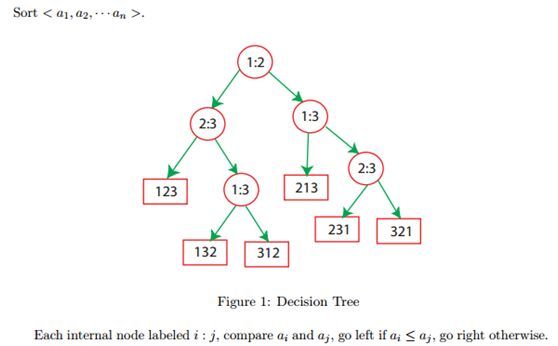
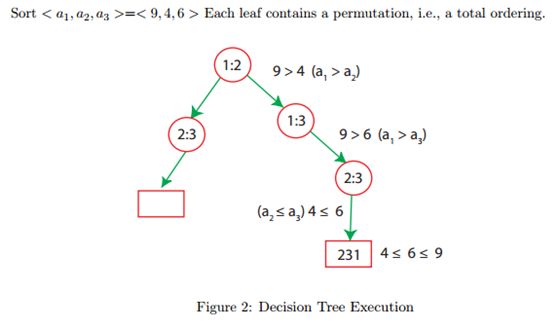
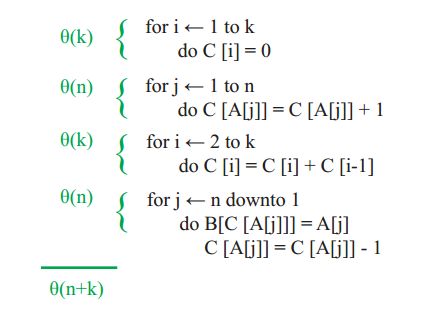
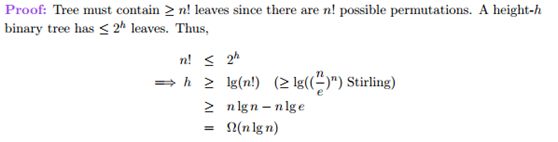- 基于Python爬虫宁夏银川天气预报数据可视化系统设计与实现(Django框架) 研究背景与意义、国内外研究现状_python的arima天气预测的研究背景(1)
HUAXIAL
2024年程序员学习信息可视化python爬虫
先自我介绍一下,小编浙江大学毕业,去过华为、字节跳动等大厂,目前阿里P7深知大多数程序员,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长,但自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!因此收集整理了一份《2024年最新Python全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友。既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课
- Python数据分析从入门到精通
莲华君
Python权威教程合集数据分析数据挖掘
目录第一部分:Python入门——学会用Python“操控”数据1.1什么是数据分析?从“数据”到“分析”:一场科学的探险数据分析的日常工作:就像用显微镜看世界1.2Python基础:数据分析的“神奇魔杖”Python基础语法:数据分析的基本“食材”变量、数据类型与运算符:它们是我们厨房里的锅碗瓢盆条件语句和循环:如何避免代码跑偏,保证数据流程的高效性1.3安装与配置Python环境安装Pytho
- Python 爬虫实战:LinkedIn用户数据抓取与职业发展路径分析
西攻城狮北
python爬虫开发语言
一、引言随着全球化的加速和数字化的普及,职业发展路径的分析变得越来越重要。LinkedIn作为全球领先的职业社交平台,拥有海量的用户数据和职业信息。通过爬取LinkedIn的用户数据,我们可以分析职业发展路径、行业趋势以及技能需求。本文将详细介绍如何使用Python爬虫技术抓取LinkedIn用户数据,并进行职业发展路径分析。二、项目背景与目标2.1项目背景LinkedIn是一个专注于职业发展的社
- Python GUI框架之PyQt详解
长安er
学习心得数据可视化pythonpyqt开发语言PyQtGUIui
目录一、PyQt核心模块概览二、核心模块详解与示例1.QtCore-核心基础模块2.QtWidgets-UI控件库3.QtGui-图形处理4.QtNetwork-网络通信5.QtSql-数据库交互6.QtWebEngine-网页渲染三、综合应用示例四、PyQt版本选择建议五、学习资源推荐PyQt是Python语言中最强大且广泛应用的GUI框架之一,基于Qt库的Python绑定实现。其模块化架构和跨
- 工具、数据与情绪:计算机技术的三重境界
狒狒的代码王国
学习方法深度学习学习
此篇文章是我对计算机应用的理解,写着玩的。第一层境界:工具的熟练与桎梏计算机语言和工具构成了我们与数字世界对话的基础语法。Java、C、C++、Python等编程语言,IntelliJIDEA、VisualStudio等开发环境,Linux、Windows等操作系统,这些都是技术人员赖以生存的"锤子与钉子"。在这个层面上,我们如同工匠学徒,专注于工具的握持方式、使用技巧和保养方法。一个优秀的程序员
- 6个Python脚本,轻松实现日常任务自动化
Python子木_
Python入门Python零基础Python学习python开发语言python学习python教程Python教学
作为程序员,咱们最怕什么?不是“技术难题”而是那些重复、无聊、繁琐的日常任务,比如文件重命名、数据备份、批量处理图像等等。说实话,看到这些任务堆起来时,我的第一反应不是做,而是去思考:有没有办法让它们自动化?答案是有的!今天,我就站在技术专家的角度,给大家推荐6个简单又实用的Python脚本,帮你轻松搞定这些日常任务,让重复工作从此告别“手动模式”。这里插播一条粉丝福利,如果你正在学习Python
- Python甘肃兰州二手房源爬虫数据可视化分析大屏全屏系统 开题报告
2501_90223162
信息可视化python爬虫
项目都录了发布和功能操作演示视频;项目的界面和功能都可以定制,包安装运行!!!如果需要联系我,可以在CSDN网站查询黄菊华老师在文章末尾可以获取联系方式Python****甘肃兰州二手房源爬虫数据可视化分析大屏全屏系统开题报告XXXX大学**/学校/**学院毕业论文(设计)开题报告书学生姓名所属学院学号专业班级论文(设计)题目Python甘肃兰州二手房源爬虫数据可视化分析大屏全屏系统设计与实现指导
- Python 爬虫实战:多数据源抓取与自动化报表生成高效流程
西攻城狮北
python爬虫自动化开发语言
目录一、准备工作1.1环境搭建1.2安装所需库二、多数据源抓取2.1确定数据源2.2使用Requests和BeautifulSoup抓取静态网页数据2.2.1发送HTTP请求2.2.2解析HTML内容2.3使用Selenium抓取动态网页数据2.3.1安装浏览器驱动2.3.2编写Selenium爬虫代码2.4使用API抓取数据2.4.1发送API请求三、数据处理与清洗3.1使用Pandas进行数据
- 加载MiniLM-L12-v2模型及知识库,调用Deepseek进行问答
欣然~
pytorch
这段Python代码实现了一个基于知识库的问答系统KnowledgeBaseSystem。该系统主要具备以下功能:加载本地模型对文本进行编码。从指定路径加载知识库文件。对知识库中的文本进行向量化处理。根据用户的问题,找出知识库中最相关的知识。调用DeepSeekAPI结合相关知识生成回答。代码详细说明导入必要的库pythonimportosimportnumpyasnpimportrequests
- 像素到数据:Selenium,OpenCV,Tesseract,Python构建的智能解析系统
赛卡
seleniumopencvpythonocr计算机视觉
基于Selenium与OCR技术的网页信息智能提取方案一、应用场景解析在Web自动化测试和数据分析领域,经常需要处理动态渲染的网页信息,特别是当页面元素以图像形式呈现时。本文介绍的解决方案结合了浏览器自动化与图像识别技术,有效解决了以下典型场景:动态渲染的可视化数据提取反爬机制中的图像验证码识别无法通过API获取的图形化数据采集页面局部区域的实时信息监控二、技术架构设计2.1系统组成浏览器控制层:
- Python 爬虫实战:影视资源网站信息抓取与下载指南
西攻城狮北
python爬虫开发语言
一、引言在互联网时代,影视资源网站成为了人们获取电影、电视剧等娱乐内容的重要渠道。对于影视爱好者来说,及时了解影视资源的更新情况和下载信息是非常重要的。然而,手动搜索和整理这些信息往往耗时费力。因此,利用Python爬虫技术自动抓取和整理影视资源网站的信息,成为了提高效率的首选方案。本文将详细介绍如何使用Python爬虫技术抓取影视资源网站的最新更新和下载信息,帮助读者构建自己的影视资源库。二、目
- Requests高级使用指南:状态保持、会话管理与异常处理
小L工程师
爬虫知识点python网络爬虫爬虫selenium课程设计数据分析
在现代网络爬虫和API交互中,简单的GET/POST请求往往不能满足需求。本文将深入探讨Pythonrequests库的高级特性,包括状态保持、会话管理以及常见异常处理,帮助你更好地模拟浏览器行为,完成复杂的网页采集任务。1.HTTP状态保持与Cookie管理1.1为什么需要CookieHTTP协议是无状态的,这意味着服务器不会记住之前的请求信息。Cookie的引入解决了这个问题,它允许服务器在客
- Python 深度学习实战:聊天机器人
AI天才研究院
AI实战DeepSeekR1&大数据AI人工智能大模型Python实战大数据人工智能语言模型JavaPython架构设计
Python深度学习实战:聊天机器人关键词:Python、深度学习、聊天机器人、Seq2Seq、注意力机制、Transformer1.背景介绍近年来,随着人工智能技术的飞速发展,聊天机器人(Chatbot)逐渐走进了大众的视野。从简单的问答系统到如今能够进行多轮对话、情感分析的智能助手,聊天机器人在客服、娱乐、教育等领域展现出了巨大的应用潜力。深度学习作为人工智能领域的核心技术之一,为聊天机器人的
- Java 8 Stream(三、Stream中间操作:filter()、distinct()、skip()、limit()、map()、flatMap()、sorted()、peek())
Dylan RD
Javajavastreamlambdaintellijidea
上文我们对Stream操作和无限流做了介绍,没看过的同学请出门左转Java8Stream(二、Stream操作和无限流)。文章目录一、分类二、介绍(一)筛选与切片1、filter()2、distinct()3、skip()4、limit()(二)映射1、map()2、flatMap()(三)排序1、sorted()(四)消费1、peek()Java8Stream本文我们主要介绍Stream中间操作
- 07_DQL
.又是新的一天.
Mysql数据库javamysql
文章目录一、准备工作二、单表查询2.1、基本查询2.1.1、查询所有列2.1.2、查询指定列2.1.3、完全重复的记录只出现一次2.1.4、列运算2.1.5、条件查询2.1.6、模糊查询2.2、排序2.3、聚合函数2.4、分组查询2.5、LIMIT子句2.6、查询语句执行顺序三、多表查询3.1、合并结果集3.2、内连接3.3、外连接3.3.1、左外连接3.3.2、右外连接3.3.3、全外连接四、子
- python爬虫项目(一百三十三):交通网站火车票余票信息实时监控
人工智能_SYBH
爬虫试读2025年爬虫百篇实战宝典:从入门到精通python爬虫开发语言音视频数据分析信息可视化
一、前言在现代社会,火车已成为人们出行的重要交通工具。尤其是在节假日、春运等特殊时期,火车票的需求量激增,余票信息的实时获取变得尤为重要。通过实现火车票余票信息的实时监控,用户可以快速获取自己所需的车票信息,避免错过最佳购票时机。本文将详细介绍如何搭建一个火车票余票信息实时监控系统,重点关注数据爬取和实时推送部分,并提供完整的代码示例。目录一、前言二、项目背景与目标2.1项目背景2.2项目目标2.
- 探索无限可能:使用Python LINE Bot SDK构建对话机器人
高慈鹃Faye
探索无限可能:使用PythonLINEBotSDK构建对话机器人去发现同类优质开源项目:https://gitcode.com/在这个数字化的时代,交互式的聊天机器人已经成为我们日常生活和工作中的一部分。通过LINE平台,我们可以利用强大的PythonLINEBotSDK轻松创建个性化的聊天机器人,并部署在Heroku云服务上,无论你是开发者新手还是经验丰富的程序员,都能快速上手。现在,让我们一起
- Python图形填充算法入门指南:闭合区域处理原理及常用算法详解
灏瀚星空
浩瀚星空的Python筑基系列python算法开发语言经验分享
Python图形填充算法入门指南:闭合区域处理原理及常用算法详解引言在计算机图形学中,填充算法是核心基础技术之一。无论是图像编辑软件中的“油漆桶工具”,还是游戏引擎中的地形渲染,甚至是医学影像分析,填充算法都扮演着关键角色。本文将带初学者系统学习填充算法的概念、分类及Python实现,助你快速掌握闭合区域处理的核心技能!一、填充算法基础概念1.1什么是填充算法?填充算法(FillingAlgori
- 深入理解 Python 中的异步操作:async 和 await
aiweker
跟我学pythonpython服务器
深入理解Python中的异步操作:async和await引言在现代编程中,异步操作是一个非常重要的概念,尤其是在处理I/O密集型任务时。使用异步操作可以显著提高程序的性能和响应速度。Python提供了async和await关键字,使得编写异步代码变得更加直观和简洁。在这篇文章中,我们将深入探讨Python的异步操作,并通过实际代码示例来说明其使用方法。目录什么是异步操作?Python中的异步编程基
- 基于PySide6与CATIA API的装配体位置管理工具开发实践
Python×CATIA工业智造
pythonCATIA二次开发
引言在工业设计领域,CATIA作为主流的三维设计软件,其装配体管理功能直接影响产品设计效率。本文介绍如何利用PySide6框架与CATIAAPI开发一款专业的装配体位置管理工具,实现零部件定位数据的自动化保存与恢复。一、技术架构1.1技术栈选择PySide6框架:Qt官方Python绑定,提供企业级GUI开发能力JSON数据格式:轻量级结构化数据存储方案,支持复杂数据结构序列化CATIAAPI:通
- [Python]如何利用Flask搭建一個Web服務器,並透過Ngrok訪問來實現LINE Bot功能?
Learn-Share_HY
PythonRaspberryPiLinuxpythonflaskNgrokollamaubuntu人工智能linux
AIChatBotIHowtoBuildAILINEBotwithOllama,FlaskandNgrok?Flask是一個輕量級的Web框架,主要用於建立基於Python的Web應用和API。它可搭建webhook本地服務器,同時提供靈活的URL路由和HTTP請求處理方式,允許開發者快速啟動並測試應用功能。由於其結構簡單,開發者常用其作為建立和測試MVP(最小可行性產品),同時其也非常適合新手作
- 大屏监控 Metabase 集成到 Java 项目
不是太高的手
数据可视化编程语言devops数据分析区块链
前言概述:Metabase可以帮助你把数据库中的数据更好的呈现给更多人,数据分析人员通过建立一个”查询“(Metabase中定义为Question)来提炼数据,再通过仪表盘(Dashboards)来组合展示给公司成员分享支持公开链接、公开嵌入、应用嵌入三种方式,前两种方式由于其公开性,只能分享一些见得人的数据,如果一些见不得人的数据就要通过第三种方式实现了。这玩意官方案例支持Python、Node
- iis+django+channels+daphne部署websocket通信包含一对一、群聊功能、上传图片
冰红茶阿伟
websocketdjangopython
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档目录前言一、安装对应库二、使用步骤1.后端配置:后端思路:2.前端代码:前端思路:3.一对一和群聊:4.发送图片:5.daphne的启动和部署:http不带证书启动:https带证书启动:总结前言django下使用websocket实现即时通信并部署到iis服务器(无nginx)踩了许多坑,记录下。一、安装对应库python版本需要在
- 将调用deepseek的python包装成一个方法,使用流式,多轮对话
痕迹*
python开发语言
要将调用DeepSeek的Python代码包装成一个方法,并支持流式输出和多轮对话,你可以按照以下步骤进行。假设你已经有了一个可以调用DeepSeekAPI的函数,并且该API支持流式输出。1.安装必要的库首先,确保你已经安装了requests库,用于发送HTTP请求。pipinstallrequests2.创建DeepSeek客户端类我们可以创建一个DeepSeekClient类来封装与Deep
- 部署django+nginx实现ws/wss的websocket生产环境通信
body221
nginxjavalinuxdockerpython
本文阐述如何使用nginx部署基于django应用的websocket通信。之后会写django基于channels实现websocket的通信文章。简单介绍下:websocket的主要协议ws/wss,类似于http/https的关系,如果使用了https那就必须使用wss协议。首先django应用启动ws服务,启动runworkerpythonmanage.pyrunworker具体实现处理的
- Windows 7 下 TensorFlow 安装入门(PyCharm 版)
架构魔术
windowstensorflowpycharm编程
Windows7下TensorFlow安装入门(PyCharm版)TensorFlow是一个流行的开源机器学习框架,广泛应用于深度学习和人工智能领域。本文将指导您在Windows7操作系统上使用PyCharm安装和配置TensorFlow。以下是详细的步骤和相应的源代码。步骤1:安装Python首先,您需要安装Python。TensorFlow支持Python3.5-3.8版本。您可以从Pytho
- PyCharm目录和软件包的区别、普通目录与源代码根目录和已排除目录的区别
被放养的研究生
PyCharmpycharmidepython
目录(Directory)和软件包(Package)的区别目录(Directory):也就是文件夹软件包:是一个包含多个模块(.py文件)的目录,并且这个目录中默认包含一个特殊的文件__init__.py特性目录软件包是否必须有init.py否是(推荐,Python3.3以后可选)Python模块功能无法直接导入可以通过import导入用途文件组织、存储文件模块化代码管理支持嵌套支持支持普通目录与
- 蓝桥杯真题1259奇怪的捐赠(python版)
被放养的研究生
#蓝桥杯蓝桥杯python
解题思路:将100万转换为7进制数,数位之和就是分成的份数num=100_0000sum=0whilenum>0:remainder=num%7num=num//7sum+=remainderprint
- WiFi_CE_占用带宽自动化测试_基于 Python + 罗德频谱仪(SCPI指令)
岁月_流沙
自动化测试_Pythonpython测试工具
2.4G_WiFi_CE_占用带宽测试标准请参考下面博客2.4G_WiFi_CE_占用带宽测试_频谱分析仪测试2.4g-CSDN博客https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_57515011/article/details/146164656?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502测试组网图:下面代码示例,只是基于罗德频谱仪测试OBW的基础操作,如有疑问,欢迎留言沟通。im
- 50G的高光谱数据+40个真实项目案例(涵盖城市、植被、水体、地质、土壤五大领域)
weixin_贾
地理遥感生态模型高光谱数据图像预处理无人机多光谱数据城市案例研究混合像元分解
本内容通过模块化设计与真实案例结合,基于Python编程入门到DeepSeek工具,把高光谱领域的全部内容都纳进来,包括辐射校正、几何校正、大气校正、光谱预处理、降维、特征提取、混合像元分解、地物分类与识别、目标检测与变化检测等都纳入本内容,覆盖全面,循序渐进。通过城市目标识别、植被指数计算、水质参数反演、地质找矿、土壤混合像元分解等多元场景的实战演练,您将掌握高光谱遥感的核心技术,并能够灵活运用
- jquery实现的jsonp掉java后台
知了ing
javajsonpjquery
什么是JSONP?
先说说JSONP是怎么产生的:
其实网上关于JSONP的讲解有很多,但却千篇一律,而且云里雾里,对于很多刚接触的人来讲理解起来有些困难,小可不才,试着用自己的方式来阐释一下这个问题,看看是否有帮助。
1、一个众所周知的问题,Ajax直接请求普通文件存在跨域无权限访问的问题,甭管你是静态页面、动态网页、web服务、WCF,只要是跨域请求,一律不准;
2、
- Struts2学习笔记
caoyong
struts2
SSH : Spring + Struts2 + Hibernate
三层架构(表示层,业务逻辑层,数据访问层) MVC模式 (Model View Controller)
分层原则:单向依赖,接口耦合
1、Struts2 = Struts + Webwork
2、搭建struts2开发环境
a>、到www.apac
- SpringMVC学习之后台往前台传值方法
满城风雨近重阳
springMVC
springMVC控制器往前台传值的方法有以下几种:
1.ModelAndView
通过往ModelAndView中存放viewName:目标地址和attribute参数来实现传参:
ModelAndView mv=new ModelAndView();
mv.setViewName="success
- WebService存在的必要性?
一炮送你回车库
webservice
做Java的经常在选择Webservice框架上徘徊很久,Axis Xfire Axis2 CXF ,他们只有一个功能,发布HTTP服务然后用XML做数据传输。
是的,他们就做了两个功能,发布一个http服务让客户端或者浏览器连接,接收xml参数并发送xml结果。
当在不同的平台间传输数据时,就需要一个都能解析的数据格式。
但是为什么要使用xml呢?不能使json或者其他通用数据
- js年份下拉框
3213213333332132
java web ee
<div id="divValue">test...</div>测试
//年份
<select id="year"></select>
<script type="text/javascript">
window.onload =
- 简单链式调用的实现技术
归来朝歌
方法调用链式反应编程思想
在编程中,我们可以经常遇到这样一种场景:一个实例不断调用它自身的方法,像一条链条一样进行调用
这样的调用你可能在Ajax中,在页面中添加标签:
$("<p>").append($("<span>").text(list[i].name)).appendTo("#result");
也可能在HQ
- JAVA调用.net 发布的webservice 接口
darkranger
webservice
/**
* @Title: callInvoke
* @Description: TODO(调用接口公共方法)
* @param @param url 地址
* @param @param method 方法
* @param @param pama 参数
* @param @return
* @param @throws BusinessException
- Javascript模糊查找 | 第一章 循环不能不重视。
aijuans
Way
最近受我的朋友委托用js+HTML做一个像手册一样的程序,里面要有可展开的大纲,模糊查找等功能。我这个人说实在的懒,本来是不愿意的,但想起了父亲以前教我要给朋友搞好关系,再加上这也可以巩固自己的js技术,于是就开始开发这个程序,没想到却出了点小问题,我做的查找只能绝对查找。具体的js代码如下:
function search(){
var arr=new Array("my
- 狼和羊,该怎么抉择
atongyeye
工作
狼和羊,该怎么抉择
在做一个链家的小项目,只有我和另外一个同事两个人负责,各负责一部分接口,我的接口写完,并全部测联调试通过。所以工作就剩下一下细枝末节的,工作就轻松很多。每天会帮另一个同事测试一些功能点,协助他完成一些业务型不强的工作。
今天早上到公司没多久,领导就在QQ上给我发信息,让我多协助同事测试,让我积极主动些,有点责任心等等,我听了这话,心里面立马凉半截,首先一个领导轻易说
- 读取android系统的联系人拨号
百合不是茶
androidsqlite数据库内容提供者系统服务的使用
联系人的姓名和号码是保存在不同的表中,不要一下子把号码查询来,我开始就是把姓名和电话同时查询出来的,导致系统非常的慢
关键代码:
1, 使用javabean操作存储读取到的数据
package com.example.bean;
/**
*
* @author Admini
- ORACLE自定义异常
bijian1013
数据库自定义异常
实例:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE test_Exception
(
ParameterA IN varchar2,
ParameterB IN varchar2,
ErrorCode OUT varchar2 --返回值,错误编码
)
AS
/*以下是一些变量的定义*/
V1 NUMBER;
V2 nvarc
- 查看端号使用情况
征客丶
windows
一、查看端口
在windows命令行窗口下执行:
>netstat -aon|findstr "8080"
显示结果:
TCP 127.0.0.1:80 0.0.0.0:0 &
- 【Spark二十】运行Spark Streaming的NetworkWordCount实例
bit1129
wordcount
Spark Streaming简介
NetworkWordCount代码
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
- Struts2 与 SpringMVC的比较
BlueSkator
struts2spring mvc
1. 机制:spring mvc的入口是servlet,而struts2是filter,这样就导致了二者的机制不同。 2. 性能:spring会稍微比struts快。spring mvc是基于方法的设计,而sturts是基于类,每次发一次请求都会实例一个action,每个action都会被注入属性,而spring基于方法,粒度更细,但要小心把握像在servlet控制数据一样。spring
- Hibernate在更新时,是可以不用session的update方法的(转帖)
BreakingBad
Hibernateupdate
地址:http://blog.csdn.net/plpblue/article/details/9304459
public void synDevNameWithItil()
{Session session = null;Transaction tr = null;try{session = HibernateUtil.getSession();tr = session.beginTran
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-观察者模式
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Observable;
import java.util.Observer;
/**
* “观
- 重置MySQL密码
chenhbc
mysql重置密码忘记密码
如果你也像我这么健忘,把MySQL的密码搞忘记了,经过下面几个步骤就可以重置了(以Windows为例,Linux/Unix类似):
1、关闭MySQL服务
2、打开CMD,进入MySQL安装目录的bin目录下,以跳过权限检查的方式启动MySQL
mysqld --skip-grant-tables
3、新开一个CMD窗口,进入MySQL
mysql -uroot
- 再谈系统论,控制论和信息论
comsci
设计模式生物能源企业应用领域模型
再谈系统论,控制论和信息论
偶然看
- oracle moving window size与 AWR retention period关系
daizj
oracle
转自: http://tomszrp.itpub.net/post/11835/494147
晚上在做11gR1的一个awrrpt报告时,顺便想调整一下AWR snapshot的保留时间,结果遇到了ORA-13541这样的错误.下面是这个问题的发生和解决过程.
SQL> select * from v$version;
BANNER
-------------------
- Python版B树
dieslrae
python
话说以前的树都用java写的,最近发现python有点生疏了,于是用python写了个B树实现,B树在索引领域用得还是蛮多了,如果没记错mysql的默认索引好像就是B树...
首先是数据实体对象,很简单,只存放key,value
class Entity(object):
'''数据实体'''
def __init__(self,key,value)
- C语言冒泡排序
dcj3sjt126com
算法
代码示例:
# include <stdio.h>
//冒泡排序
void sort(int * a, int len)
{
int i, j, t;
for (i=0; i<len-1; i++)
{
for (j=0; j<len-1-i; j++)
{
if (a[j] > a[j+1]) // >表示升序
- 自定义导航栏样式
dcj3sjt126com
自定义
-(void)setupAppAppearance
{
[[UILabel appearance] setFont:[UIFont fontWithName:@"FZLTHK—GBK1-0" size:20]];
[UIButton appearance].titleLabel.font =[UIFont fontWithName:@"FZLTH
- 11.性能优化-优化-JVM参数总结
frank1234
jvm参数性能优化
1.堆
-Xms --初始堆大小
-Xmx --最大堆大小
-Xmn --新生代大小
-Xss --线程栈大小
-XX:PermSize --永久代初始大小
-XX:MaxPermSize --永久代最大值
-XX:SurvivorRatio --新生代和suvivor比例,默认为8
-XX:TargetSurvivorRatio --survivor可使用
- nginx日志分割 for linux
HarborChung
nginxlinux脚本
nginx日志分割 for linux 默认情况下,nginx是不分割访问日志的,久而久之,网站的日志文件将会越来越大,占用空间不说,如果有问题要查看网站的日志的话,庞大的文件也将很难打开,于是便有了下面的脚本 使用方法,先将以下脚本保存为 cutlog.sh,放在/root 目录下,然后给予此脚本执行的权限
复制代码代码如下:
chmo
- Spring4新特性——泛型限定式依赖注入
jinnianshilongnian
springspring4泛型式依赖注入
Spring4新特性——泛型限定式依赖注入
Spring4新特性——核心容器的其他改进
Spring4新特性——Web开发的增强
Spring4新特性——集成Bean Validation 1.1(JSR-349)到SpringMVC
Spring4新特性——Groovy Bean定义DSL
Spring4新特性——更好的Java泛型操作API
Spring4新
- centOS安装GCC和G++
liuxihope
centosgcc
Centos支持yum安装,安装软件一般格式为yum install .......,注意安装时要先成为root用户。
按照这个思路,我想安装过程如下:
安装gcc:yum install gcc
安装g++: yum install g++
实际操作过程发现,只能有gcc安装成功,而g++安装失败,提示g++ command not found。上网查了一下,正确安装应该
- 第13章 Ajax进阶(上)
onestopweb
Ajax
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/
- How to determine BusinessObjects service pack and fix pack
blueoxygen
BO
http://bukhantsov.org/2011/08/how-to-determine-businessobjects-service-pack-and-fix-pack/
The table below is helpful. Reference
BOE XI 3.x
12.0.0.
y BOE XI 3.0 12.0.
x.
y BO
- Oracle里的自增字段设置
tomcat_oracle
oracle
大家都知道吧,这很坑,尤其是用惯了mysql里的自增字段设置,结果oracle里面没有的。oh,no 我用的是12c版本的,它有一个新特性,可以这样设置自增序列,在创建表是,把id设置为自增序列
create table t
(
id number generated by default as identity (start with 1 increment b
- Spring Security(01)——初体验
yang_winnie
springSecurity
Spring Security(01)——初体验
博客分类: spring Security
Spring Security入门安全认证
首先我们为Spring Security专门建立一个Spring的配置文件,该文件就专门用来作为Spring Security的配置