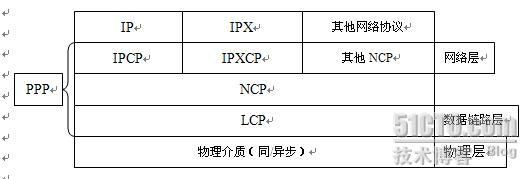
ppp协议
广域网连接使用的数据链路层协议有帧中继,
PPP
,
ATM
等,其中应用最广泛的时
PPP
协议,
PPP
是
Point to Point Protocol
点对点协议的简称,
PPP
以及
生出的
PPPoE,PPPoA
等协议成为目前广域网连接和宽带接入中使用最多的数据链路层协议
PPP
协议的优点:
PPP
协议提供了一种在点对点链路上封装多种网络数据报文(
IP
,
IPX
,和
AppleTalk
)的标准方法,与
SLIP
协议相比,
PPP
协议具有以下优点:
(1)
支持同步,异步串行链路
(2)
支持多种网络层协议
(3)
支持各种连接参数的协商
(4)
支持错误检测
(5)
支持用户认证
(6)
允许进行数据压缩
PPP
协议由
3
个部分组成:协议封装方式,
LCP
协议和
NCP
协议
协议封装方式:提供了一种将网络层协议封装到串行链路的方法,
PPP
既支持面向字符的异步串行链路,也支持面向比特的同步串行链路
LCP(Link Control Protocols
链路控制协议
)
:为了能适应复杂多变网络环境,
PPP
协议提供一种链路控制协议来配置和测试数据通信链路,他能用来协商
PPP
协议的一些配置参数选项;处理不同大小的数据帧;检测链路环路,一些链路的错误;终止一条链路。
NCP(Network Control Protocols
网络控制协议
)
:
PPP
的网络控制协议根据不同的网络层协议可提供一族网络控制协议,常用的提供给
TCP/IP
网络使用的
IPCP
网络控制协议和提供给
SPX/IPX
网络使用的
IPXCP
网络控制协议等,但最为常用的是
IPCP
协议,当点对点的两端进行
NCP
参数配置协商时,主要是用来协商通信双方的网络层地址等。
PPP
链路的工作过程
(1)
链路不可用阶段(
Link Dead Phase
)在最开始,整条链路处于链路不可用状态,此阶段有时也称为物理不可用阶段,
PPP
链路都需从这个阶段开始和结束,当通信双方的两端检测到物理线路激活时,就会从当前这个阶段进入到链路建立阶段
(2)
链路建立阶段
(Link Establishment Phase)
在此阶段,
PPP
链路将进行
LCP
相关协商,协商内容包括工作方式,认证方式,连路压缩等,
LCP
在协商成功后进入
Opened
状态,表示底层链路已经建立,如果链路协商失败,则会返回到第一阶段,在链路建立阶段成功后,如果配置了
PPP
认证,则会进入认证阶段,如果没有配置
PPP
认证,则会直接进入网络层协议阶段
(3)
认证阶段
(Authentication Phase)
在此阶段,
PPP
将进行用户认证工作,
PPP
支持
PAP
和
CHAP
两种认证方式,关于这两种认证方式在后面将会详细介绍,如果认证失败,
PPP
链路会进入链路终止阶段,拆除链路,
LCP
状态转为
DOWN
,如果认证成功就进入网络层协议阶段
(4)
网络层协议阶段
(Network-Layer Protocol Phase)
一旦
PPP
完成了前面几个阶段,每种网络层协议(
IP
,
IPX
等)会通过各自相应网络控制协议进行配置,只有相应的网络层协议协商成功后,该网络层协议才可以通过这条
PPP
链路发送报文,对于
IPCP
协议,协商的内容主要包括双方的
IP
地址等
(5)
链路终止阶段
(Link Termination Phase) PPP
能在任何时候终止链路,载波丢失,认证失败后用户人为关闭链路等情况均会导致链路终止,
PPP
协议通过交换
LCP
的链路之中报文来关闭链路,当链路关闭时,连路层会通知网络层做相应的操作,而且也会通过物理层强制关断链路
PPP
协议的封装
PPP
协议属于数据链路层协议,他可以将多种网络协议封装在
PPP
帧中,从而达到支持多种网络层协议的目的,
PPP
协议才用了同
HDLC
协议很相似的帧格式,
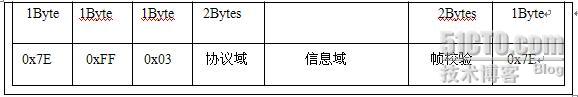
与
SLIP
协议类似,
PPP
协议也规定了帧的定界字节,每一个
PPP
数据帧均是一个标志字节起始和结束的,该字节为
0x7E
紧接在起始标志字节后的一个字节是地址域,该字节为
0xFF,
在
OSI 7
层模型中,网络的数据链路层要进行通信,首先必须获知对方的地址。
同地址域一样,
PPP
数据帧的控制域也没有实际意义,按照协议的规定通信双方将该字节的内容填充为
0x03
协议域用来说明
PPP
所封装的协议报文类型,它可用来区分
PPP
数据帧中信息域所承载的数据报文的内容,协议域的取值不同,后面的信息字段所代表的类型就不同协议域的具体取值见下表

帧校验序列域主要是对
PPP
数据帧传输的正确性进行检测的,它采用
CRC
算法,当数据帧在传输时因为噪声干扰等因素发生变化时,接收端就可以根据帧校验域的内容判断出来,将错误的帧丢弃,帧校验域的长度默认为
2
字节,但是通过
LCP
协商,它也可以为
4
个字节
LCP
协议
LCP
协议负责数据链路的建立,配置,维护,测试和终止,在数据建立阶段,
LCP
协议进行链路层参数的协商,此时
PPP
数据帧的协议域为
0xC021
,信息域的内容为
LCP
数据报文
LCP
协议在对链路配置过程中需要进行一些可选配置参数选项的协商,其中比较重要的协商选项由以下几个
1.
MRU(Maxium Receive Unit
最大接收单元
)
、
2.
Magic Number (
魔术字
)
3.
认证方式
4.
链路压缩
5.
多链路捆绑
NCP
协议
NCP
协议的数据报文是在网络层协议阶段被交换的,在这个阶段所需的一些配置参数选项协商完后,就可以进行网络层的通信,也即是在点对点的链路上可以开始传送网络层的数据报文了,
NCP
协议主要包括
IPCP(IP Control Protocol ,IP
控制协议
) IPXCP(IPXControl Protocol ,IPX
控制协议
)
等,但在实际应用当中最常预见的只有
IPCP
协议,
IPCP
控制协议主要是负责协商
IP
网络层协议通信所需配置参数的选项,
IPCP
协议主要协商的参数有以下几个,
1.
IP
2.
TCP/IP
头压缩
PPP
认证
PPP
支持两种认证方式,
PAP
认证和
CHAP
认证
1.
PAP
认证
PAP
(
Password Authentication Protocol,
密码认证协议)
PAP
为两次握手认证协议,
被认证方发起认证请求,发送用户名和口令到主认证方
主认证让根据本端用户表查看是否有此用户以及口令是否正确,然后返回认证通过或不通过,
2.
CHAP
认证
CHAP
是
Challenge Hand Authentication Protocol
质询握手认证协议的简称,与
PAP
认证比起来,
CHAP
认证更具有安全性,在
PAP
认证中,被认证方采用明文的方式直接将用户名和密码发送给主认证方,这很容易引起密码的泄漏
CHAP
为三次握手协议,它只在网络上传送用户名而不传送口令,因此安全性比
PAP
高,
CHAP
认证的程序如下
(
1).
主认证方主动发起认证请求,主认证方向被认证方发送一些随机产生的报文
(Challenge)
,并同时将本端的用户名附带上一起发送给被认证方
(2).
被认证方接到主认证方的认证请求后,被认证方根据此报文中主认证方的用户名查
找用户密码
(3).
主认证方接受到该报文后,根据此报文中被认证方的用户名,在自己的本地用户数据库中查找被认证方用户名对应的被认证方密码
(CHAP
认证密码
)
,利用报文
ID
,该密码和
MD5
算法对原随机报文加密,然后将加密的结果和被认证方发来的加密结果进行比较
配置实例:

PPP(pap)
r1
Router>enable
Router#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#line Console 0
Router(config-line)#exec-timeout 0 0
Router(config-line)#logging synchronous
Router(config-line)#exit
Router(config)#no ip domain lookup
Router(config)#no cdp run
Router(config)#exit
00:01:55: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#hostname r1
r1(config)#username benet password cisco \\主认证端数据库,是被认证的用户名和密码
r1(config)#interface s0/0
r1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
r1(config-if)#encapsulation ppp \\端口封装成PPP协议
r1(config-if)#ppp authentication pap \\启用PAP认证
r1(config-if)#no shutdown
r1(config-if)#exit
00:05:51: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
r1(config)#exit
00:05:56: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
00:06:48: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
r1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Serial0/0 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
r1#ping 192.168.1.2
Router#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#line Console 0
Router(config-line)#exec-timeout 0 0
Router(config-line)#logging synchronous
Router(config-line)#exit
Router(config)#no ip domain lookup
Router(config)#no cdp run
Router(config)#exit
00:01:55: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#hostname r1
r1(config)#username benet password cisco \\主认证端数据库,是被认证的用户名和密码
r1(config)#interface s0/0
r1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
r1(config-if)#encapsulation ppp \\端口封装成PPP协议
r1(config-if)#ppp authentication pap \\启用PAP认证
r1(config-if)#no shutdown
r1(config-if)#exit
00:05:51: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
r1(config)#exit
00:05:56: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
00:06:48: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
r1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Serial0/0 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
r1#ping 192.168.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 48/66/72 ms
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 48/66/72 ms
r2
Router>enable
Router#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#line console 0
Router(config-line)#exec-timeout 0 0
Router(config-line)#logging synchronous
Router(config-line)#exit
Router(config)#no ip domain lookup
Router(config)#no cdp run
Router(config)#exit
00:03:04: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#hostname r2
r2(config)#exit
00:03:21: %IP_SNMP-3-SOCKET: can't open UDP socket
r2#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
r2(config)#interface s0/0
r2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
r2(config-if)#encapsulation ppp \\将端口封装成PPP协议
r2(config-if)#ppp pap sent-username benet password cisco \\被认证端PAP认证的用户名和密码
r2(config-if)#no shutdown
r2(config-if)#exit
r2(config)#exit
00:06:45: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
00:06:46: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
r2#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Serial0/0 192.168.1.2 YES manual up up
Serial0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
r2#ping 192.168.1.1
Router#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#line console 0
Router(config-line)#exec-timeout 0 0
Router(config-line)#logging synchronous
Router(config-line)#exit
Router(config)#no ip domain lookup
Router(config)#no cdp run
Router(config)#exit
00:03:04: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Router#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#hostname r2
r2(config)#exit
00:03:21: %IP_SNMP-3-SOCKET: can't open UDP socket
r2#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
r2(config)#interface s0/0
r2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
r2(config-if)#encapsulation ppp \\将端口封装成PPP协议
r2(config-if)#ppp pap sent-username benet password cisco \\被认证端PAP认证的用户名和密码
r2(config-if)#no shutdown
r2(config-if)#exit
r2(config)#exit
00:06:45: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
00:06:46: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
r2#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Serial0/0 192.168.1.2 YES manual up up
Serial0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
r2#ping 192.168.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 48/77/96 ms
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 48/77/96 ms
(chap)
r1>enable
r1#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
r1(config)#username r2 password cisco \\被认证端用户名和密码
r1(config)#interface s0/0
r1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
r1(config-if)#encapsulation ppp
r1(config-if)#ppp authentication chap \\启用chap认证
r1(config-if)#no shutdown
r1(config-if)#exit
r1(config)#exit
00:09:23: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
00:09:23: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
00:11:01: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
r1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Serial0/0 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
r1#ping 192.168.1.2
r1#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
r1(config)#username r2 password cisco \\被认证端用户名和密码
r1(config)#interface s0/0
r1(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
r1(config-if)#encapsulation ppp
r1(config-if)#ppp authentication chap \\启用chap认证
r1(config-if)#no shutdown
r1(config-if)#exit
r1(config)#exit
00:09:23: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
00:09:23: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
00:11:01: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
r1#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Serial0/0 192.168.1.1 YES manual up up
Serial0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
r1#ping 192.168.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 52/77/96 ms
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 52/77/96 ms
r2>enable
r2#config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
r2(config)#interface s0/0
r2(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
r2(config-if)#encapsulation ppp
r2(config-if)#ppp chap password cisco \\向主认证端发送自己的密码
r2(config-if)#no shutdown
r2(config-if)#exit
r2(config)#exit
00:10:45: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
00:10:45: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
00:10:47: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0, changed state to up
r2#show ip interface brief
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Serial0/0 192.168.1.2 YES manual up up
Serial0/1 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/2 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
Serial0/3 unassigned YES unset administratively down down
r2#ping 192.168.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 36/64/72 ms
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 36/64/72 ms