MIT Introduction to Algorithms 学习笔记(一)
MIT Introduction to Algorithms 学习笔记
http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/electrical-engineering-and-computer-science/6-006-introduction-to-algorithms-fall-2011/
整个课程分成8个部分:
Lecture 1: Introduction and Peak Finding
Peak Finder
在数组中找到一个峰值。
在数组中,如果b≥c且b≥a,那么b是一个峰值。如果i≥h,i是一峰值。
最简单的算法就是从数组的第一个元素和它的相邻的元素比较。算法运行时间为Θ(n)。
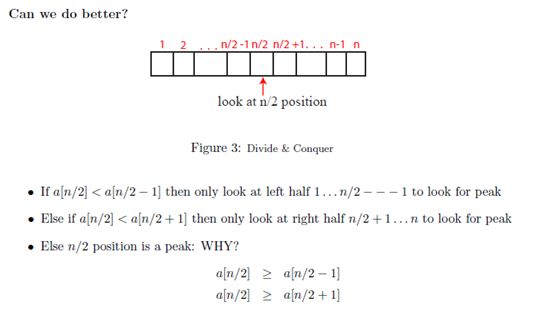
另外就是使用二分法:
算法运行时间为Θ(log2(n)):
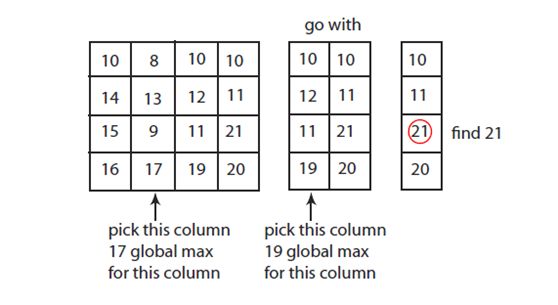
Two-dimensional Version
在二维数组中如果a ≥ b, a ≥ d, a ≥ c, a ≥ e,那么a是峰值。
过程如下:
假设二维数组大小为(m,n),算法运行时间为Θ(n log n):
python代码:
def getMaxIndex(sList): #print(sList) iMax = 0 Max = sList[0] for i in range(0,len(sList)): if sList[i] > Max: Max = sList[i] iMax = i return iMax def isPeak(sList,iPos): #print(sList) sLen =len(sList) if(1 == sLen): return 0 elif(sLen - 1 == iPos): if(sList[iPos] < sList[iPos - 1]): return -1 else: return 0 elif(0 == iPos): if(sList[iPos] < sList[iPos + 1]): return 1 else: return 0 elif(sList[iPos] < sList[iPos - 1]): return -1 elif(sList[iPos] < sList[iPos + 1]): return 1 elif(sList[iPos] >= sList[iPos + 1] and sList[iPos] >= sList[iPos - 1]): return 0 def PeakFinder_2D(sList2d,startPos,endPos): rowLen = endPos - startPos + 1 tmpList1 = [] if(0 == rowLen): return -1,-1,-1 iMid = int(rowLen / 2) + startPos colLen = len(sList2d[iMid]) if(0 == colLen): return -1,-1,-1 iMaxValInCol = getMaxIndex(sList2d[iMid]) for i in range(0,len(sList2d[iMid])): tmpList1.append(sList2d[i][iMaxValInCol]) bIsPeak = isPeak(tmpList1, iMid); print(iMid,iMaxValInCol,sList2d[iMid],bIsPeak) if(0 == bIsPeak): return iMid,iMaxValInCol,sList2d[iMid][iMaxValInCol] elif(-1 == bIsPeak) : return PeakFinder_2D(sList2d,startPos,iMid - 1) elif(1 == bIsPeak): return PeakFinder_2D(sList2d,iMid + 1,endPos) return -1,-1,-1