Linux Command Line
网络监控
一. ss
display socket statistics.
参数简单易用,还提供了很多 TCP 协议栈的参数,而且在 socket 数量巨大时,比 netstat 的输出快多了,大爱啊!
-a: all,显示所有的 socket,默认只显示非 listening 状态的
-t: tcp,显示 tcp socket
-u: udp,显示 udp socket
-w: raw,显示 raw sockt
-x: unix,显示 unix domain socket。可以看到 virtual box 使用了 domain socket。

-p: processes,显示开启此 socket 的进程,不过很多时候无法显示,不知道为什么
-n: not,不解析服务名称,默认会显示知名协议名而非端口号,但很多知名协议,其实并不熟悉其端口号
-l: listening,显示处于 listening 状态的 socket
-i: internal,显示 tcp 的内部信息

-s: summary,显示汇总信息

一种常用的场景,显示本机开放的 tcp/udp 端口,现在可以用 ss 来查看:

看了才知道,原来 Fedora 默认开启了 25 等端口。接下来又涉及到另外一个问题,在 -p 参数无法显示进程名称的情况下,如何知道某个端口是哪个进程开的呢?这就要用到接下来的 lsof!
二. lsof
对于一切皆文件的 Linux,list open files 无疑非常管用,常用参数 mark 下,以备后续快速查询。
1. -i
internet,即跟网络有关,用法:
lsof -i[46] [protocol][@hostname|hostaddr][:service|port]
46 --> IPv4 or IPv6
protocol --> TCP or UDP
hostname --> Internet host name
hostaddr --> IPv4地址
service --> /etc/service中的 service name (可以不止一个)
port --> 端口号 (可以不止一个)
例:
lsof -i 显示所有的连接
该命令也可查看本机开放的端口,还能显示对应的进程,但其缺点是慢,在连接数巨大的情况下基本不可用。
lsof [email protected]:513-515 显示到 10.143.0.10 的 513-515 端口的 tcp 连接
注意,udp 是无连接的,所以无法通过该命令显示到其它服务器的 UDP 连接。
比如前面提到的问题,想知道本机的 29754 端口是哪个进程开启的:

2. 不带参数,直接接文件名
查看该文件正在被哪些进程打开
lsof abc.txt
3. -c
command,命令,对应进程名称,列出该进程所打开的文件,用法:
lsof -c nginx 显示 nginx 进程现在打开的文件
4. -a
and,lsof 的参数之间是 OR 的关系,该参数将 OR 修改成 AND。
5. -s [p:s]
直接 -s 也可使用,用于显示 file 的 size,但最常用的还是接 [p:s] 选项,p 表示 protocol,s 表示 state,此时一定要同时带上 -i 选项:“If only TCP and UDP files are to be listed, as controlled by the specified exclusions and inclusions, the -i option must be specified, too”。
lsof -s tcp:established -i tcp
三. nmap
network mapper,扫描神器!
3 种需求:活着?端口?版本?
-sP: Ping Scan - go no further than determining if host is online
-A: Enables OS detection and Version detection
不带选项运行时,输出是否 up 及开放的端口。
1. 主机发现
其实把主机发现定义为是否活着不妥,在 IP 确定的情况下是 OK 的,但如果不知道有哪些 IP,就需要主动来发现了。
-sL: List Scan - simply list targets to scan
说是简单的列举参数中的所有主机,在大部分情况下好像是的,但其实会为每个主机做一次反向域名解析,在全都解析不出来的时候,就变成了 simply list。其作用体现在,如果解析出域名来了,那么也许能从中发现一些信息。
-sP: Ping Scan - go no further than determining if host is online
man 里称其为地毯式 ping,我比较喜欢这个名字。
关于其行为,实测后发现有 2 点需要注意:
a. 不仅仅发送 ICMP Echo 报文,还会有 SYN 报文、ACK 报文以及 ICMP TimeStamp 报文,而如果扫描的是局域网,还会发送 ARP 请求
b. root 用户和非 root 用户的行为不同,这个也好理解。对于 root 用于,有权限使用 rawsocket 仅仅发送 SYN 报文,且在收到 SYN+ACK 后直接 RST 掉,而非 root 用户,则只能调用 connect,一旦目的端口是开放的,那么协议栈会回复 ACK,这样就会在目标服务器上留下记录。看来还是 root 用户比较安全。
-P0: Treat all hosts as online -- skip host discovery
p: probe,0 意味着关闭。
忽略上一条主机发现,对列表中的每一个 IP 地址进行扫描。默认情况下,如果 nmap 需要进行高强度扫描,会先用主机发现确定正在运行的机器,进而只对运行的机器进行高强度扫描。
-PS/PA/PU [portlist]: TCP SYN/ACK or UDP discovery probes to given ports
如果非 root 用户,对于 SYN Probe 还能使用 connect 完成,但 ACK Probe 就无法做到了。
ACK Probe 存在的意义,在于比 SYN Probe 更有可能绕开防火墙。
-PE/PP/PM: ICMP echo, timestamp, and netmask request discovery probes
ICMP Echo 很有可能被防火墙封锁,但是 timestamp 和 netmask request 往往就不会了。
2. 端口扫描
这是最常用的功能,也是 nmap 设计的初衷。
-sS/sT/sA/sW/sM: TCP SYN/Connect()/ACK/Window/Maimon scans
--scanflags <flags>: Customize TCP scan flags
这个选项是大杀器啊,可以构造 TCP 标志位的任意组合。
-p <port ranges>: Only scan specified ports
指定扫描端口。
3. 应用版本及操作系统版本探测
记住 -A 就行了。
4. 时间和性能
-T0-5
数字越高扫描越快,对带宽的要求也越高。加速扫描是以缩短超时时间为代价的,因此准确性会降低。
默认为 T3,未做任何优化。
5. 防火墙/IDS躲避
-f; --mtu <val>: fragment packets (optionally w/given MTU)
可用于发送分片报文。正常情况下使用场景不多,可用于测试。
--data-length <number>
发送报文时,附加指定长度的随机数据,但无法发送指定的内容。
6. 输出
-v verbose
输出详细信息,类似 tcpdump 的 -v,可最多附加 2 个 v 以输出更详细的内容,而 tcpdump 最多可附加 3 个。
四. traceroute
这个命令倒没什么好说的,通过 IP 头中的 TTL 字段递增的方法,来探测路径中的各个 Router。
默认的探测协议是 UDP,目的端口大于 30000,因为基本不会有应用把端口开在这个范围内。
-I: 使用 ICMP 协议
-T: 使用 TCP 协议
-p: 指定目的端口
-m: 指定 TTL 上限,默认为 30
-N: 指定探测包的总并发数量
-q: 指定针对一个 route 的探测包的并发数量
manual 宣称可以利用其来探测路径 MTU,但实际只会显示第一条的 MTU。

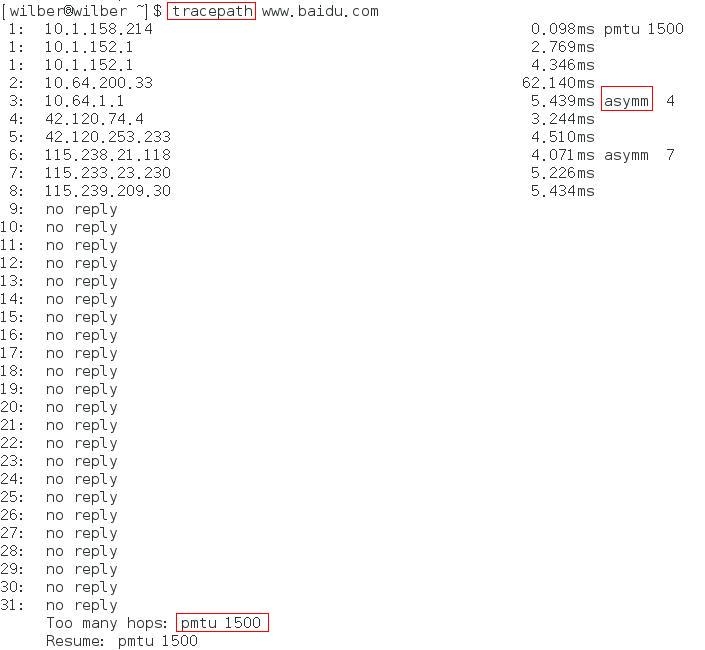
五. tracepath
该命令同 traceroute 的区别在于,能显示完整的路径 MTU 及对称/非对称信息。
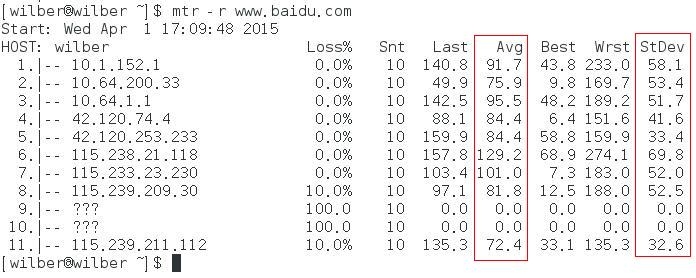
六. mtr
相比而言,该命令比较小众,在 Fedora 17 中默认没有安装。
其主要作用等同上面的 2 个命令,但又集成了 ping 的部分功能,可以输出网络质量状况,平均值表示网络质量,方差表示网络抖动。
-r:report 模式
七. ip
ip addr 替代 ifconfig
ip route 替代 netstat -r
ip -s link 替代 netstat -i
八. iwconfig
性能监控
一. vmstat
虚拟内存统计工具,但能提供包括 CPU、内存、IO、swap 在内的各种监控数据。

Procs
r: The number of runnable processes (running or waiting for run time). 运行或等待运行
b: The number of processes in uninterruptible sleep. block
Memory
swpd: the amount of virtual memory used.
free: the amount of idle memory.
buff: the amount of memory used as buffers.
cache: the amount of memory used as cache.
Swap
si: Amount of memory swapped in from disk (/s).
so: Amount of memory swapped to disk (/s).
IO
bi: Blocks received from a block device (blocks/s).
bo: Blocks sent to a block device (blocks/s).
System
in: The number of interrupts per second, including the clock.
cs: The number of context switches per second.
CPU
These are percentages of total CPU time.
us: Time spent running non-kernel code. (user time, including nice time)
sy: Time spent running kernel code. (system time)
id: Time spent idle. Prior to Linux 2.5.41, this includes IO-wait time.
wa: Time spent waiting for IO. Prior to Linux 2.5.41, included in idle.
st: Time stolen from a virtual machine. Prior to Linux 2.6.11, unknown.
-f: the number of forks since boot
-m: displays slabinfo
-s: displays a table of various event counters and memory statistics

-d: Report disk statistics

-D: Report some summary statistics about disk activity

二. mpstat
mpstat -P ALL interval count
监控 CPU 的运行状况,与 top 的输出差别不大,但支持查看 CPU 收到的中断数。
其 -A 的输出比较复杂。
三. iostat
iostat interval count
同时输出 cpu 和磁盘 IO,分析 IO 瓶颈时有用。
-k Display statistics in kilobytes per second.
-m Display statistics in megabytes per second.
tps Indicate the number of transfers per second that were issued to the device. A transfer is an I/O request to the device. Multiple logical requests can be combined into a single I/O request to the device. A transfer is of indeterminate size.

四. ifstat
interface statistics
查看网卡流量,相对于 iptraf 等,还是方便很多的,一是支持同时显示多张网卡的流量,二是延时低。
-l Enables monitoring of loopback interfaces for which statistics are available. By default, ifstat monitors all non-loopback interfaces that are up.
-a Enables monitoring of all interfaces found for which statistics are available.
-t Adds a timestamp at the beginning of each line.
-S Keep stats updated on the same line if possible (no scrolling nor wrapping).
-b Reports bandwith in kbits/sec instead of kbytes/sec.

五. dstat
号称是以上 xxstat 的集大成者,但实际上,其特点仅仅在于集成和汇总,例如,同时输出包括 CPU、IO、内存、网络的实时状况,而如果想观察每一个 CPU、每一块网卡的情况,就必须在命令行中一一指定,这显然谈不上用户友好。
-c, --cpu enable cpu stats (system, user, idle, wait, hardware interrupt, software interrupt)
-d, --disk enable disk stats (read, write)
-g, --page enable page stats (page in, page out)
-i, --int enable interrupt stats
-l, --load enable load average stats (1 min, 5 mins, 15mins)
-m, --mem enable memory stats (used, buffers, cache, free)
-n, --net enable network stats (receive, send)
-N eth1,total include eth1 and total
-p, --proc enable process stats (runnable, uninterruptible, new)
-r, --io enable I/O request stats (read, write requests)
-s, --swap enable swap stats (used, free)
-y, --sys enable system stats (interrupts, context switches)
--aio enable aio stats (asynchronous I/O)
--fs enable filesystem stats (open files, inodes)
--ipc enable ipc stats (message queue, semaphores, shared memory)
--lock enable file lock stats (posix, flock, read, write)
--raw enable raw stats (raw sockets)
--socket enable socket stats (total, tcp, udp, raw, ip-fragments)
--tcp enable tcp stats (listen, established, syn, time_wait, close)
--udp enable udp stats (listen, active)
--unix enable unix stats (datagram, stream, listen, active)
--vm enable vm stats (hard pagefaults, soft pagefaults, allocated, free)

六. nstat
七. sar
八. perf
九. stap
十. pidstat
十一. blktrace
九. strace
十. ltrace
十一. df
df displays the amount of disk space available on the file system containing each file name argument.
df -h:human-readable
df -i:显示 inode 的使用情况,小文件众多的场景下,有可能磁盘未满但 inode 耗光

df --total:显示总的使用情况

十二. du
du summarize disk usage of each FILE, recursively for directories.
du -s:显示当前目录总的空间占用
du -d --max-depth=:分目录统计空间占用
本文出自 “wilber” 博客,谢绝转载!