贝叶斯推断及其互联网应用: 已知推断未知概率
已知推断未知概率, 也叫贝叶斯分类
先上问题吧,我们统计了14天的气象数据(指标包括outlook,temperature,humidity,windy),并已知这些天气是否打球(play)。如果给出新一天的气象指标数据:sunny,cool,high,TRUE,判断一下会不会去打球。
table 1
这个问题可以用决策树的方法来求解,当然我们今天讲的是朴素贝叶斯法。这个一”打球“还是“不打球”是个两类分类问题,实际上朴素贝叶斯可以没有任何改变地解决多类分类问题。决策树也一样,它们都是有导师的分类方法。
朴素贝叶斯模型有两个假设:所有变量对分类均是有用的,即输出依赖于所有的属性;这些变量是相互独立的,即不相关的。之所以称为“朴素”,就是因为这些假设从未被证实过。
注意上面每项属性(或称指标)的取值都是离散的,称为“标称变量”。
step1.对每项指标分别统计:在不同的取值下打球和不打球的次数。
table 2
step2.分别计算在给定“证据”下打球和不打球的概率。
这里我们的“证据”就是sunny,cool,high,TRUE,记为E,E1=sunny,E2=cool,E3=high,E4=TRUE。
A、B相互独立时,由:
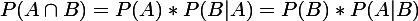
得贝叶斯定理:

得:

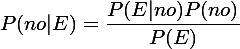
又因为4个指标是相互独立的,所以
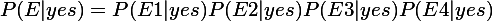
我们只需要比较P(yes|E)和P(no|E)的大小,就可以决定打不打球了。所以分母P(E)实际上是不需要计算的。
P(yes|E)*P(E)=2/9×3/9×3/9×3/9×9/14=0.0053
P(no|E)*P(E)=3/5×1/5×4/5×3/5×5/14=0.0206
所以不打球的概率更大。
零频问题
注意table 2中有一个数据为0,这意味着在outlook为overcast的情况下,不打球和概率为0,即只要为overcast就一定打球,这违背了朴素贝叶斯的基本假设:输出依赖于所有的属性。
数据平滑的方法很多,最简单最古老的是拉普拉斯估计(Laplace estimator)--即为table2中的每个计数都加1。它的一种演变是每个计数都u(0<u<1)。
Good-Turing是平滑算法中的佼佼者,有兴趣的可以了解下。我在作基于隐马尔可夫的词性标注时发现Good-Turing的效果非常不错。
对于任何发生r次的事件,都假设它发生了r*次:
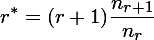
nr是历史数据中发生了r次的事件的个数。
数值属性
当属性的取值为连续的变量时,称这种属性为“数值属性“。通常我们假设数值属性的取值服从正态分布。
正态分布的概率密度函数为:
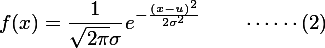
现在已知天气为:outlook=overcast,temperature=66,humidity=90,windy=TRUE。问是否打球?
f(温度=66|yes)=0.0340
f(湿度=90|yes)=0.0221
yes的似然=2/9×0.0340×0.0221×3/9×9/14=0.000036
no的似然=3/5×0.0291×0.0380×3/5×9/14=0.000136
不打球的概率更大一些。
用于文本分类
朴素贝叶斯分类是一种基于概率的有导师分类器。
词条集合W,文档集合D,类别集合C。
根据(1)式(去掉分母)得文档d属于类别cj的概率为:
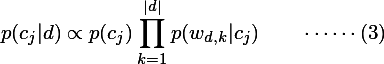
p(cj)表示类别j出现的概率,让属于类别j的文档数量除以总文档数量即可。
而已知类别cj的情况下词条wt出现的后验概率为:类别cj中包含wt的文档数目 除以 类别cj中包含的文档总数目 。
结束语
实践已多次证明,朴素贝叶斯在许多数据集上不逊于甚至优于一些更复杂的分类方法。这里的原则是:优先尝试简单的方法。
机器学习的研究者尝试用更复杂的学习模型来得到良好的结果,许多年后发现简单的方法仍可取得同样甚至更好的结果。
实现代码:
Classifier.java
NaiveBayes.java
LabelBo.java
先上问题吧,我们统计了14天的气象数据(指标包括outlook,temperature,humidity,windy),并已知这些天气是否打球(play)。如果给出新一天的气象指标数据:sunny,cool,high,TRUE,判断一下会不会去打球。
table 1
| outlook | temperature | humidity | windy | play |
| sunny | hot | high | FALSE | no |
| sunny | hot | high | TRUE | no |
| overcast | hot | high | FALSE | yes |
| rainy | mild | high | FALSE | yes |
| rainy | cool | normal | FALSE | yes |
| rainy | cool | normal | TRUE | no |
| overcast | cool | normal | TRUE | yes |
| sunny | mild | high | FALSE | no |
| sunny | cool | normal | FALSE | yes |
| rainy | mild | normal | FALSE | yes |
| sunny | mild | normal | TRUE | yes |
| overcast | mild | high | TRUE | yes |
| overcast | hot | normal | FALSE | yes |
| rainy | mild | high | TRUE | no |
这个问题可以用决策树的方法来求解,当然我们今天讲的是朴素贝叶斯法。这个一”打球“还是“不打球”是个两类分类问题,实际上朴素贝叶斯可以没有任何改变地解决多类分类问题。决策树也一样,它们都是有导师的分类方法。
朴素贝叶斯模型有两个假设:所有变量对分类均是有用的,即输出依赖于所有的属性;这些变量是相互独立的,即不相关的。之所以称为“朴素”,就是因为这些假设从未被证实过。
注意上面每项属性(或称指标)的取值都是离散的,称为“标称变量”。
step1.对每项指标分别统计:在不同的取值下打球和不打球的次数。
table 2
| outlook | temperature | humidity | windy | play | |||||||||
| yes | no | yes | no | yes | no | yes | no | yes | no | ||||
| sunny | 2 | 3 | hot | 2 | 2 | high | 3 | 4 | FALSE | 6 | 2 | 9 | 5 |
| overcast | 4 | 0 | mild | 4 | 2 | normal | 6 | 1 | TRUR | 3 | 3 | ||
| rainy | 3 | 2 | cool | 3 | 1 |
step2.分别计算在给定“证据”下打球和不打球的概率。
这里我们的“证据”就是sunny,cool,high,TRUE,记为E,E1=sunny,E2=cool,E3=high,E4=TRUE。
A、B相互独立时,由:
得贝叶斯定理:
得:
又因为4个指标是相互独立的,所以
我们只需要比较P(yes|E)和P(no|E)的大小,就可以决定打不打球了。所以分母P(E)实际上是不需要计算的。
P(yes|E)*P(E)=2/9×3/9×3/9×3/9×9/14=0.0053
P(no|E)*P(E)=3/5×1/5×4/5×3/5×5/14=0.0206
所以不打球的概率更大。
零频问题
注意table 2中有一个数据为0,这意味着在outlook为overcast的情况下,不打球和概率为0,即只要为overcast就一定打球,这违背了朴素贝叶斯的基本假设:输出依赖于所有的属性。
数据平滑的方法很多,最简单最古老的是拉普拉斯估计(Laplace estimator)--即为table2中的每个计数都加1。它的一种演变是每个计数都u(0<u<1)。
Good-Turing是平滑算法中的佼佼者,有兴趣的可以了解下。我在作基于隐马尔可夫的词性标注时发现Good-Turing的效果非常不错。
对于任何发生r次的事件,都假设它发生了r*次:
nr是历史数据中发生了r次的事件的个数。
数值属性
当属性的取值为连续的变量时,称这种属性为“数值属性“。通常我们假设数值属性的取值服从正态分布。
| outlook | temperature | humidity | windy | play | |||||||||
| yes | no | yes | no | yes | no | yes | no | yes | no | ||||
| sunny | 2 | 3 | 83 | 85 | 86 | 85 | FALSE | 6 | 2 | 9 | 5 | ||
| overcast | 4 | 0 | 70 | 80 | 96 | 90 | TRUR | 3 | 3 | ||||
| rainy | 3 | 2 | 68 | 65 | 80 | 70 | |||||||
| 64 | 72 | 65 | 95 | ||||||||||
| 69 | 71 | 70 | 91 | ||||||||||
| 75 | 80 | ||||||||||||
| 75 | 70 | ||||||||||||
| 72 | 90 | ||||||||||||
| 81 | 75 | ||||||||||||
| sunny | 2/9 | 3/5 | mean value | 73 | 74.6 | mean value | 79.1 | 86.2 | FALSE | 6/9 | 2/5 | 9/15 | 5/14 |
| overcast | 4/9 | 0/5 | deviation | 6.2 | 7.9 | deviation | 10.2 | 9.7 | TRUR | 3/9 | 3/5 |
正态分布的概率密度函数为:
现在已知天气为:outlook=overcast,temperature=66,humidity=90,windy=TRUE。问是否打球?
f(温度=66|yes)=0.0340
f(湿度=90|yes)=0.0221
yes的似然=2/9×0.0340×0.0221×3/9×9/14=0.000036
no的似然=3/5×0.0291×0.0380×3/5×9/14=0.000136
不打球的概率更大一些。
用于文本分类
朴素贝叶斯分类是一种基于概率的有导师分类器。
词条集合W,文档集合D,类别集合C。
根据(1)式(去掉分母)得文档d属于类别cj的概率为:
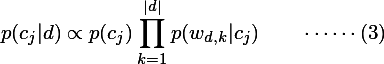
p(cj)表示类别j出现的概率,让属于类别j的文档数量除以总文档数量即可。
而已知类别cj的情况下词条wt出现的后验概率为:类别cj中包含wt的文档数目 除以 类别cj中包含的文档总数目 。
结束语
实践已多次证明,朴素贝叶斯在许多数据集上不逊于甚至优于一些更复杂的分类方法。这里的原则是:优先尝试简单的方法。
机器学习的研究者尝试用更复杂的学习模型来得到良好的结果,许多年后发现简单的方法仍可取得同样甚至更好的结果。
实现代码:
Classifier.java
/**
*
* 描述: 算法接口.
* @author
*
*/
public interface Classifier {
/**
* 处理模型数据.
* @param lable 标签名称.
* @param value 标签值.
* @param cnt 数量(该条数据的数量)
* @param target 目标名称.
* @param targetValue 目标值.
*/
void train(String[] lable, String[] value, int cnt, String target, String targetValue);
/**
* 先验概率计算出其后验概率.
* @param features 属性值.
* @return 后验概率较大的数值.
*/
String predict(String[] features);
}
NaiveBayes.java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
*
* 描述: 朴树贝叶斯算法.
* @author
*
*/
public class NaiveBayes implements Classifier {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(NaiveBayes.class);
// 小数点后6位
private static final int AFTER_POINT = 6;
// 所有标签名称
private String[] labelName;
// 目标名称
private String targetName;
// 目标标签
private String[] targetLabelName;
// 标签列表
private List<LabelBo> lstLabelBo;
// 目标值列表
private Set<String> setTargetVal;
/**
* 构造函数.
*/
public NaiveBayes() {
this.lstLabelBo = new ArrayList<LabelBo>();
this.setTargetVal = new TreeSet<String>();
}
public void setLabelName(String[] labelName) {
this.labelName = labelName;
}
public void setTargetLabelName(String[] targetLabelName) {
this.targetLabelName = targetLabelName;
}
public void setTargetName(String targetName) {
this.targetName = targetName;
}
public String[] getLabelName() {
return labelName;
}
public List<LabelBo> getLstLabelBo() {
return lstLabelBo;
}
public String[] getTargetLabelName() {
return targetLabelName;
}
public String getTargetName() {
return targetName;
}
public Set<String> getSetTargetVal() {
return setTargetVal;
}
/**
* 读文件.
* @param path 路径.
*/
public void readFile(String path) {
if (null == this.labelName || null == this.targetName) {
return;
}
try {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(path));
String line;
boolean isTrue = false;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
if ("@data".equals(line)) {
isTrue = true;
continue;
}
if (!isTrue) {
continue;
}
String[] atts = line.split(",");
this.train(this.labelName, atts, 1, this.targetName, atts[atts.length - 1]);
}
reader.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
LOG.error("Read naivebayes mode data failed, not found file, " + ex.getMessage());
} catch (IOException ex) {
LOG.error("Read naivebayes mode data failed, IO exception, " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
@Override
public void train(String[] lable, String[] value, int cnt, String target, String targetValue) {
for (int i = 0; i < lable.length; i++) {
LabelBo labelBo = null;
for (LabelBo lb : this.lstLabelBo) {
if (lable[i].equals(lb.getLableName()) && value[i].equals(lb.getItemName())) {
labelBo = lb;
break;
}
}
if (null == labelBo) {
labelBo = new LabelBo();
labelBo.setLableName(lable[i]);
labelBo.setItemName(value[i]);
this.lstLabelBo.add(labelBo);
}
int index = labelBo.addName(targetValue);
labelBo.addCount(index, cnt);
}
}
/**
* 计算比例.
*/
public void rate() {
Map<String, Integer> mapTotal = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
for (LabelBo lb : this.lstLabelBo) {
for (int i = 0; i < lb.getLstCount().size(); i++) {
String tmp = lb.getLableName() + "." + lb.getLstName().get(i);
if (mapTotal.containsKey(tmp)) {
mapTotal.put(tmp, mapTotal.get(tmp) + lb.getLstCount().get(i));
} else {
mapTotal.put(tmp, lb.getLstCount().get(i));
}
}
}
for (LabelBo lb : this.lstLabelBo) {
List<Integer> lst = lb.getLstTotal();
for (int i = 0; i < lb.getLstName().size(); i++) {
String tmp = lb.getLableName() + "." + lb.getLstName().get(i);
lst.add(mapTotal.get(tmp));
}
}
// 目标计算
List<LabelBo> lstTmpLabelBo = new ArrayList<LabelBo>();
for (LabelBo lb : this.lstLabelBo) {
if (this.targetName.equalsIgnoreCase(lb.getLableName())) {
lstTmpLabelBo.add(lb);
}
}
int total = 0;
for (LabelBo labelBo : lstTmpLabelBo) {
if (null != labelBo) {
for (int i = 0; i < labelBo.getLstCount().size(); i++) {
total += labelBo.getLstCount().get(i);
this.setTargetVal.add(labelBo.getLstName().get(i));
}
}
}
for (LabelBo labelBo : lstTmpLabelBo) {
for (int i = 0; i < labelBo.getLstName().size(); i++) {
labelBo.getLstTotal().set(i, total);
}
}
}
@Override
public String predict(String[] features) {
String score = "";
double rate = 0;
Set<String> lstTv = this.getSetTargetVal();
// double total = 0;
for (String v : lstTv) {
String result = this.doPredict(this.targetLabelName, features, this.targetName, v);
if (rate < Double.valueOf(result)) {
rate = Double.valueOf(result);
score = v;
// total += Double.valueOf(result);
}
// System.out.println(result + ":" + v);
}
return score + ":" + rate;
}
/**
* 计算后验概率.
* @param lable 标签名称
* @param features 标签值
* @param target 目标名称
* @param targetValue 目标值
* @return 结果.
*/
private String doPredict(String[] lable, String[] features, String target, String targetValue) {
int pre = 1;
int dev = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < lable.length; i++) {
LabelBo labelBo = null;
for (LabelBo lb : this.lstLabelBo) {
if (lable[i].equalsIgnoreCase(lb.getLableName()) && features[i].equalsIgnoreCase(lb.getItemName())) {
labelBo = lb;
break;
}
}
if (null == labelBo) {
continue;
}
List<String> lstName = labelBo.getLstName();
for (String str : lstName) {
if (targetValue.equals(str)) {
pre *= labelBo.getLstCount().get(lstName.indexOf(str));
dev *= labelBo.getLstTotal().get(lstName.indexOf(str));
}
}
}
LabelBo labelBo = null;
for (LabelBo lb : this.lstLabelBo) {
if (target.equalsIgnoreCase(lb.getLableName()) && targetValue.equalsIgnoreCase(lb.getItemName())) {
labelBo = lb;
break;
}
}
if (null != labelBo) {
List<String> lstName = labelBo.getLstName();
for (String str : lstName) {
if (targetValue.equals(str)) {
pre *= labelBo.getLstCount().get(lstName.indexOf(str));
dev *= labelBo.getLstTotal().get(lstName.indexOf(str));
}
}
}
BigDecimal result = new BigDecimal(pre).divide(new BigDecimal(dev), AFTER_POINT, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
return result.toString();
}
/**
* 重置.
*/
public void reset() {
this.lstLabelBo.clear();
this.setTargetVal.clear();
}
/**
* 打印数据.
*/
public void print() {
for (LabelBo key : this.lstLabelBo) {
System.out.println(key.getLableName() + "=======>" + key.getItemName());
List<String> lstName = key.getLstName();
List<Integer> lstCount = key.getLstCount();
List<Integer> lstTotal = key.getLstTotal();
for (int i = 0; i < lstName.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(lstName.get(i) + ":" + lstCount.get(i) + "/" + lstTotal.get(i));
}
}
}
}
LabelBo.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
* 描述: 标签对象.
* @author
*
*/
public class LabelBo {
private String lableName;
private String itemName;
// 目标项对应的值.
private List<String> lstName;
private List<Integer> lstCount;
private List<Integer> lstTotal;
/**
* 构造方法.
*/
public LabelBo() {
this.lstCount = new ArrayList<Integer>();
this.lstName = new ArrayList<String>();
this.lstTotal = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
public void setLableName(String lableName) {
this.lableName = lableName;
}
public String getLableName() {
return lableName;
}
public void setItemName(String itemName) {
this.itemName = itemName;
}
public String getItemName() {
return itemName;
}
public List<String> getLstName() {
return lstName;
}
public List<Integer> getLstCount() {
return lstCount;
}
public List<Integer> getLstTotal() {
return lstTotal;
}
/**
* 添加标签对应的种类名称.
* @param name 名称.
* @return 下标.
*/
public int addName(String name) {
if (!this.lstName.contains(name)) {
this.lstName.add(name);
}
return this.lstName.indexOf(name);
}
/**
* 添加标签对应的种类名称的数量.
* @param index 下标.
* @param count 数量.
*/
public void addCount(int index, Integer count) {
if (this.lstCount.size() - 1 < index) {
this.lstCount.add(count);
return;
}
int temp = this.lstCount.get(index) + count;
this.lstCount.set(index, temp);
}
public void setLstRate(List<Integer> lstTotal) {
this.lstTotal = lstTotal;
}
}