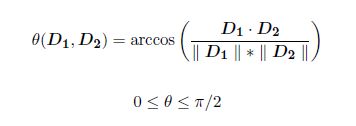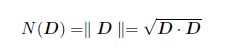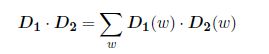MIT Introduction to Algorithms 学习笔记(二)
Lecture 2: Models of Computation(Ⅰ)
什么是算法(Algorithm)?
l Mathematical abstraction of computer program
l Computational procedure to solve a problem
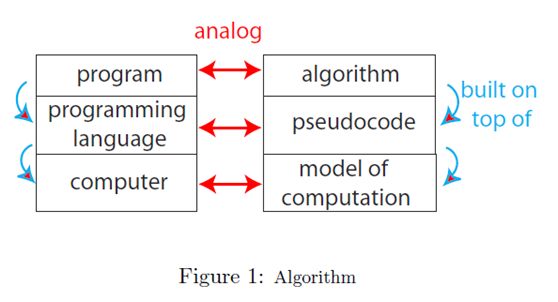
算法和程序的类比:
两种计算模型( Model of computation):
Random Access Machine (RAM)
Random Access Memory (RAM) modeled by a big array
Θ(1) registers (each 1 word)
In Θ(1) time, can
load word @ ri into register rj
compute (+, −, ∗, /, &, |, ˆ) on registers
store register rj into memory @ ri
What’s a word? w ≥ lg (memory size) bits
realistic and powerful → implement abstractions
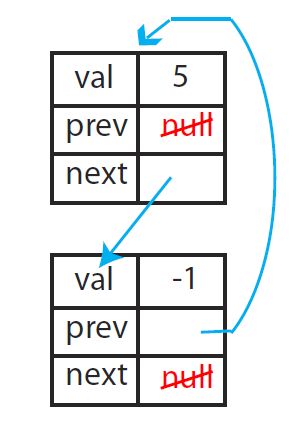
Pointer Machine
dynamically allocated objects (namedtuple)
object has O(1) fields
field = word (e.g., int) or pointer to object/null (a.k.a. reference)
weaker than (can be implemented on) RAM
2. Document Distance Problem — compute d(D1,D2)
主要用于查找相似的文件,检测重复(维基百科和谷歌)和抄袭,网络搜索。
什么是Word 和Document?
Word = sequence of alphanumeric characters
Document = sequence of words (ignore space, punctuation, etc.)
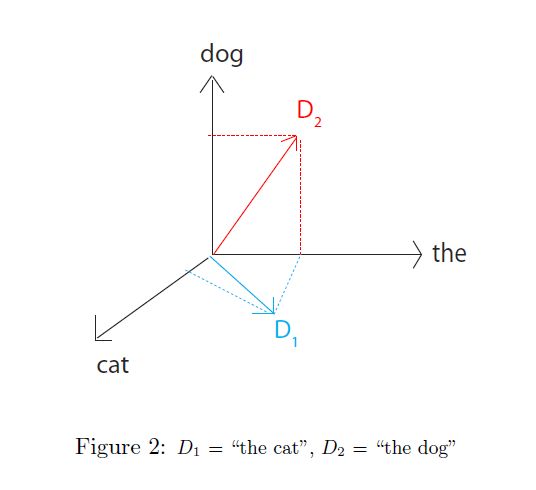
把文件D(document D)看作一个向量(vector):D[w] = # 代表W在文件中出现的次数 .例如:
用向量D1和D2的夹角表示2个文件之间的重叠度。
其中,
Document Distance Algorithm
a) split each document into words
b) count word frequencies (document vectors)
c) sort into order
d) compute dot product (Compute θ)
代码(V1):
# docdist1.py # Author: Ronald L. Rivest # Date Last Modified: February 14, 2007 # Changelog: # Version 1: # Initial version # # Usage: # docdist1.py filename1 filename2 # # This program computes the "distance" between two text files # as the angle between their word frequency vectors (in radians). # # For each input file, a word-frequency vector is computed as follows: # (1) the specified file is read in # (2) it is converted into a list of alphanumeric "words" # Here a "word" is a sequence of consecutive alphanumeric # characters. Non-alphanumeric characters are treated as blanks. # Case is not significant. # (3) for each word, its frequency of occurrence is determined # (4) the word/frequency lists are sorted into order alphabetically # # The "distance" between two vectors is the angle between them. # If x = (x1, x2, ..., xn) is the first vector (xi = freq of word i) # and y = (y1, y2, ..., yn) is the second vector, # then the angle between them is defined as: # d(x,y) = arccos(inner_product(x,y) / (norm(x)*norm(y))) # where: # inner_product(x,y) = x1*y1 + x2*y2 + ... xn*yn # norm(x) = sqrt(inner_product(x,x)) import math # math.acos(x) is the arccosine of x. # math.sqrt(x) is the square root of x. import string # string.join(words,sep) takes a given list of words, # and returns a single string resulting from concatenating them # together, separated by the string sep . # string.lower(word) converts word to lower-case import sys ################################## # Operation 1: read a text file ## ################################## def read_file(filename): """ Read the text file with the given filename; return a list of the lines of text in the file. """ try: fp = open(filename) L = fp.readlines() except IOError: print "Error opening or reading input file: ",filename sys.exit() return L ################################################# # Operation 2: split the text lines into words ## ################################################# def get_words_from_line_list(L): """ Parse the given list L of text lines into words. Return list of all words found. """ word_list = [] for line in L: words_in_line = get_words_from_string(line) word_list = word_list + words_in_line return word_list def get_words_from_string(line): """ Return a list of the words in the given input string, converting each word to lower-case. Input: line (a string) Output: a list of strings (each string is a sequence of alphanumeric characters) """ word_list = [] # accumulates words in line character_list = [] # accumulates characters in word for c in line: if c.isalnum(): character_list.append(c) elif len(character_list)>0: word = string.join(character_list,"") word = string.lower(word) word_list.append(word) character_list = [] if len(character_list)>0: word = string.join(character_list,"") word = string.lower(word) word_list.append(word) return word_list ############################################## # Operation 3: count frequency of each word ## ############################################## def count_frequency(word_list): """ Return a list giving pairs of form: (word,frequency) """ L = [] for new_word in word_list: for entry in L: if new_word == entry[0]: entry[1] = entry[1] + 1 break else: L.append([new_word,1]) return L ############################################################### # Operation 4: sort words into alphabetic order ### ############################################################### def insertion_sort(A): """ Sort list A into order, in place. From Cormen/Leiserson/Rivest/Stein, Introduction to Algorithms (second edition), page 17, modified to adjust for fact that Python arrays use 0-indexing. """ for j in range(len(A)): key = A[j] # insert A[j] into sorted sequence A[0..j-1] i = j-1 while i>-1 and A[i]>key: A[i+1] = A[i] i = i-1 A[i+1] = key return A ############################################# ## compute word frequencies for input file ## ############################################# def word_frequencies_for_file(filename): """ Return alphabetically sorted list of (word,frequency) pairs for the given file. """ line_list = read_file(filename) word_list = get_words_from_line_list(line_list) freq_mapping = count_frequency(word_list) insertion_sort(freq_mapping) print "File",filename,":", print len(line_list),"lines,", print len(word_list),"words,", print len(freq_mapping),"distinct words" return freq_mapping def inner_product(L1,L2): """ Inner product between two vectors, where vectors are represented as alphabetically sorted (word,freq) pairs. Example: inner_product([["and",3],["of",2],["the",5]], [["and",4],["in",1],["of",1],["this",2]]) = 14.0 """ sum = 0.0 i = 0 j = 0 while i<len(L1) and j<len(L2): # L1[i:] and L2[j:] yet to be processed if L1[i][0] == L2[j][0]: # both vectors have this word sum += L1[i][1] * L2[j][1] i += 1 j += 1 elif L1[i][0] < L2[j][0]: # word L1[i][0] is in L1 but not L2 i += 1 else: # word L2[j][0] is in L2 but not L1 j += 1 return sum def vector_angle(L1,L2): """ The input is a list of (word,freq) pairs, sorted alphabetically. Return the angle between these two vectors. """ numerator = inner_product(L1,L2) denominator = math.sqrt(inner_product(L1,L1)*inner_product(L2,L2)) return math.acos(numerator/denominator) def main(): if len(sys.argv) != 3: print "Usage: docdist1.py filename_1 filename_2" else: filename_1 = sys.argv[1] filename_2 = sys.argv[2] sorted_word_list_1 = word_frequencies_for_file(filename_1) sorted_word_list_2 = word_frequencies_for_file(filename_2) distance = vector_angle(sorted_word_list_1,sorted_word_list_2) print "The distance between the documents is: %0.6f (radians)"%distance if __name__ == "__main__": main()