nn -t -L 100 -s 1 >temp_file